Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2007; 13(8): 1175-1181
Published online Feb 28, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i8.1175
Published online Feb 28, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i8.1175
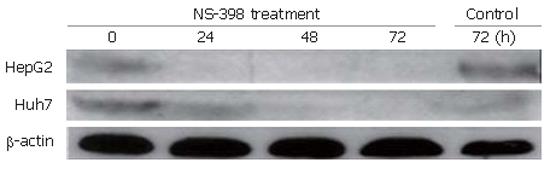
Figure 1 Immunoblot analysis for COX-2 protein levels in HepG2 and Huh7 cells.
Cells were treated with 100 μmol/L NS-398 for 0, 24, 48 and 72 h. Control cells were treated with DMSO without NS-398. The upper bands represent 72 kDa COX-2-specific staining while the lower bands are β-actin controls. COX-2 expression was detectable but low in both cell lines. Decreased changes were observed in COX-2 expression with increasing time.
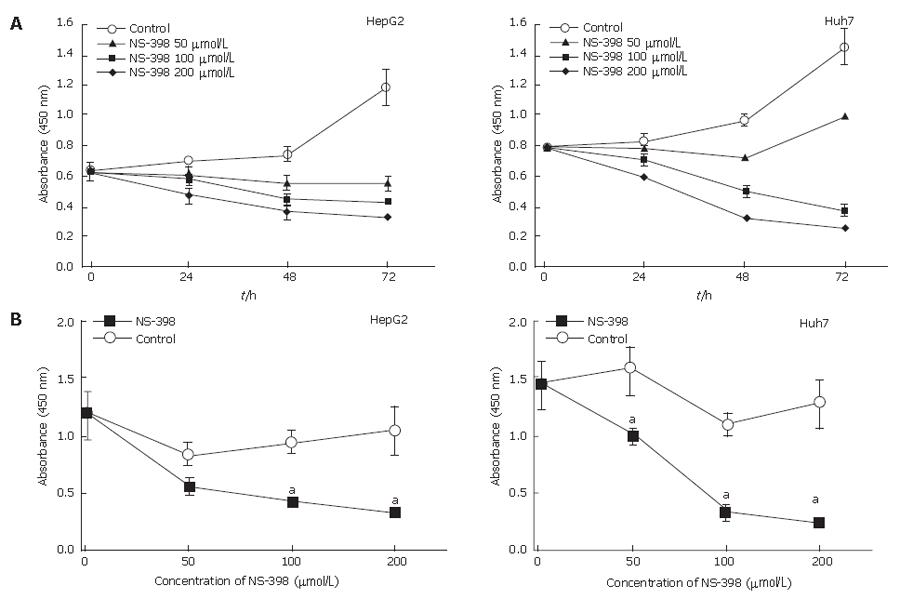
Figure 2 Proliferation of HepG2 and Huh7 cells inhibited by NS-398.
A: Time-dependent growth-inhibitory effect of NS-398. One hundred μmol/L NS-398 was added to HepG2 and Huh7 cells, which were cultured for 24, 48 or 72 h, and subjected to WST-1 assay. Absorbance was detected at 450 nm with an ELISA plate reader, and the growth rates of both cell lines treated with NS-398 were reduced compared to controls. Control cells were treated with an equivalent volume of DMSO without NS-398, respectively; B: Dose-dependent growth-inhibitory effect of NS-398. Cells treated with various concentrations of NS-398 were cultured for 72 h, and quantified by WST-1 assay. Data from 3 independent experiments are shown as e mean ± SD (aP < 0.05).
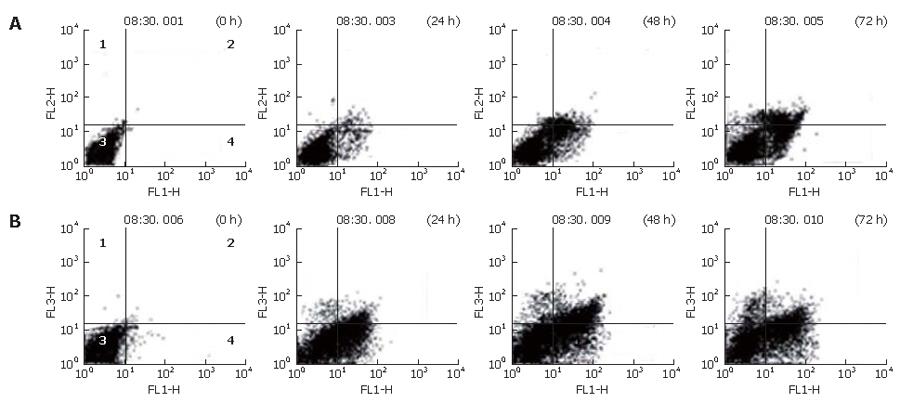
Figure 3 Flow cytometric analysis after exposure of HepG2 (A) and Huh7 (B) cells to NS-398.
