Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2006; 12(6): 951-955
Published online Feb 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i6.951
Published online Feb 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i6.951
Figure 1 Genomic status of MYH in patients with multiple colorectal adenomas determined by quantitative DNA-PCR analysis.
Representative examples for exons 3-9 amplification are shown. Two hundred nanograms of DNA obtained from 30 patients and 5 healthy controls were used as templates for PCR amplification of 16 exonic regions using 14 intronic primer sets. GAPDH was used as an internal control for PCR. Ten microliters of PCR product was resolved on 20 g/L agarose gel and visualized by ethidium bromide staining. No significant reduction of gene levels was identified in samples from patients as compared with normal controls. Lanes N1-N5: Normal controls; Lanes P1-P15: Patients.
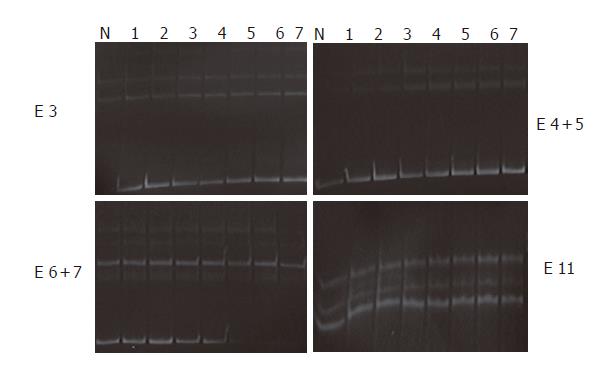
Figure 2 Non-isotopic PCR-SSCP analysis of MYH.
For detection of sequence alterations, all of the 16 exons and flanking intronic sequences were amplified by PCR as 14 separate fragments, and 20 μL of PCR product was subjected to non-isotopic SSCP analysis. Genomic DNA isolated from the healthy controls was used as normal controls. None of patient samples showed abnormal migration shift of single strand DNA molecules. Lane N: Normal control; Lanes 1-7: Patients; Lane E: Exons.
-
Citation: Kim H, Kim HJ, Chi SG, Lee SK, Joo GR, Dong SH, Kim BH, Chang YW, Lee JI, Chang R. Absence of
MutY homologue mutation in patients with multiple sporadic adenomatous polyps in Korea. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(6): 951-955 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i6/951.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i6.951