Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2006; 12(6): 902-907
Published online Feb 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i6.902
Published online Feb 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i6.902
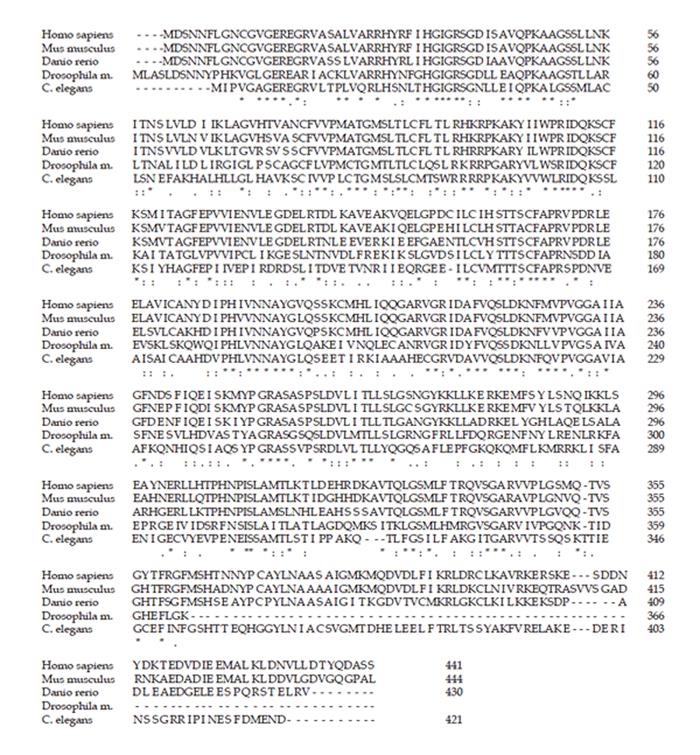
Figure 3 Alignment of SLA/LP protein sequences.
The SLA/LP amino acid sequences of various eukaryotic species were aligned by ClustalW. The presumed residues that mediate binding to the cofactor pyridoxal phosphate are highlighted in bold and underlined; residues that function in dimerization are highlighted in bold and italic. The immunodominant epitope sequence (390-428) of the human SLA/LP protein is marked in bold.
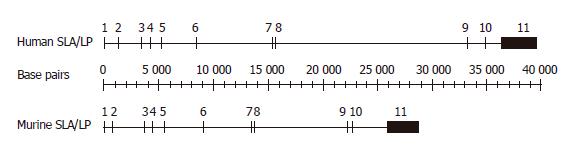
Figure 1 Organization of SLA/LP genes in man and mouse.
The exon/intron structure of the human and mouse SLA/LP gene is represented schematically. Exon sequences (numbered boxes) are highly conserved and of similar size and number in man and mouse. Intron sequences, marked as lines, differ in both species.
Figure 2 SLA/LP splice variants in man and mouse.
The amino acid sequences of the long and short SLA/LP splice variants in humans and their putative homologs in mouse are aligned. The protein variants differ only in their amino-terminal sequence, 11 or 30 residues in the human protein and 12 or 30 residues in the murine protein, as depicted in the upper panel. The other residues (lower panel) are identical in the respective splice variants within each species.
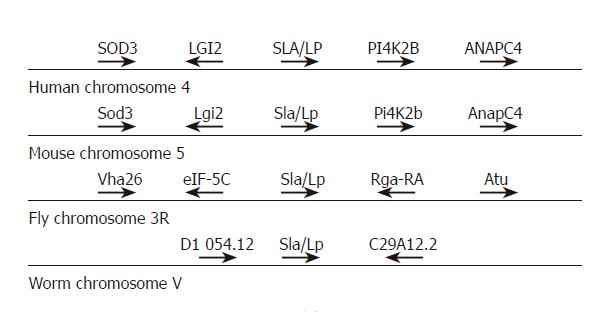
Figure 4 Chromosomal localization of SLA/LP genes.
The genes adjacent to the SLA/LP loci on human chromosome 4, mouse chromosome 5, fly chromosome 3R, and worm chromosome V are represented schematically.
- Citation: Wang CX, Teufel A, Cheruti U, Grötzinger J, Galle PR, Lohse AW, Herkel J. Characterization of human gene encoding SLA/LP autoantigen and its conserved homologs in mouse, fish, fly, and worm. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(6): 902-907
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i6/902.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i6.902