Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2006; 12(46): 7472-7477
Published online Dec 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7472
Published online Dec 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7472
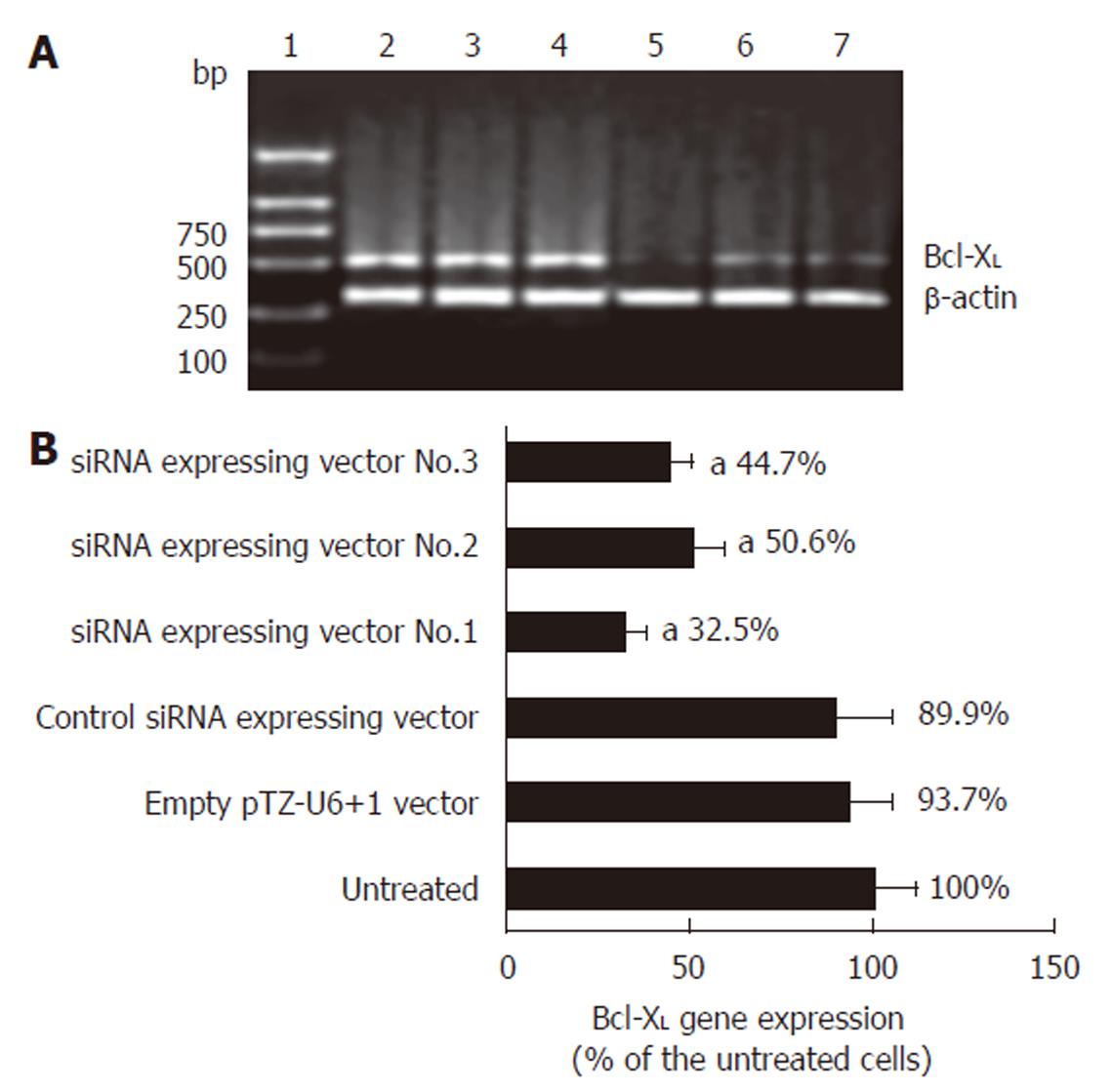
Figure 1 RT-PCR analysis of the effect of siRNA-expressing vector on Bcl-XL gene expression.
A: Argarose gel electrophoresis of the RT-PCR products. L1: DNA marker; L2: RT-PCR product of the untreated cells; L3: RT-PCR product of the empty pTZ-U6+1 vector treated cells; L4: RT-PCR product of the control siRNA-expressing vector treated cells; L5: RT-PCR product of the siRNA-expressing vector No.1 treated cells; L6: RT-PCR product of the siRNA-expressing vector No.2 treated cells; L7: RT-PCR product of the siRNA-expressing vector No.3 treated cells. B: Quantification of the RT-PCR products (mean ± SD, n = 3, aP < 0.05 vs untreated esophageal cancer cells).
Figure 2 Western blotting analysis and effect of siRNA-expressing vectors.
L1: Untreated esophageal cancer cells; L2: Esophageal cancer cells were transfected with empty pTZ-U6+1 vector; L3: Esophageal cancer cells were transfected with control siRNA expressing vector; L4: Esophageal cancer cells were transfected with siRNA-expressing vector No.1.
