Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2007; 13(34): 4539-4550
Published online Sep 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i34.4539
Published online Sep 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i34.4539
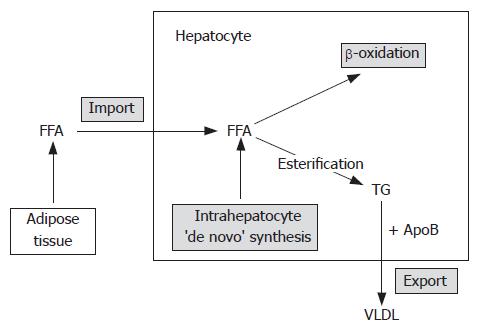
Figure 1 Lipid metabolism within the hepatocytes.
Liver lipid content is determined by the equilibrium of several processes: import of free fatty acids (FFAs) from the adipose tissue, de novo FFA synthesis in hepatocytes, beta-oxidation of FFAs, esterification of FFAs into triglycerides and export of triglycerides as very low density lipoproteins (VLDL). Hepatic steatosisis is a consequence of imbalance in those processes in favour of excessive triglyceride (TG) accumulation. FFA:free fatty acids; TG: triglycerides; VLDL: very low density lipoproteins; Apo B:apolipoprotein B.
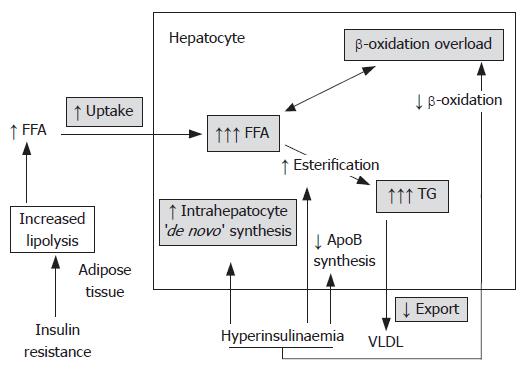
Figure 2 Effects of insulin resistance on lipid metabolism.
Insulin resistance and resulting hyperinsulinemia lead to hepatocyte lipid accumulation in the liver by several mechanisms. In adipose tissue, insulin resistance enhances triglyceride (TG) lipolysis and inhibits esterification of free fatty acids (FFAs). The result are increased circulating levels of FFAs, which are then taken up by the liver. Additionally, in hepatocytes hyperinsulinemia increases the ‘de novo’ synthesis of fatty acids and inhibits their beta oxidation. The consequence is accumulation of FFAs within hepatocytes. Hepatic TG synthesis is driven by the increased hepatocyte FFA content and favoured by insulin-mediated upregulation of lipogenic enzymes, such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ) and sterol regulatory element binding protein 1 (SREBP-1). Meanwhile, reduced very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) production and TG export may be impaired by decreased synthesis of apolipoprotein B (apo B) or reduced binding of TG to apo B by microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP). The resulting accumulation of fat within the hepatocytes initiates further damage causing hepatic insulin resistance and reactive oxygen species production. (abbrevations: ↑ -icreased; ↓ -inhibits; FFA: free fatty acid; TG: triglyceride; VLDL: very low density lipoprotein; Apo B: apolipoprotein B.
- Citation: Duvnjak M, Lerotić I, Baršić N, Tomašić V, Jukić LV, Velagić V. Pathogenesis and management issues for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(34): 4539-4550
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i34/4539.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i34.4539