Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2006; 12(32): 5140-5147
Published online Aug 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i32.5140
Published online Aug 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i32.5140
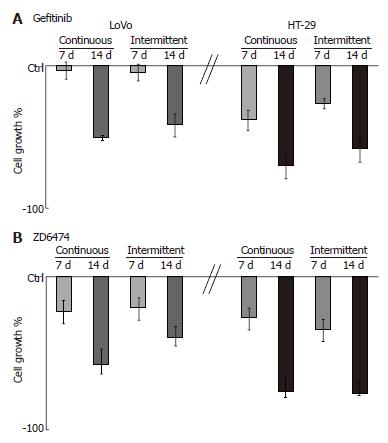
Figure 1 Drug-dependent cell growth inhibition.
LoVo and HT-29 cells were incubated with gefitinib (0.12 and 1.2 µmol/L, respectively) or ZD6474 (0.6 and 5 µmol/L, respectively) for 7 and 14 d with continuous and intermittent exposure. Cell survival was determined by cell counts.
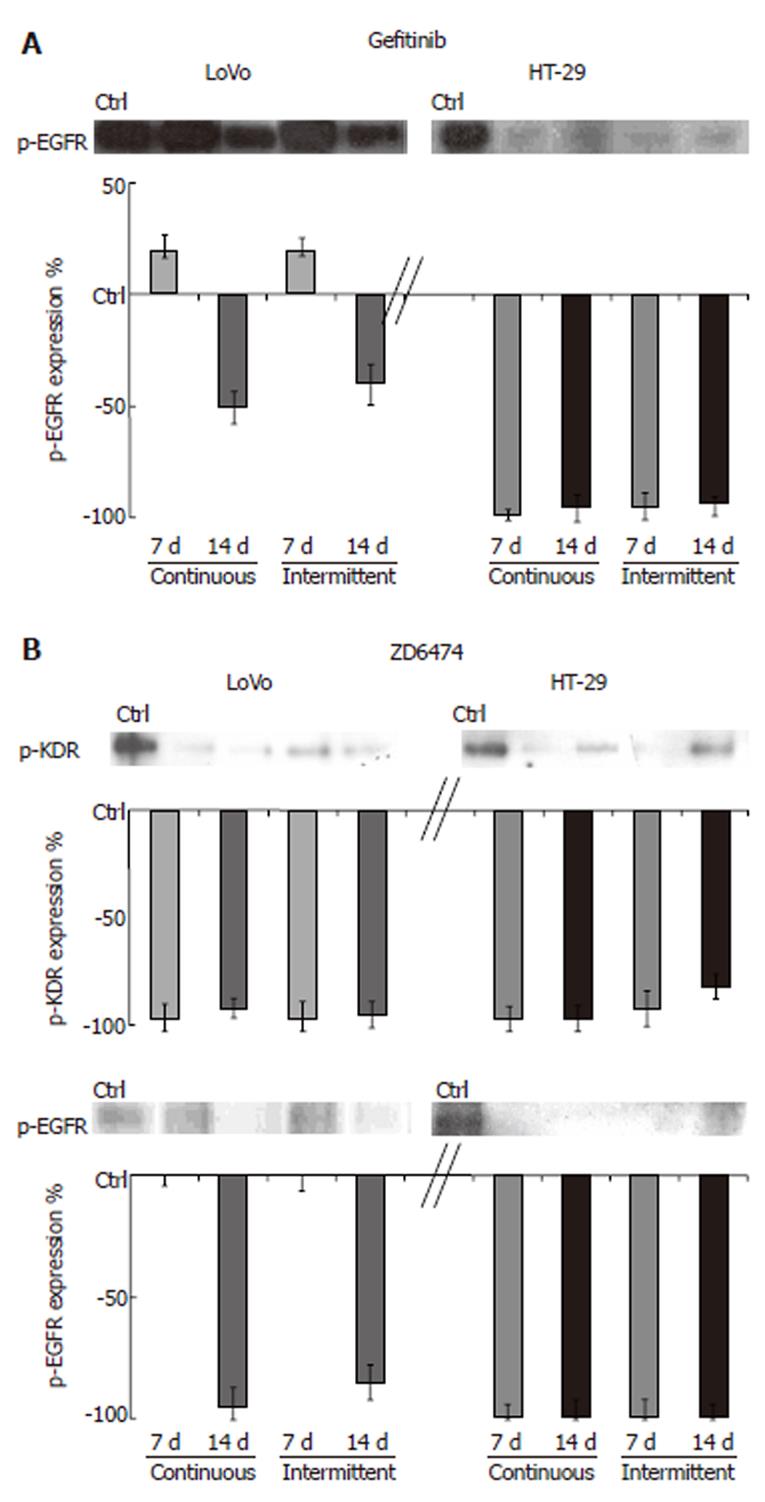
Figure 2 p-EGFR and p-KDR modulation after prolonged exposure to gefitinib or ZD6474.
