Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2007; 13(20): 2872-2877
Published online May 28, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i20.2872
Published online May 28, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i20.2872
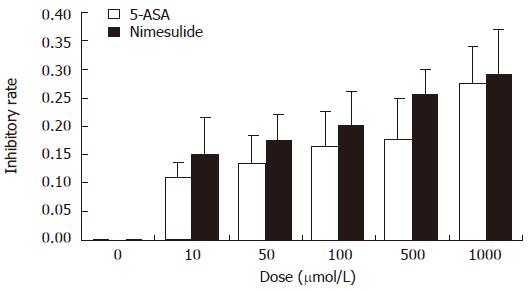
Figure 1 Dose-dependent inhibitory effect of 5-ASA and nimesulide on proliferation of HT-29 colon carcinoma cells.
The cells were pretreated with different doses of 5-ASA or nimesulide respectively (10, 50, 100, 500, 1000 μmol/L) for 48 h, then dye uptake was measured at 490 nm using an ELISA reader. Data were expressed as mean ± SE of five independent samples. Compared with the control group, the inhibitory rate was markedly increased in a dose-dependent manner (P < 0.05).
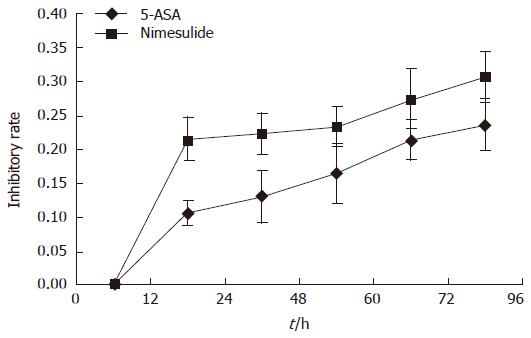
Figure 2 Time-dependent inhibitory effect of 5-ASA or nimesulide on proliferation of HT-29 colon carcinoma cells.
The cells were pretreated with 100 μmol/L 5-ASA or 100 μmol/L Nimesulide respectively for 12, 24, 48, 72, 96 h), then dye uptake was measured at 490 nm using an ELISA reader. Data were expressed as mean ± SE of five independent samples. The inhibitory rate was markedly increased in a time-dependent manner.
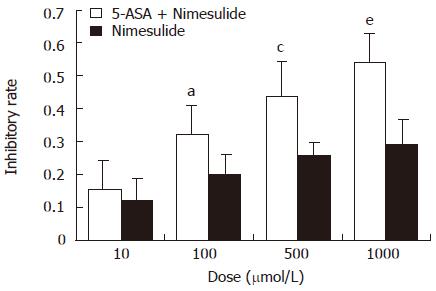
Figure 3 Inhibitory effect of 5-ASA in combination with nimesulide on proliferation of HT-29 colon carcinoma cells.
The cells were pretreated with 100 μmol/L 5-ASA (final concentration) in combination with different doses of nimesulide (10,100, 500, 1000 μmol/L) for 48 h, then dye uptake was measured at 490 nm using an ELISA reader. The inhibitory rate was markedly increased in a dose-dependent manner. Data were expressed as mean ± SE of three independent samples. a,c,eP < 0.05 vs the corresponding concentration of nimesulide.
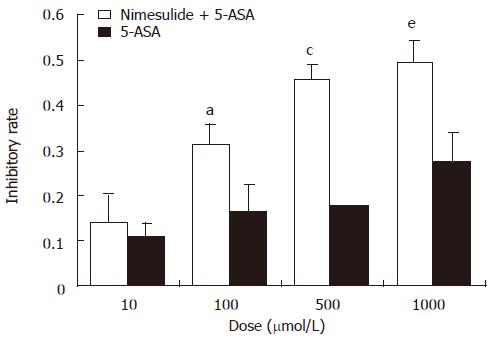
Figure 4 Dose-dependent inhibitory effect of nimesulide in combination with 5-ASA on proliferation of HT-29 colon carcinoma cells.
The cells were pretreated with 100 μmol/L nimesulide (final concentration) in combination with different doses of 5-ASA (10, 100, 500,1000 μmol/L) for 48 h, then dye uptake was measured at 490 nm using an ELISA reader. The inhibitory rate was markedly increased in a dose-dependent manner. Data were expressed as mean ± SE of three independent samples. a,c,eP < 0.05 vs the corresponding concentration of 5-ASA .
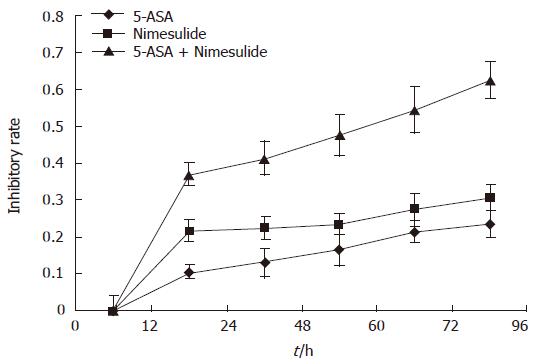
Figure 5 Time-dependent inhibitory effect of 5-ASA in combination with nimesulide on proliferation of HT-29 colon carcinoma cells.
The cells were pretreated with 5-ASA in combination with nimesulide at the final dose of 100 μmol/L for different times (0, 12, 24, 48, 72, 96 h), then dye uptake was measured at 490 nm using an ELISA reader. Data were expressed as mean ± SE of five independent samples.
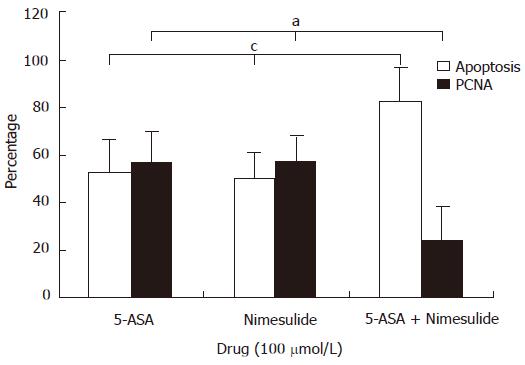
Figure 6 Inhibitory effect of 5-ASA in combination with nimesulide on proliferation and apoptosis of HT-29 colon carcinoma cells.
The cells were pretreated with 5-ASA in combination with nimesulide (the final concentration was 100 μmol/L) for 48 h, then the expression of PCNA and apoptosis was detected with kits according the manufacturer's introductions. Data were expressed as mean ± SE of three independent samples. aP < 0.05, cP < 0.05, vs 5-ASA or nimesulide alone.
-
Citation: Fang HM, Mei Q, Xu JM, Ma WJ. 5-aminosalicylic acid in combination with nimesulide inhibits proliferation of colon carcinoma cells
in vitro . World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(20): 2872-2877 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i20/2872.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i20.2872