Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2006; 12(24): 3895-3900
Published online Jun 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i24.3895
Published online Jun 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i24.3895
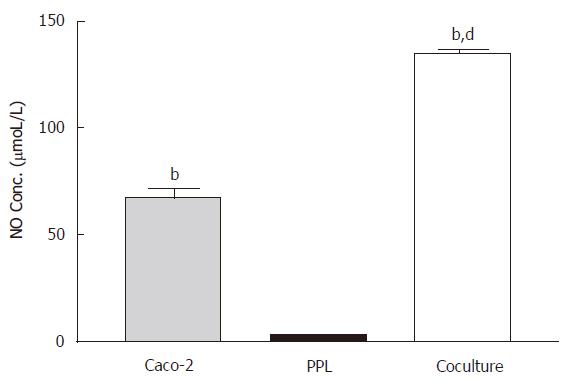
Figure 1 Enhancement of the constitutive NO release in the Caco-2 cocultured with lymphocytes of Peyer’s patch.
The level of NO in different culture conditions (Caco-2 alone: gray bar; PPL alone: black bar; coculture: white bar) was measured by Griess reagent system and the bar values were derived based on a standard curve. The values represent the means ± SE for 6-12 different samples; bP < 0.001 vs PPL; dP < 0.001 vs Caco-2.
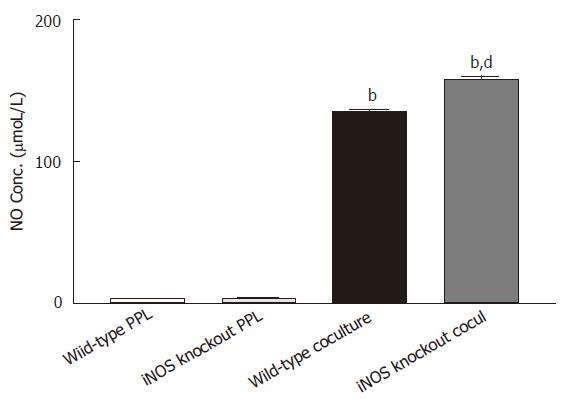
Figure 2 Release of NO is upregulated to the epithelial source Caco-2 cocultured with PPL from iNOS knockout mice.
Two sets of cocultures were established (Caco-2 cocultured with PPL of wild-type mice; and Caco-2 cocultured with PPL of iNOS knockout mice). The data are indicated by the following bars (white bar: PPL only from wild-type control mice; light gray bar: PPL only from iNOS knockout mice; black bar: coculture of Caco-2 and PPL from wild-type control mice; dark gray bar: coculture of Caco-2 and PPL from iNOS knockout mice). The level of NO production was measured by Griess colorimetric assay and the bar values were derived based on a standard curve. The values present the means ± SE for 6-8 different samples; bP < 0.001 vs its own PPL; dP < 0.001 vs wild-type coculture.
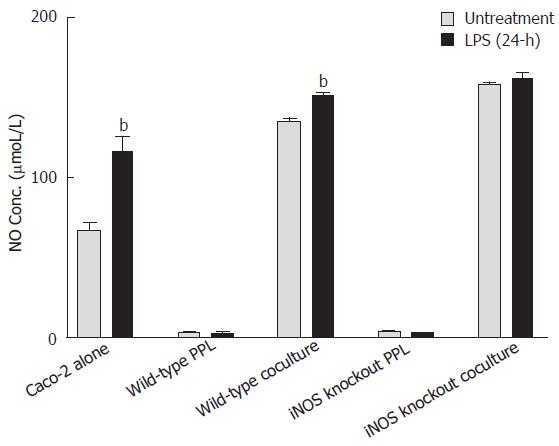
Figure 3 Comparison of NO release induced by Shigella LPS in various Caco-2 and PPL culture configurations.
Shigella LPS was added to five different cultures (set 1: Caco-2 alone; set 2: wild-type PPL only; set 3: Caco-2 and wild-type PPL coculture; set 4: iNOS knockout PPL alone; set 5: Caco-2 and iNOS knockout PPL coculture) and the level of NO release was measured by Griess colorimetric assay and derived based on a standard curve. The black bar and the gray bar represent 24 h treatment with and without LPS, respectively. The values represent the means ± SE for 6-14 different samples. Statistical significance relative to its own un-treatment group was indicated by bP < 0.001.
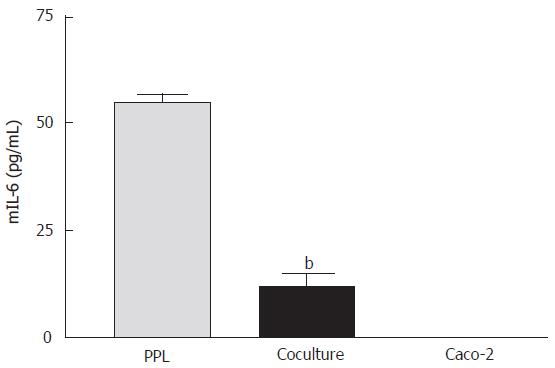
Figure 4 Suppression of mIL-6 release from PPL by cocultured Caco-2 epithelial cells.
The bars (gray: wild-type PPL only; black: coculture of Caco-2 and PPL; white: Caco-2 only control) indicate the level of mIL-6 release 4 d after culture. The level of mIL-6 was measured by mIL-6 ELISA and the values were derived based on a standard curve. The values represent means ± SE; n = 4; bP < 0.001 vs PPL.
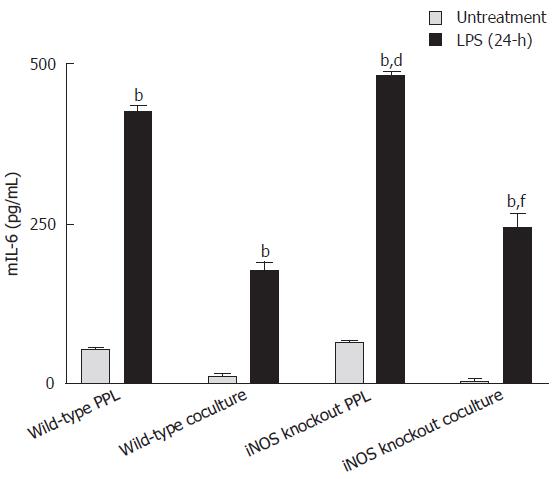
Figure 5 Comparison of mIL-6 release induced by Shigella LPS in various Caco-2 and PPL culture configurations.
Shigella LPS was added to four different cultures (set 1: wild-type PPL only; set 2: Caco-2 and wild-type PPL coculture; set 3: iNOS knockout PPL only; set 4: Caco-2 and iNOS knockout PPL coculture) and the level of mIL-6 release was measured by mIL-6 ELISA and the values were derived based on a standard curve. The black bar and the gray bar represent 24 h treatment with and without LPS, respectively. The values represent the mean ± SE for 4 different samples; bP < 0.001 vs its own untreatment group, dP < 0.001 vs wild-type PPL 24-h after challenge Shigella LPS and fP < 0.001 vs wild-type coculture 24-h after Shigella LPS challenge.
- Citation: Chen J, Ng CP, Rowlands DK, Xu PH, Gao JY, Chung YW, Chan HC. Interaction between enteric epithelial cells and Peyer’s patch lymphocytes in response to Shigella lipopolysaccharide: Effect on nitric oxide and IL-6 release. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(24): 3895-3900
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i24/3895.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i24.3895