Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 15, 2004; 10(22): 3245-3250
Published online Nov 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i22.3245
Published online Nov 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i22.3245
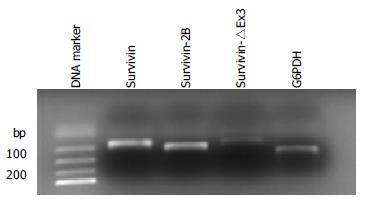
Figure 1 Amplification, separation and visualization of survivin (185 bp), survivin-2B (214 bp) survivin-△Ex3 (184 bp), and G6PDH (256 bp) mRNA (40 cycles) in a typical case.
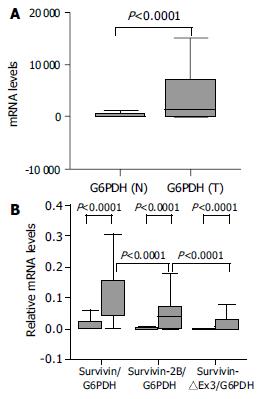
Figure 2 A: RT-PCR amplification of G6PDH in paired samples of normal gastric mucosa and gastric carcinoma.
B: Relative (G6PDH-normalised) mRNA levels of survivin variants in paired samples of normal gastric mucosa and gastric carcinoma. Two-tailed P values were calculated by the Mann-Whitney U test.
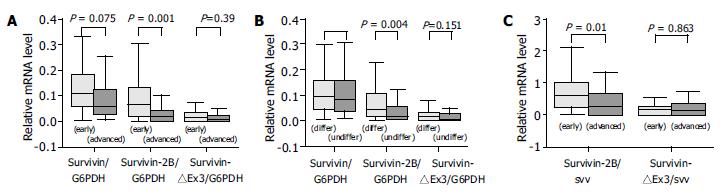
Figure 3 Relative mRNA levels of survivin variants.
A: Significant decrease of relative (G6PDH-normalised) mRNA levels of survivin-2B in advanced stages (P = 0.001, Mann-Whitney U test). B: Significant decrease of relative (G6PDH-normalised) mRNA levels of survivin-2B in undifferentiated type (P = 0.004, Mann-Whitney U test). C: Significantly lower ratio of survivin-2B/survivin in advanced stages than that in early stages (P = 0.018, Mann-Whitney U test).
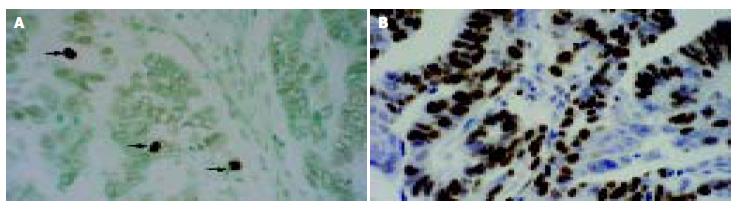
Figure 4 Histochemical staining for Ki-67 and apoptotic tumor cells.
A: TUNEL in situ labeling for detecting apoptotic cells and bodies (arrows, magnification × 400) in adenocarcinoma. B: Ki-67 nuclear immunohistochemical staining revealing proliferating tumor cells in adenocarcinoma (magnification × 400).
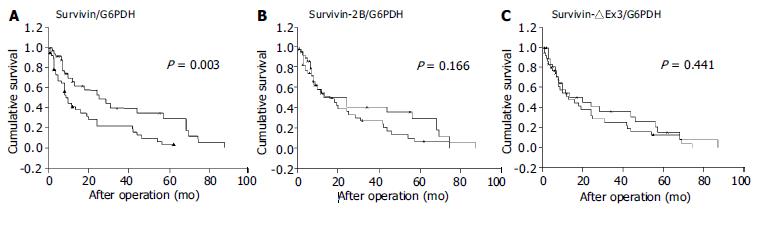
Figure 5 postoperative survivals of 79 gastric carcinoma patients.
A: Shorter survival time of patients with high expression of wild-type survivin mRNA compared to patients with low expression of wild-type survivin expression (P = 0.003, log-rank test).B: No significance in expression of survivin-2B mRNA (P = 0.166, log-rank test). C: No significance in expression of survivin-△Ex3 mRNA (P = 0.441, log-rank test).
- Citation: Meng H, Lu CD, Sun YL, Dai DJ, Lee SW, Tanigawa N. Expression level of wild-type survivin in gastric cancer is an independent predictor of survival. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(22): 3245-3250
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i22/3245.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i22.3245