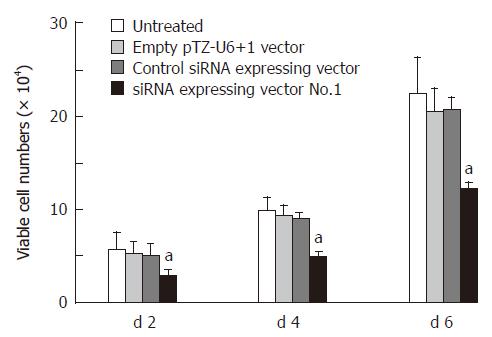
Figure 3 Effect of siRNA-expressing vector on cell growth post transfection (mean ± SD, n = 3, aP < 0.
05 vs untreated esophageal cancer cells).
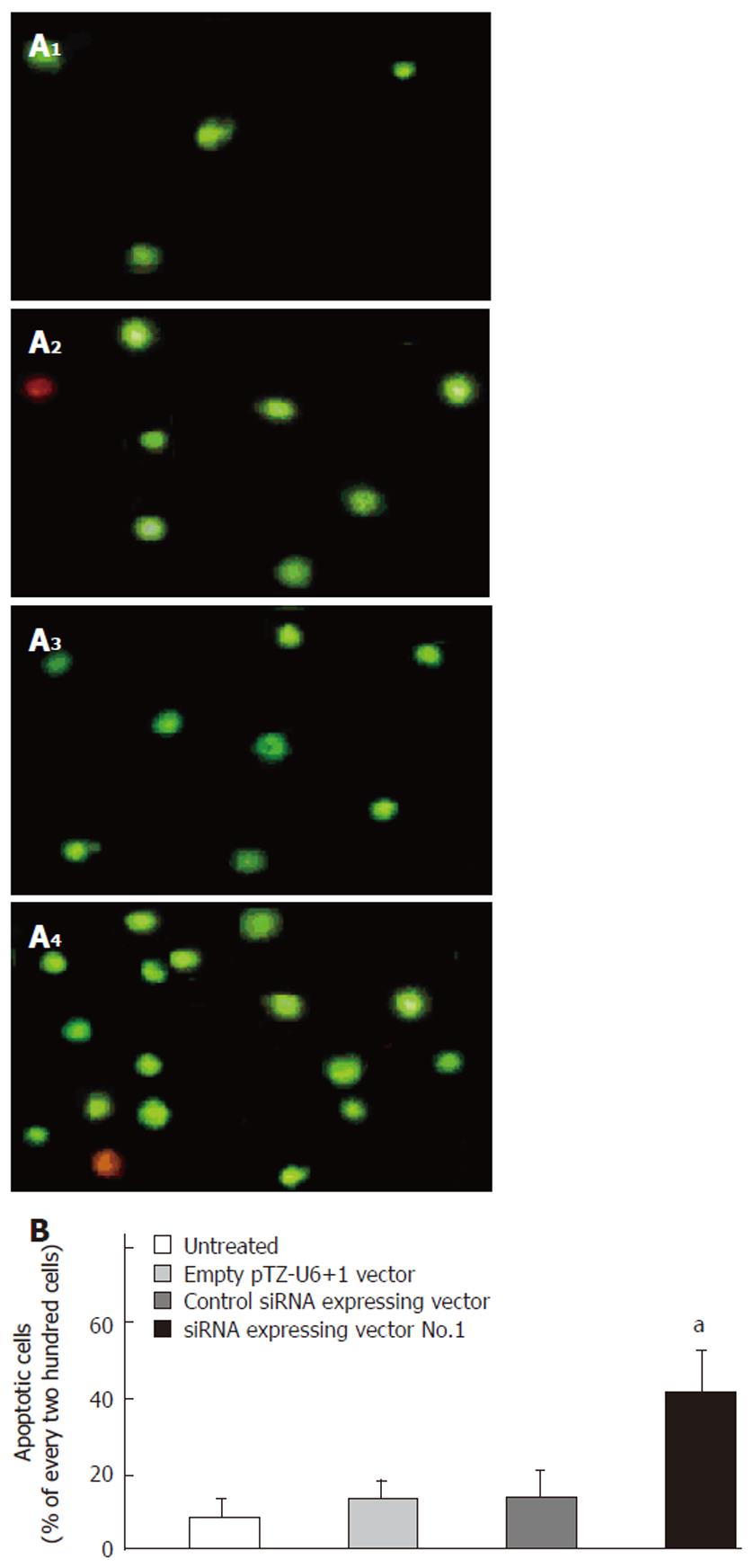
Figure 4 Effect of siRNA-expressing vector targeting Bcl-XL on apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells.
A: Photographs of YO-PRO-1 staining under the inverted fluorescence microscope at 72 h after transfection. 1: Untreated esophageal cancer cells; 2: Esophageal cancer cells were transfected with empty pTZ-U6+1 vector; 3: Esophageal cancer cells were transfected with control siRNA-expressing vector; 4: Esophageal cancer cells were transfected with siRNA-expressing vector No.1. B: Percentage of apoptotic cells in every 200 cells (mean ± SD, n = 3, aP < 0.05 vs untreated cells).
- Citation: Xie YE, Tang EJ, Zhang DR, Ren BX. Down-regulation of Bcl-XL by RNA interference suppresses cell growth and induces apoptosis in human esophageal cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(46): 7472-7477
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i46/7472.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7472