Cells were incubated with gefitinib or ZD6474 for 7 and 14 d with continuous and intermittent exposure. Drug-dependent modulation of p-EGFR (180 kDa) and p-KDR (195 kDa) was determined by immunoprecipitation followed by Western blotting. All data are shown relative to the baseline level (control = 0), which was similar after 7 and 14 d.
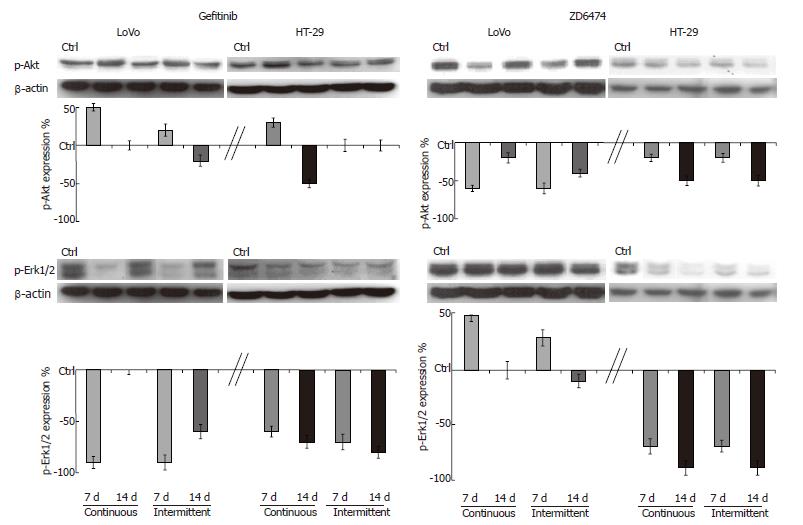
Figure 3 p-Akt and p-Erk1/2 modulation after prolonged exposure to gefitinib or ZD6474.
Cells were incubated with gefitinib or ZD6474 for 7 and 14 d with continuous and intermittent exposure. Drug-dependent p-Akt and p-Erk1/2 modulation was determined by Western blotting. All data are shown relative to the baseline level (control = 0), which was similar after 7 and 14 d.
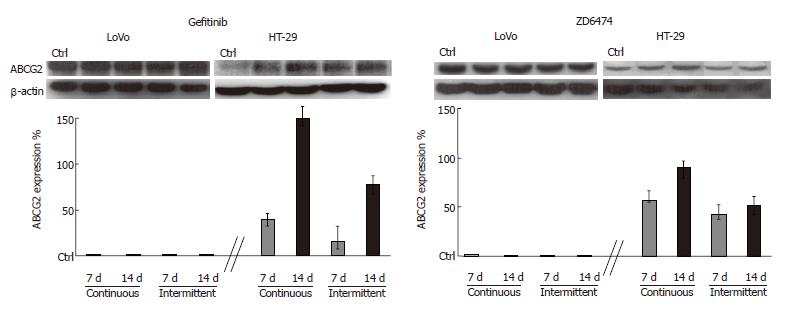
Figure 4 Increased ABCG2 expression after prolonged exposure to gefitinib or ZD6474.
Cells were incubated with gefitinib or ZD6474 for 7 and 14 d with continuous and intermittent exposure. Drug-dependent increases in ABCG2 expression were determined by Western blotting. All data are shown relative to the baseline level (control = 0), which was similar after 7 and 14 d.
- Citation: Azzariti A, Porcelli L, Xu JM, Simone GM, Paradiso A. Prolonged exposure of colon cancer cells to the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor gefitinib (Iressa™) and to the antiangiogenic agent ZD6474: Cytotoxic and biomolecular effects. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(32): 5140-5147
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i32/5140.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i32.5140