Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 15, 2004; 10(6): 804-808
Published online Mar 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i6.804
Published online Mar 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i6.804
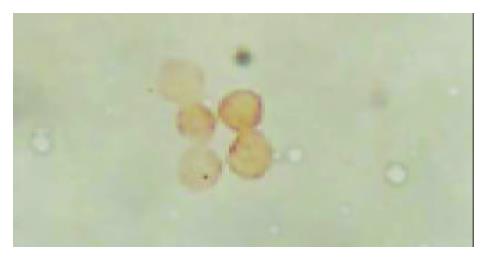
Figure 1 Immunohistochemical staining showed that there was CD34 expression on the membranes of the cells, these cells had small and round nuclei, even chromatins and the thickness of nuclear membrane was normal (amplification ×1000).
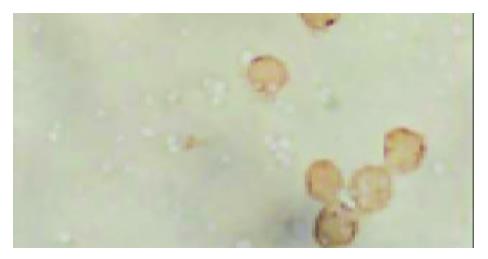
Figure 2 Immunohistochemical staining showed that there was CD45 expression on the membranes of the cells, these cells had small and round nuclei, even chromatins and the thickness of nuclear membrane was normal (amplification ×1000).
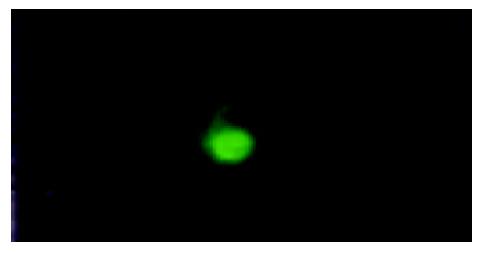
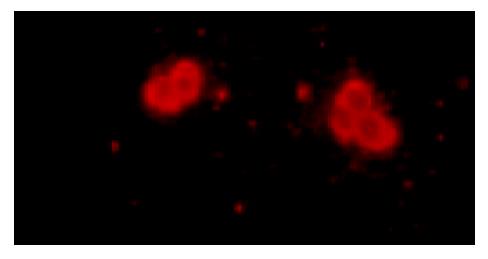
Figure 3 Immunofluorescence staining the cells, which had small and round nuclei, even chromatins and the thickness of nuclear membrane was normal (amplification ×200), had posi-tive expressions of hTERT.
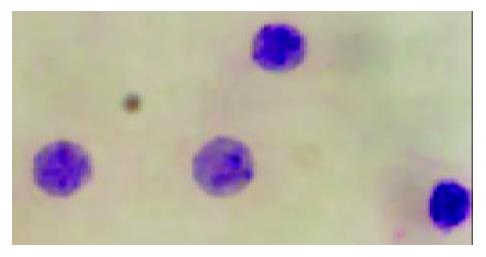
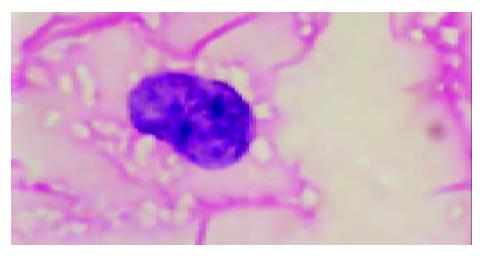
Figure 4 The cells, which had small and round nuclei, even chromatins and the thickness of nuclear membrane was nor-mal (HE staining, amplification×1000), might be hematopoie-sis precursors.
Figure 5 The cells, which had larger nuclei, abnormal forms and thicker membrane, and massed chromatins and more than one nuclei could also be found in this kind of cells, had posi-tive expression of CEA (Immunofluorescence staining, ampli-fication ×200).
Figure 6 The cells, which had larger nuclei, abnormal forms and thicker membrane, and massed chromatins and more than one nuclei could also be found in this kind of cells, had posi-tive expressions of CEA and hTERT, and negative expressions of CD34 and CD45, were considered as the disseminated car-cinoma cells escaped from the primary neoplasm focus (HE staining, amplification ×1000).
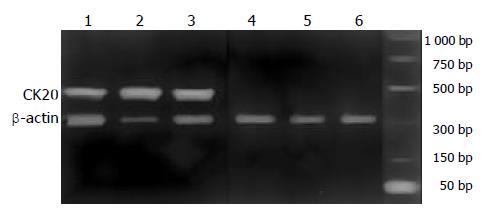
Figure 7 RT-PCR for CK20 and β-actin.
M: Marker; Lanes1-4 blood from gastric cancer; Lanes5-6 blood from chronic gastritis.
- Citation: Chen XM, Chen GY, Wang ZR, Zhu FS, Wang XL, Zhang X. Detection of micrometastasis of gastric carcinoma in peripheral blood circulation. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(6): 804-808
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i6/804.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i6.804