Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 15, 2004; 10(16): 2334-2339
Published online Aug 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i16.2334
Published online Aug 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i16.2334
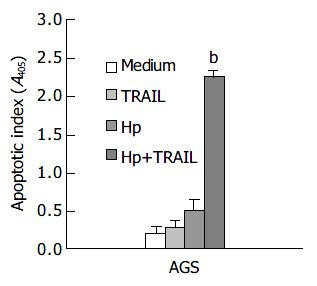
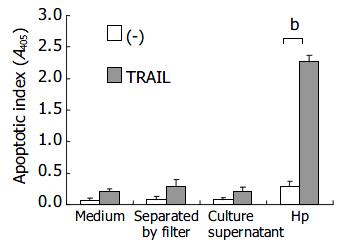
Figure 1 Effects of TRAIL and H pylori on apoptosis in human gastric epithelial cell line AGS (bP<0.
01 when compared with medium control, TRAIL or H pylori alone).
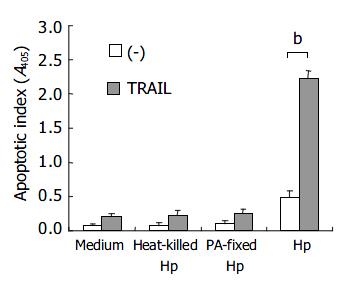
Figure 2 AGS cells incubated with heat killed, paraformalde-hyde-fixed (PA-fixed) or live H pylori (ATCC strain 43504) under the concentration of 4 × 107 CFU/5 × 104 cells for 12 h.
Open bar: without TRAIL; filled bar: with TRAIL (bP < 0.01).
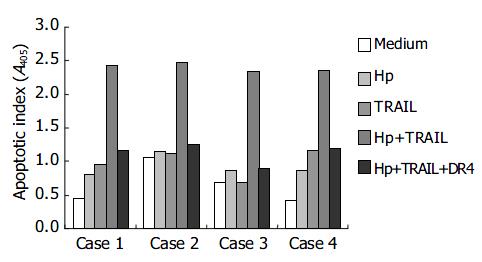
Figure 3 Enhancement of TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by H pylori in primary human gastric epithelial cells.
Figure 4 Induction of TRAIL sensitivity specific for H pylori in human gastric epithelial cells (bP < 0.
01 when compared with H pylori alone without adding TRAIL samples).
Figure 5 Enhancement of direct bacteria-cell contact depen-dent TRAIL sensitivity by H pylori (bP < 0.
01).
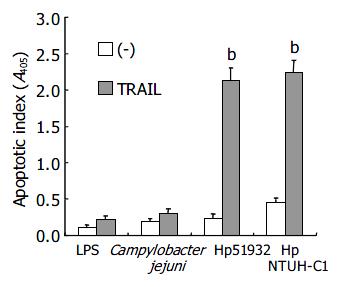
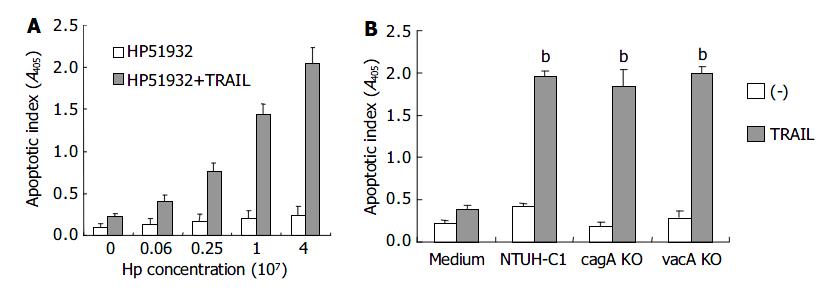
Figure 6 Effects of vacA and cagA on induction of TRAIL sensitivity by H pylori.
A: AGS cells (5 × 104 cells) were incubated with a different concentration of H pylori (ATCC strain 51932) for 12 h. B: AGS cells were incubated with H pylori NTUH-C1 and its cagA, vacA gene knock out mutant strains (cagA KO, vacA KO) in the concentration of 4 × 107 CFU/5 × 104 cells for 12 h (bP < 0.01 when compared with H pylori alone without adding TRAIL samples).
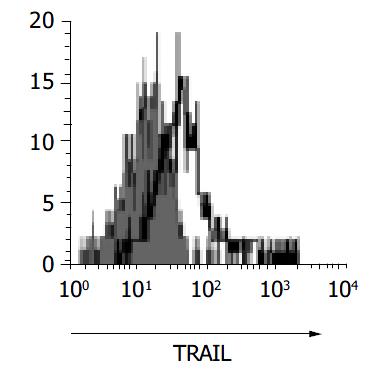
Figure 7 Expression of TRAIL on surface of T cells isolated from gastric mucosa.
-
Citation: Wu YY, Tsai HF, Lin WC, Chou AH, Chen HT, Yang JC, Hsu PI, Hsu PN.
Helicobacter pylori enhances tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis in human gastric epithelial cells. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(16): 2334-2339 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i16/2334.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i16.2334