Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2005; 11(24): 3655-3659
Published online Jun 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i24.3655
Published online Jun 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i24.3655
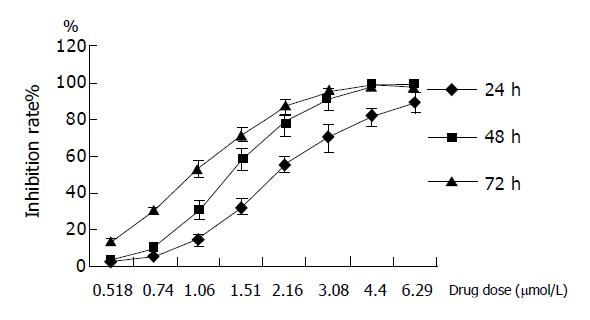
Figure 1 Inhibitory effect of GA on proliferation in BGC-823 cells.
Dose- and time-dependent inhibitions were observed after cells treated with GA for 24, 48, and 72 h, respectively.
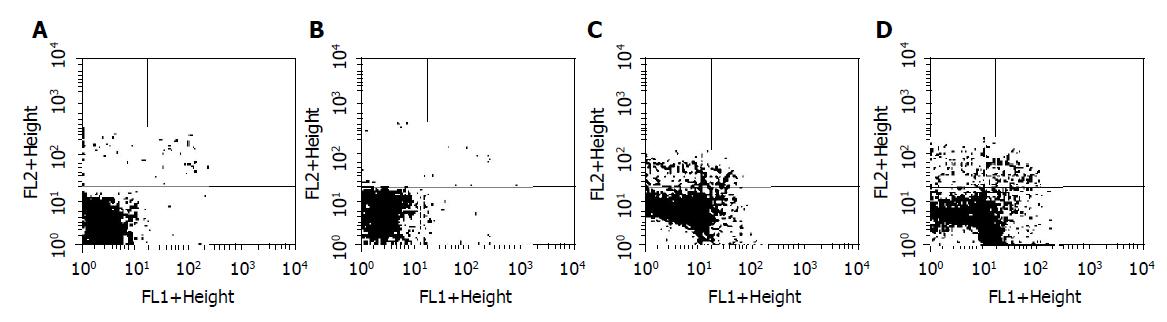
Figure 2 Fluorescence-activated cell sorter analysis for Annexin-V and PI staining of BGC-823 cells incubated with 1.
2 μmol/L GA for 24, 48, and 72 h, respectively. A: control, LL: 91.34%, UR: 1.66%, LR: 2.79%; B: GA (1.2 μmol/L, 24 h), LL: 95.03%, UR: 0.71%, LR: 2.03%; C: GA (1.2 μmol/L, 48 h), LL: 52.26%, UR: 4.31%, LR: 12.96%; D: GA (1.2 μmol/L, 72 h), LL: 37.51%, UR: 4.88%, LR: 24.58%.
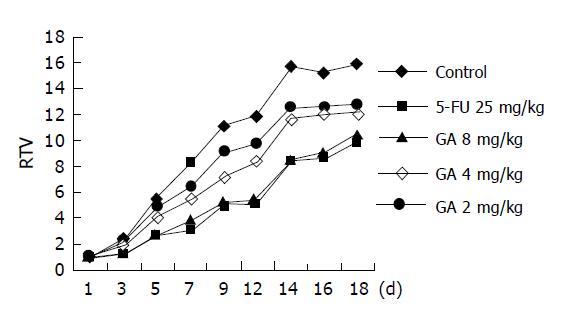
Figure 3 Inhibition of GA on transplantation tumor induced by BGC-823 in BALB/cA nude mice (control, n = 12; GA and 5-FU, n = 6).
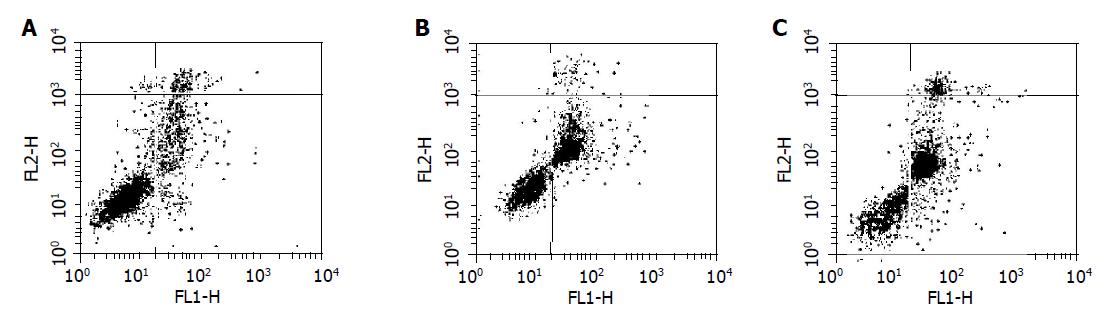
Figure 4 Fluorescence-activated cell sorter analysis for Annexin-V and PI staining of BGC-823 tumor tissue incubated with GA and early apoptotic cells were localized in the lower right quadrant of a dot-plot graph.
A: control, LL:85.28%, UR:5.97%, LR:5.28%; B: 5FU 25 mg/kg, positive group, LL:57.50%, UR:3.54%, LR:38.85%; C: GA (8 mg/kg) LL:65.08%, UR:6.74%, LR:25%.
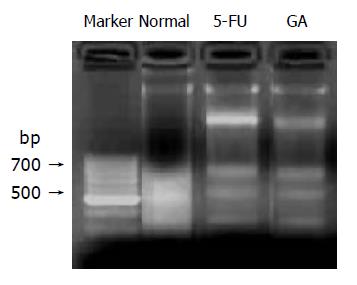
Figure 5 DNA fragmentation assay was used to confirm the late apoptotic change of nuclei on BGC-823 tumor tissue after treatment of GA.
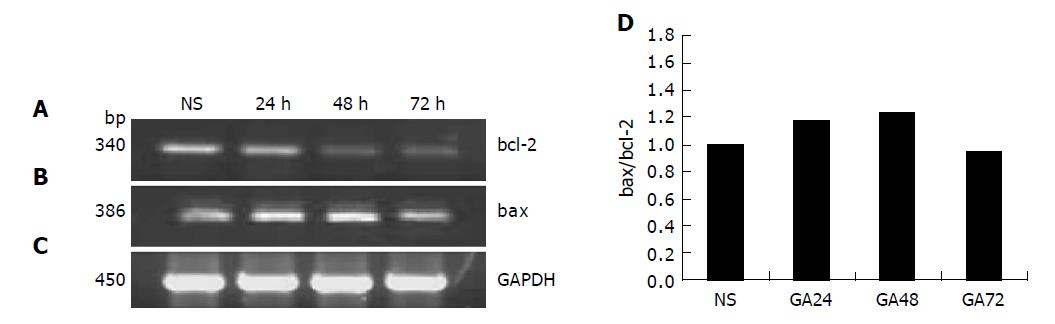
Figure 6 A: RT-PCR assay of bcl-2 gene expression in BGC-823 cells after the cells were treated with 0.
8 μmol/L GA for 24, 48 and 72 h, respectively; B: RT-PCR assay of bax gene expression in BGC-823 cells after the cells were treated with 0.8 μmol/L GA for 24, 48, and 72 h, respectively; C: GAPDH; D: bax/bcl-2.
- Citation: Liu W, Guo QL, You QD, Zhao L, Gu HY, Yuan ST. Anticancer effect and apoptosis induction of gambogic acid in human gastric cancer line BGC-823. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(24): 3655-3659
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i24/3655.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i24.3655