Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. May 15, 2004; 10(10): 1402-1408
Published online May 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i10.1402
Published online May 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i10.1402
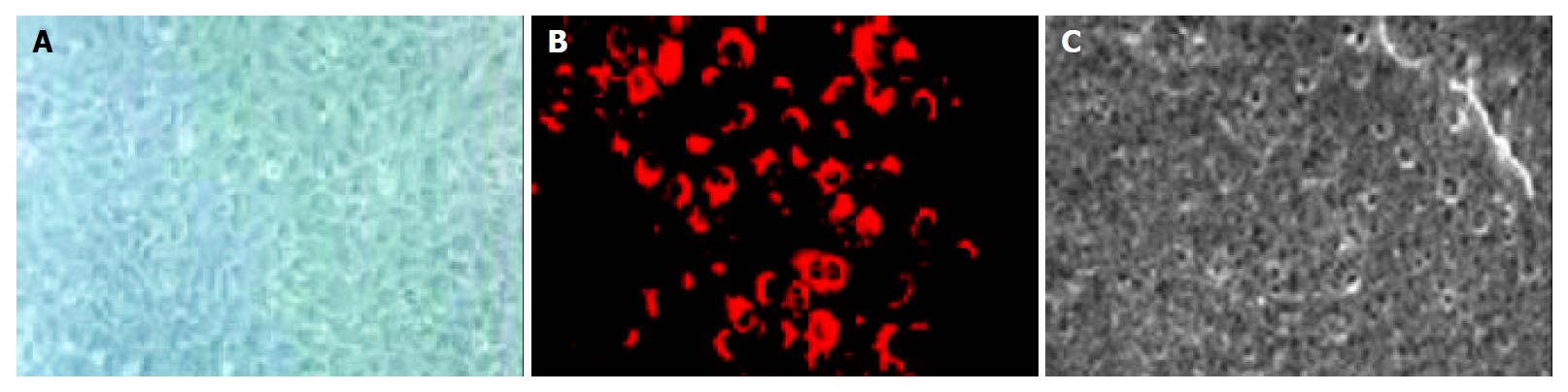
Figure 1 Cultured human liver cancer vascular endothelia.
A: Morphology of cultured human liver cancer vascular endothelial cells; B: Uptake of Ac-LDL; C: Electron microscope for fenestration.
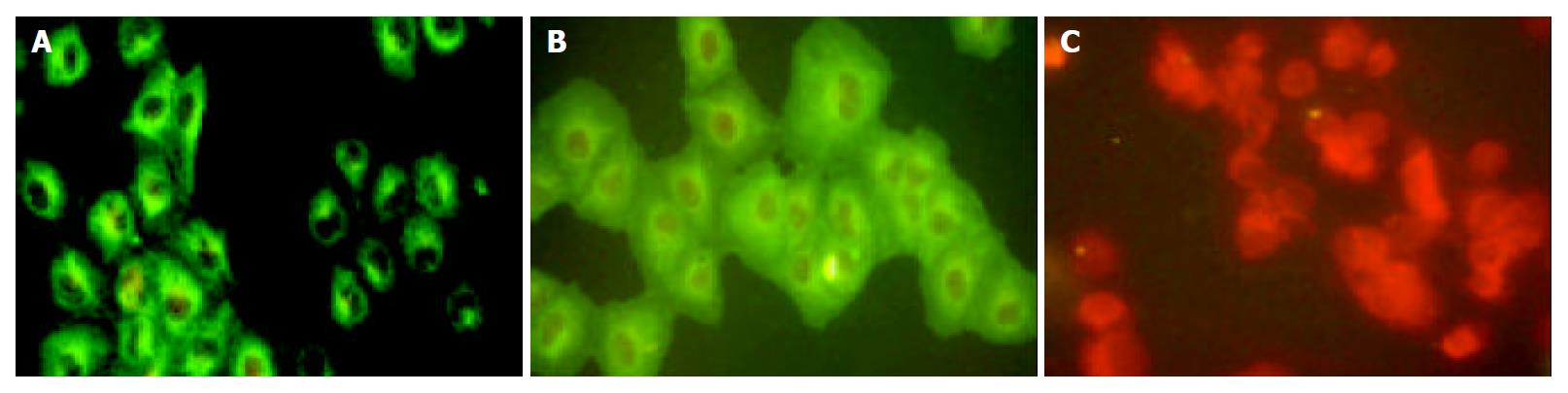
Figure 2 Immunofluorescence analysis of endothelial cells stained with the sera diluted 1:5000 isolated from the mice immunized with HLCVECs.
A: HLCVECs; B: Activated HUVECs; C: HUVECs.
