Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2007; 13(14): 2066-2071
Published online Apr 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i14.2066
Published online Apr 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i14.2066
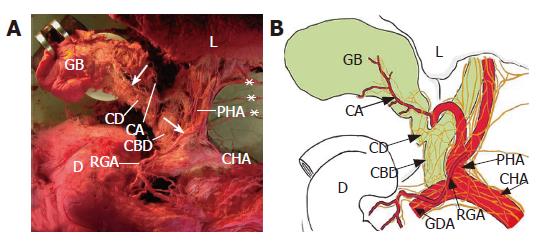
Figure 1 Innervation of the gallbladder (GB) from the ventral aspect (A) in a cadaver and a schematic representation of it (B).
The branches innervating the GB originate from the anterior hepatic plexus, and run along the cystic duct (CD) and the cystic artery (CA). The hepatic divisions (*) of the vagus join in the anterior hepatic plexus in the proper hepatic artery (PHA). Arrows indicate nerve branches. CBD: common bile duct; CHA: common hepatic artery; D: duodenum; GDA: gastroduodenal artery; L: liver; RGA: right gastric artery.
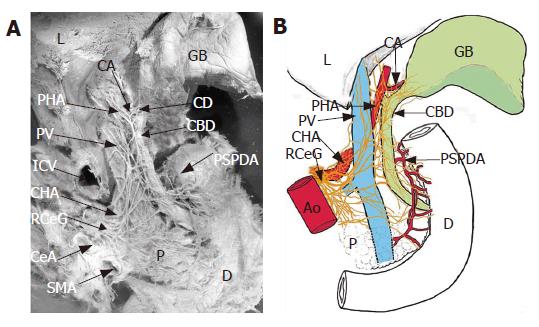
Figure 2 Innervation of the gallbladder (GB) from the dorsal aspect (A) in a cadaver and a schematic representation of it (B).
The branches innervating the GB arise from the posterior hepatic plexus, and run along the cystic duct (CD). Ao: aorta; CA: cystic artery; CBD: common bile duct; CeA: celiac artery; CHA: common hepatic artery; D: duodenum; IVC: inferior vena cave; L: liver; PHA: proper hepatic artery; PSPDA: posterior superior pancreatoduodenal artery; PV: portal vein; RCeG: right celiac ganglion; SMA: superior mesenteric artery.
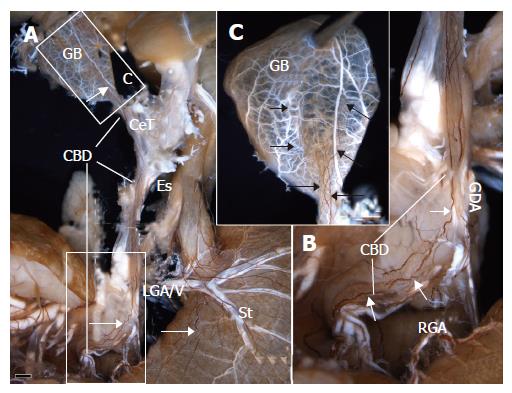
Figure 3 Innervation of the gallbladder (GB) in S.
murinus revealed on whole-mount immunostaining (A) and high magnification of the boxed areas (B and C). Arrows indicate the stained/labeled nerve branches or bundles. CBD: common bile duct; CeT: celiac trunk; Es: esophagus; GDA: gastroduodenal artery; LGA/V: left gastric artery/vein; RGA: right gastric artery; St: stomach. Scale bar = 2 mm in A.
-
Citation: Yi SQ, Ohta T, Tsuchida A, Terayama H, Naito M, Li J, Wang HX, Yi N, Tanaka S, Itoh M. Surgical anatomy of innervation of the gallbladder in humans and
Suncus murinus with special reference to morphological understanding of gallstone formation after gastrectomy. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(14): 2066-2071 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i14/2066.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i14.2066