Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2006; 12(16): 2517-2522
Published online Apr 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i16.2517
Published online Apr 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i16.2517
Figure 1 Histological analysis of mouse liver.
A: X15-myc control; B: X15-myc mouse treated with DL suspension; C: Normal mouse liver. (A1, B1, C1 = x100 and A2, B2, C2 = x400).
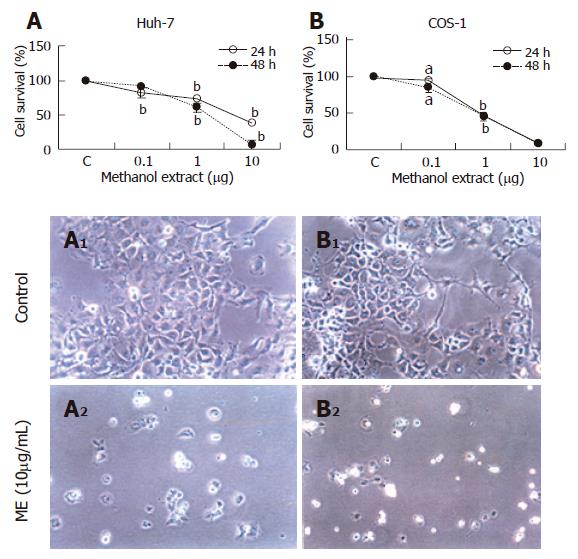
Figure 2 Cytotoxic effect of methanolic extract of DL on cancer cell lines.
Huh-7 (A) and COS-1 cells (B) were incubated with different concentrations of ME and analyzed for cell viability at 24h or 48h (n = 6), mean ± SE. aP < 0.001; bP < 0.01; A1 and B1 are control Huh-7 and COS-1 cells; A2 and B2 are ME-treated Huh-7 and COS-1 cells (x200).
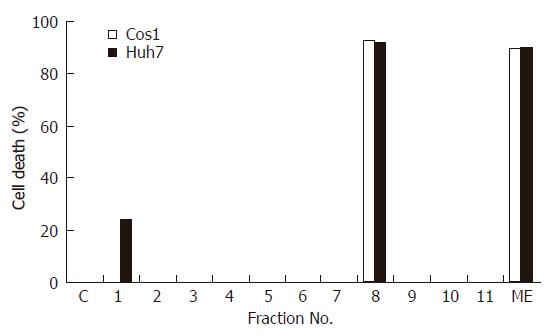
Figure 3 Cytotoxic effect of different fractions of the methanolic extract of DL on cancer cell lines.
Huh-7 and COS-1 cells were incubated with either ME or its eleven fractions (all at 10 mg/L). Cell viability was measured at 48 h and results are expressed as % cell death.
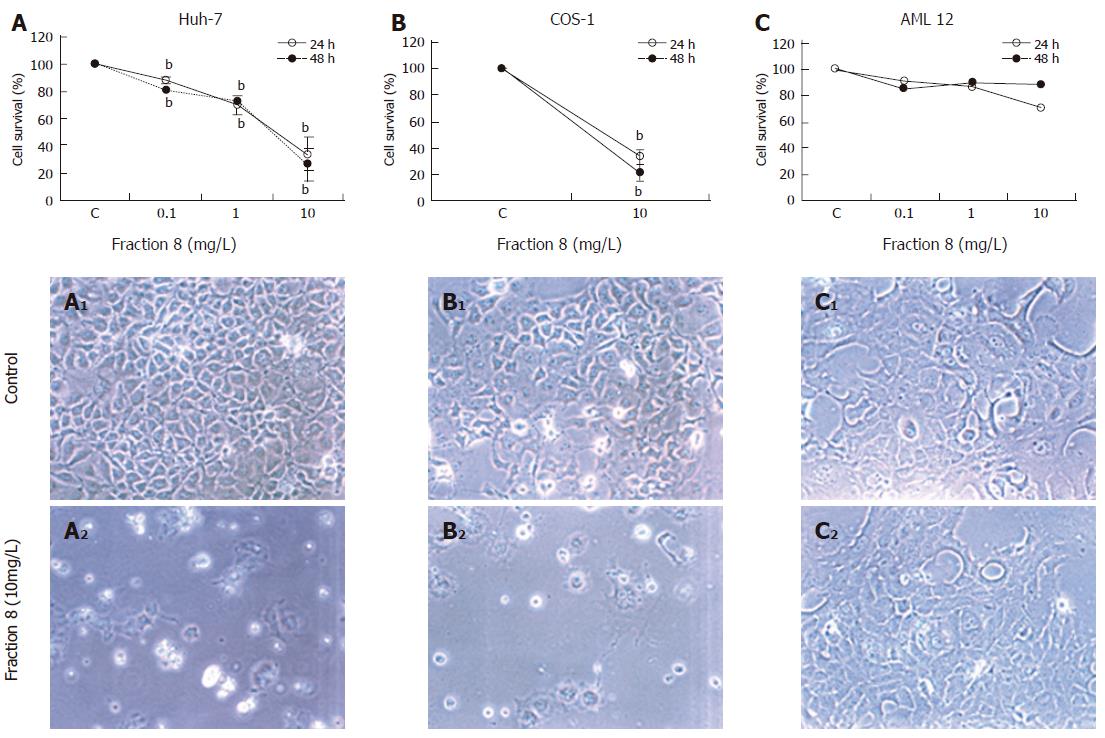
Figure 4 Cytotoxic effect of fraction 8 of the DL methanolic extract on different cell lines.
