Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2007; 13(23): 3262-3264
Published online Jun 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i23.3262
Published online Jun 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i23.3262
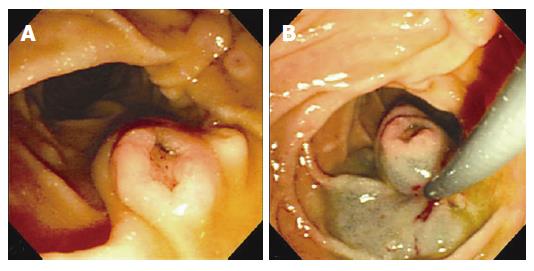
Figure 1 A: Gastroduodenoscopic examination and polypectomy.
1.1 cm sized, centrally depressed, sessile tumor was seen in the contralateral portion to the ampulla of Vater; B: After submucosal injection with a mixture of saline, epineprine and indigocarmine, snare polypectomy was successfully performed.
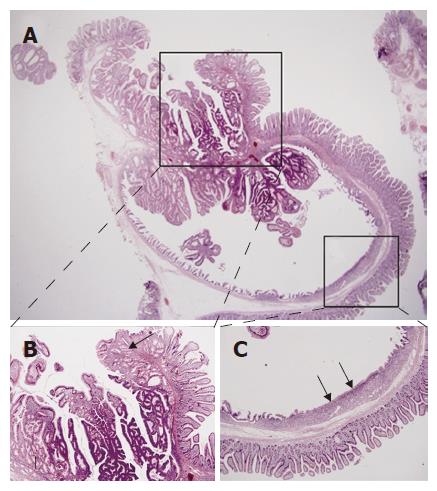
Figure 2 A: Inverted cystic lesion extends along the Brunner gland duct into the submucosa (HE, × 15); B: Normal or hyperplastic Brunner’s glands (arrows) are seen beneath the tubulovillous adenomatous lesion growing into the cyst lumen (HE, × 40); C: The flat surface epithelium and small mucus glands (arrows) are seen among the villiform epithelium (HE, × 40).
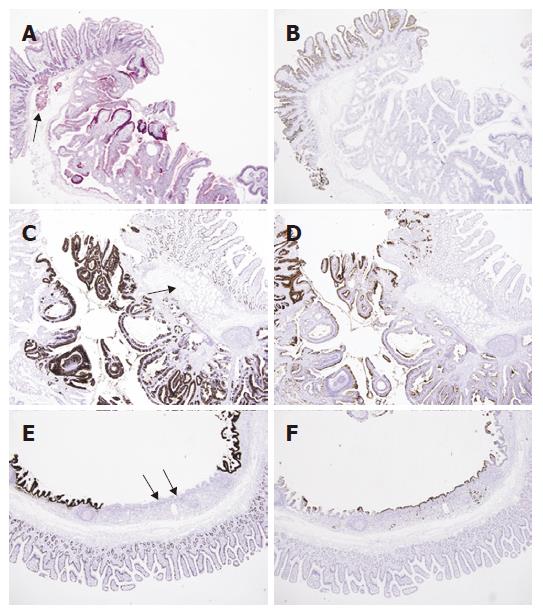
Figure 3 A: PAS staining shows positive reaction in the cytoplasm of normal Brunner’s glands (arrow) and tubulovillous glands (PAS, × 40); B: The duodenal surface epithelium is positive for CD10 along the luminal border (arrow), but the Brunner’s glands and adenomatous lesion are negative (Immunohistochemistry CD10, × 40); C: The immunohistochemical stain for MUC2 shows focal positive staining in duodenal mucosa and tubulvillous lesion, but not in Brunner’s glands (arrow) (Immunohistochemistry MUC2, × 40); D: whereas the staining for MUC5AC shows negative staining in duodenal mucosa and Brunner’s glands (arrow), but partly positive in adenomatous lesion (Immunohistochemistry MUC5AC, × 40); E: The area corresponding to the Figure 2B was negative for MUC2 in surface and glandular epithelium (arrows) (Immunohistochemistry MUC2, × 40); F: but positive for MUC5AC (arrows) (Immunohistochemistry MUC5AC, × 40).
- Citation: Kim JH, Choi JW, Seo YS, Lee BJ, Yeon JE, Kim JS, Byun KS, Bak YT, Kim I, Park JJ. Inverted cystic tubulovillous adenoma involving Brunner’s glands of duodenum. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(23): 3262-3264
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i23/3262.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i23.3262