Cells were treated with 100 μmol/L NS-398 for 24, 48, and 72 h, stained with annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide and analyzed on a FACScalibur flow cytometer. Quadrants 2-4 represent secondary necrotic cells, viable cells, and apoptotic cells, respectively.
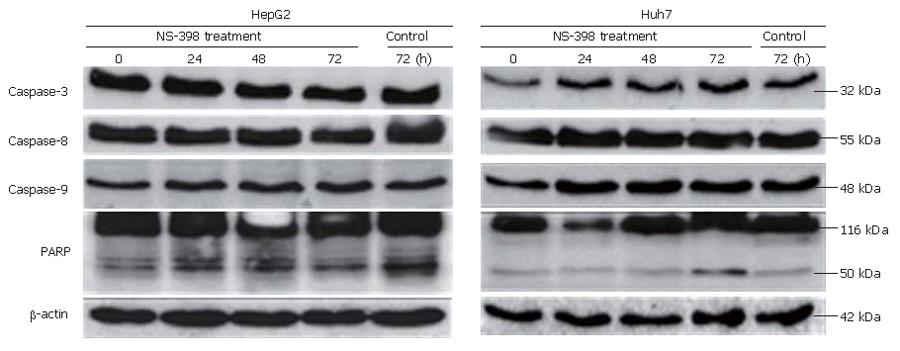
Figure 4 No evidence of activation of the caspase pathway and PARP by NS-398.
No evidence of apoptosis in HepG2 and Huh7 cells was observed after NS-398 treatment. No caspase pathway activation or PARP cleavage was detected in both cell lines.
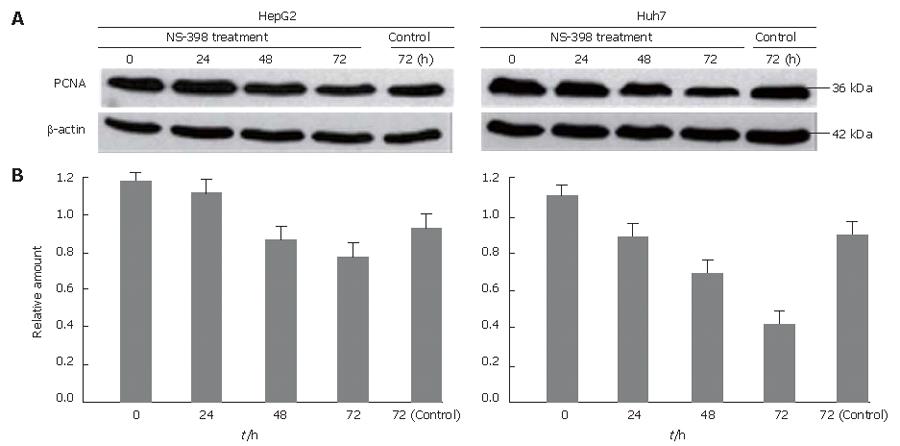
Figure 5 Inhibition of PCNA expression by NS-398.
A: Down-regulation of PCNA expression in both cell lines after NS-398 treatment. Cells were treated for 24, 48, and 72 h with 100 μmol/L NS-398. Controls were treated with an equivalent volume of DMSO without NS-398. PCNA expressions in HepG2 and Huh7 cells were inhibited in a time-dependent (as shown above) and dose-independent (data not shown) manner; B: Quantification of the relative amount of each band by image analysis.
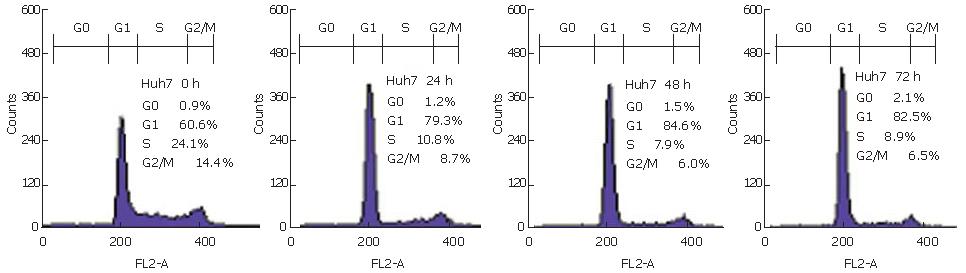
Figure 6 Inhibition of cell cycle arrest in Huh7 by NS-398.
The cell cycle distribution was determined using a FACScan flow cytometer. Cells were harvested at 24, 48 and 72 h after treatment with 100 μmol/L NS-398 and collected. RNA was digested and DNA content was stained with propidium iodide (PI). Representative DNA histograms for Huh7 cells were shown.
-
Citation: Baek JY, Hur W, Wang JS, Bae SH, Yoon SK. Selective COX-2 inhibitor, NS-398, suppresses cellular proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines
via cell cycle arrest. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(8): 1175-1181 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i8/1175.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i8.1175