Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2007; 13(2): 289-293
Published online Jan 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i2.289
Published online Jan 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i2.289
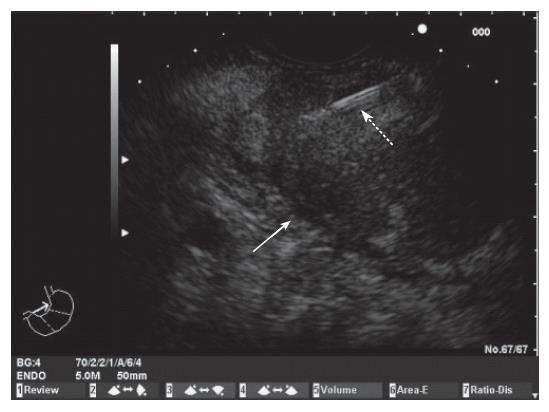
Figure 1 Endoscopic ultrasound image of a mass in the body of the pancreas.
Fine needle aspiration of the mass (White arrow: pancreatic mass; Dotted arrow: FNA needle).
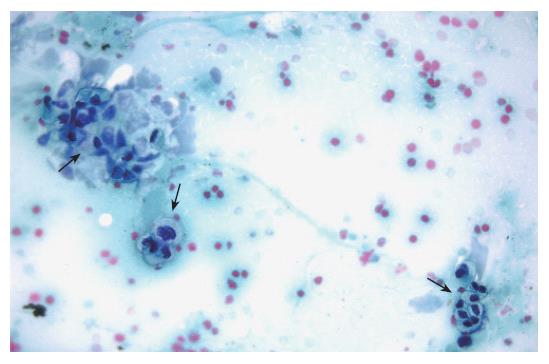
Figure 2 Cytological evaluation of a pancreatic sample obtained by EUS-guided FNA.
The presence of marked cellular atypia (arrows) supports the diagnosis of adenocarcinoma of the pancreas (Papanicolau staining × 40).
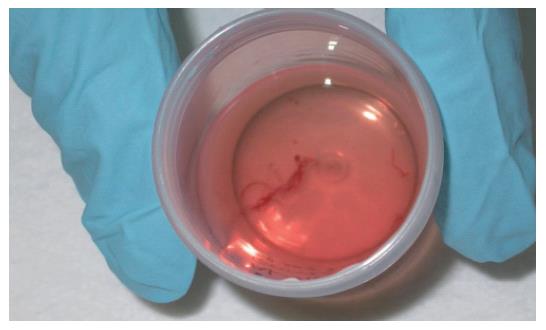
Figure 3 Core of pancreatic tissue obtained by expelling the content of the needle into a tube with 10% formol solution by careful injection of saline solution after EUS-guided FNA.
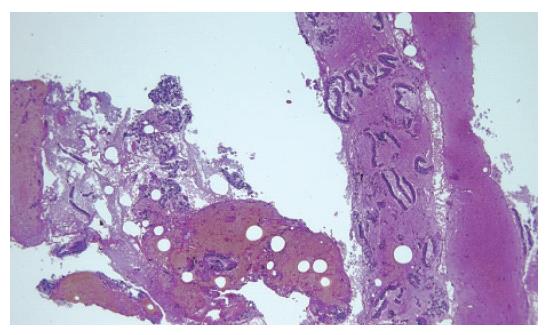
Figure 4 Adenocarcinoma of the pancreas.
Histological study of the tissue sample obtained by EUS-guided FNA (HE × 5).
- Citation: Iglesias-Garcia J, Dominguez-Munoz E, Lozano-Leon A, Abdulkader I, Larino-Noia J, Antunez J, Forteza J. Impact of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle biopsy for diagnosis of pancreatic masses. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(2): 289-293
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i2/289.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i2.289