Huh-7 (A), COS-1 (B) and AML12 cells (C) were incubated with different concentrations of fraction 8 and cell viability was measured at 24 and 48 h (mean ± SE, bP < 0.01). A1, B1 and C1 are control Huh-7, COS1 and AML12 cells; A2, B2 and C2 are fraction 8 treated Huh-7, COS-1 and AML12 cells (x200).
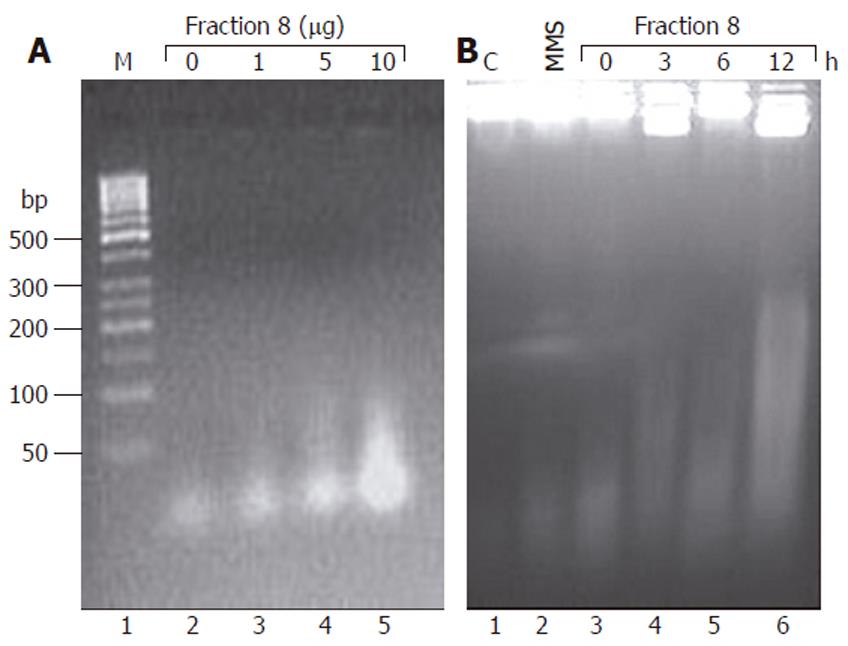
Figure 5 Effect of fraction 8 on DNA fragmentation in Huh-7 cells.
Huh-7 cells were treated either with different concentrations (1, 5 and 10 mg/L) of fraction 8 for 3 h (A) or for 3, 6 and 12 h with 10 mg/L of fraction 8 (B). Total DNA was extracted after proteinase K and RNase A treatment and resolved by agarose gel electrophoresis. C: DNA from control cells; M: 100 base pair (bp) ladder; MMS, DNA from cells treated with methyl methanesulfonate (2 g/L) for 15 min.
- Citation: Choedon T, Mathan G, Arya S, Kumar VL, Kumar V. Anticancer and cytotoxic properties of the latex of Calotropis procera in a transgenic mouse model of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(16): 2517-2522
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i16/2517.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i16.2517