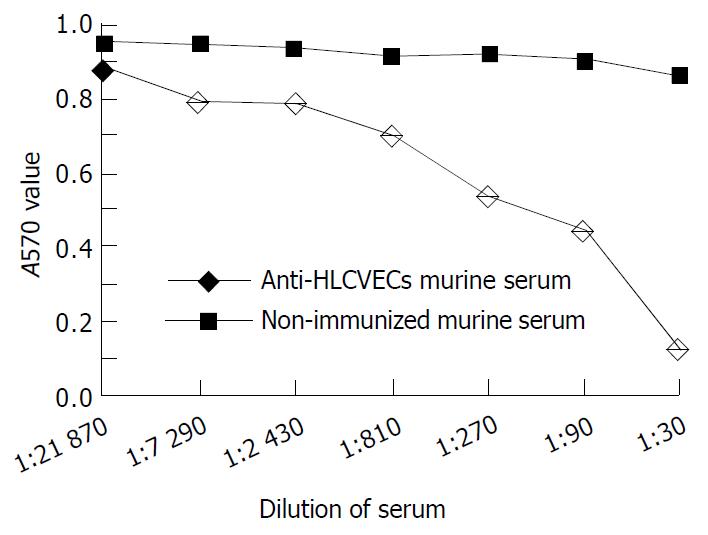
Figure 3 Inhibition of the HLCVECs proliferation by HLCVECs immunized murine serum from 1 of 6 immunized mice and 1 of 4 non-immunized mice.
Points are the average of three wells.
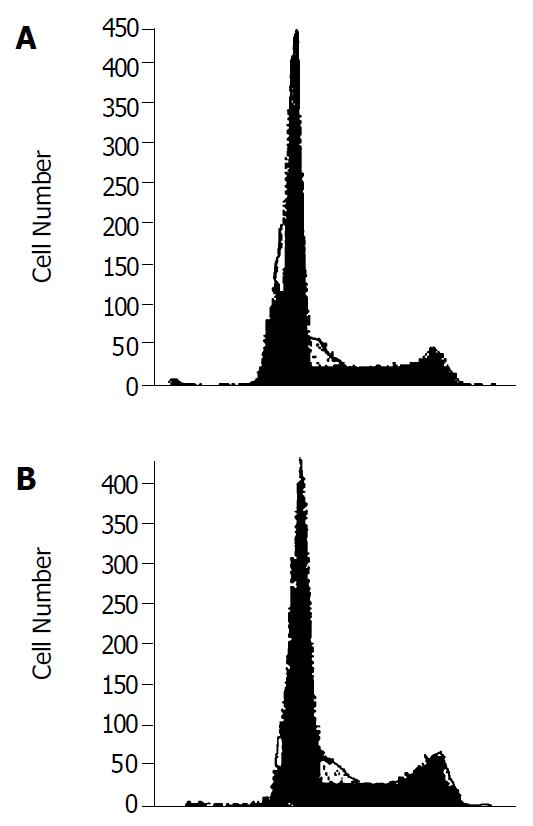
Figure 4 Cell cycle analysis of HLCVECs after treatment with immune sera or non-immune sera.
A: HLCVECs treated with immune sera for 6 h; B: HLCVECs treated with non-immune sera for 6 h.
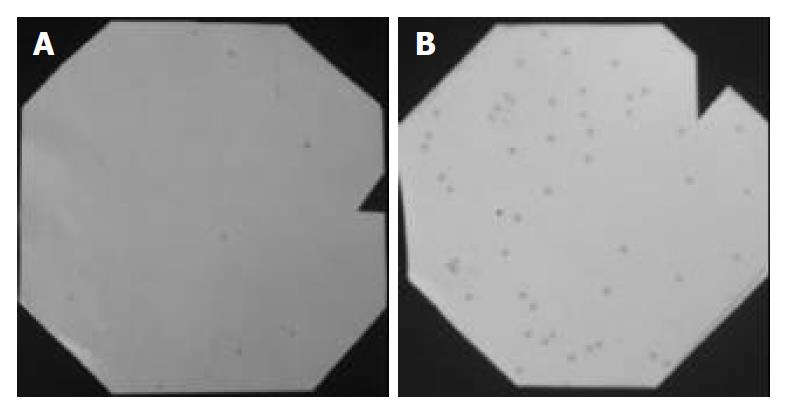
Figure 5 Positive dots of phage clone of screening by immune sera.
A: The first cycle of screening by immune sera; B: The second cycle of screening by immune sera.
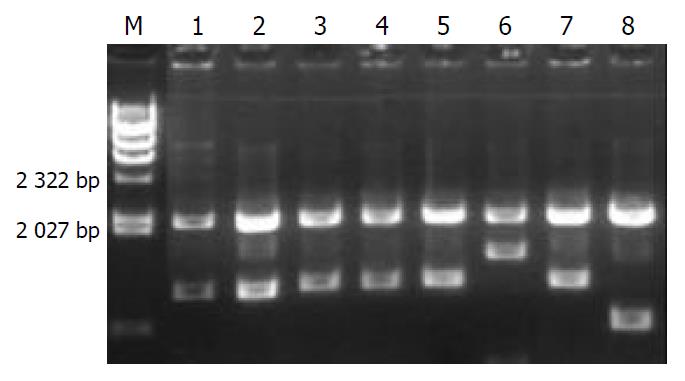
Figure 6 Electrophoresis analysis of enzymatic digestion of SEREX positive clones.
M, λHind III marker, from above to below: 20130, 9416, 6557, 4316, 2322, 2027, 564 bp; Lanes 1-8, positive clones digested with EcoR I and Xhol I.
- Citation: Zhong X, Ran YL, Lou JN, Hu D, Yu L, Zhang YS, Zhou Z, Yang ZH. Construction of human liver cancer vascular endothelium cDNA expression library and screening of the endothelium-associated antigen genes. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(10): 1402-1408
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i10/1402.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i10.1402