Copyright
©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2005; 11(32): 4967-4973
Published online Aug 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i32.4967
Published online Aug 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i32.4967
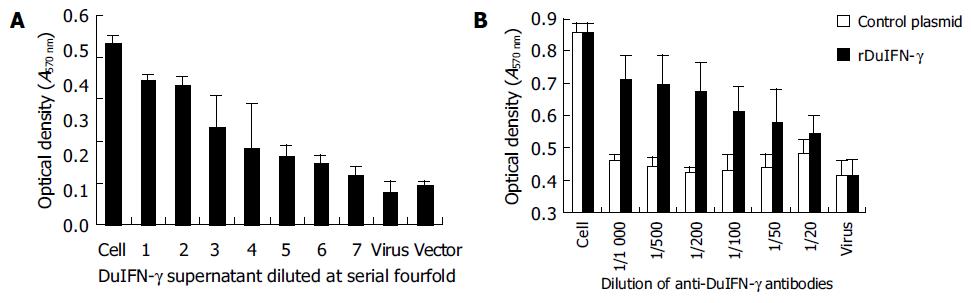
Figure 1 Titration of recombinant DuIFN-g by MTT (A) and neutralization of antiviral activity by anti-DuIFN-g (B).
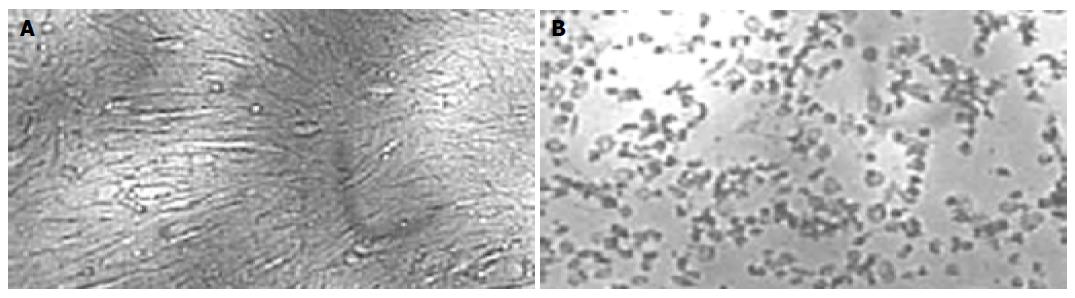
Figure 2 Morphology of normal duck fibroblasts (A) and cytopathic effect (CPE) of duck fibroblasts when infected with VSV (B).
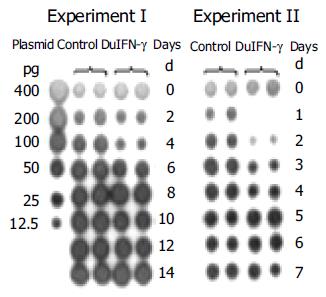
Figure 3 Effects of recombinant DuIFN-g on release of DHBV DNA from LMH-D2 cells.
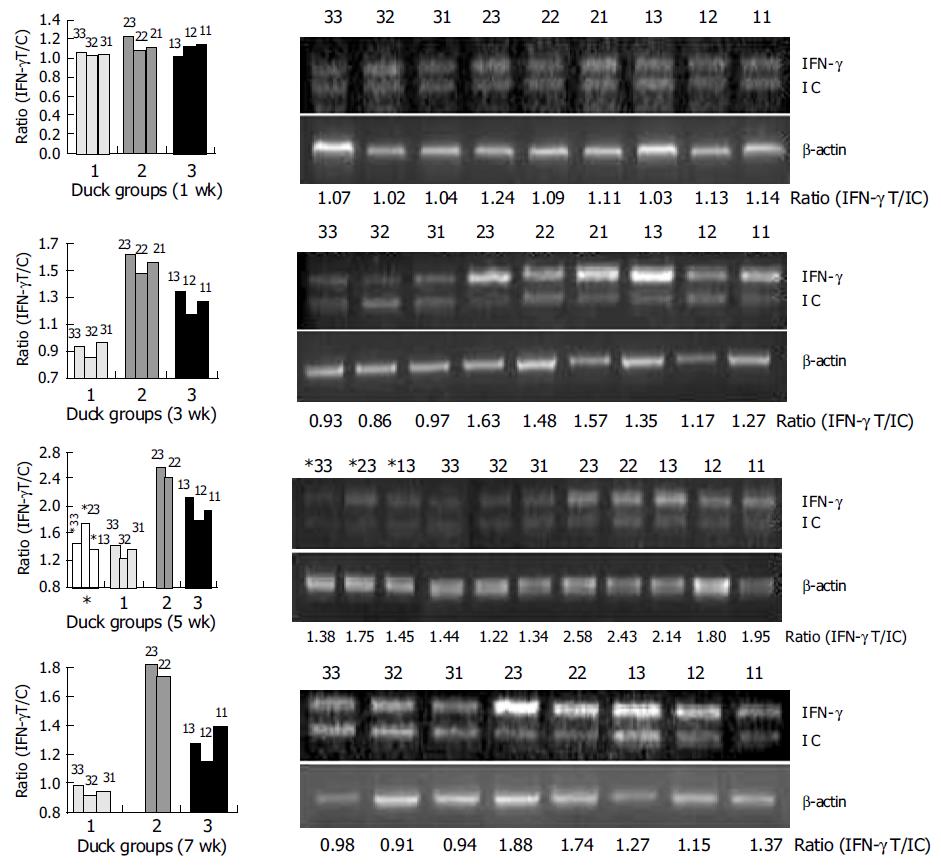
Figure 4 Detection of DuIFN-g mRNA of PBMCs from ducks after immunization.
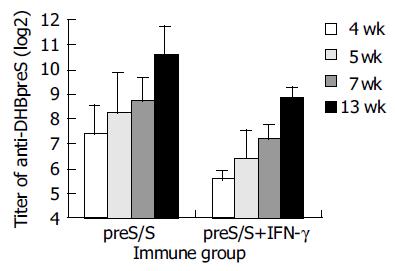
Figure 5 Anti-DHBpreS antibody responses following DNA immunization of DHBV-free ducks.
Figure 6 Exclusion of DHBV from bloodstream in DNA-vaccinated ducks following challenge with viruses.
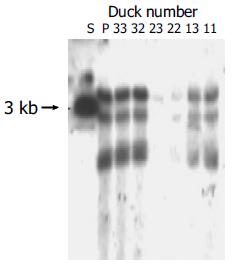
Figure 7 Detection of DHBV cccDNA in ducks’ liver tissues after being challenged with high dose of DHBV.
S: Full length fragment of DHBV genome, 3.0 kb. P: Positive control ducks infected DHBV.
- Citation: Long JE, Huang LN, Qin ZQ, Wang WY, Qu D. IFN-γ increases efficiency of DNA vaccine in protecting ducks against infection. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(32): 4967-4973
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i32/4967.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i32.4967