Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 16, 2023; 11(11): 2541-2548
Published online Apr 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i11.2541
Published online Apr 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i11.2541
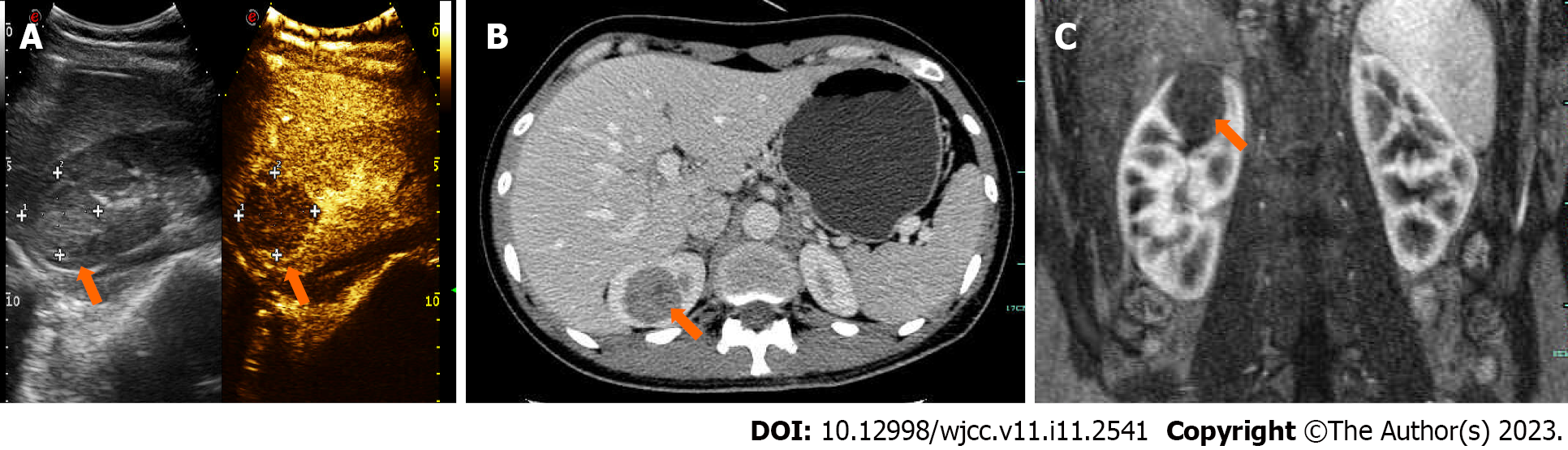
Figure 1 Imaging examinations.
A: Contrast-enhanced ultrasonographic examination of the kidney shows a medium echogenic mass presenting with low enhancement characterized by a “slow in and fast out” pattern; B: Computed tomography (CT) image selected from the enhanced CT urography scan sequence shows an endogenic round-like mass in the upper pole of the right kidney, which is approximately 3 cm in diameter; C: Coronal magnetic resonance imaging shows a right upper pole renal mass (endogenic type) with no significant abnormalities in the bilateral adrenal glands.
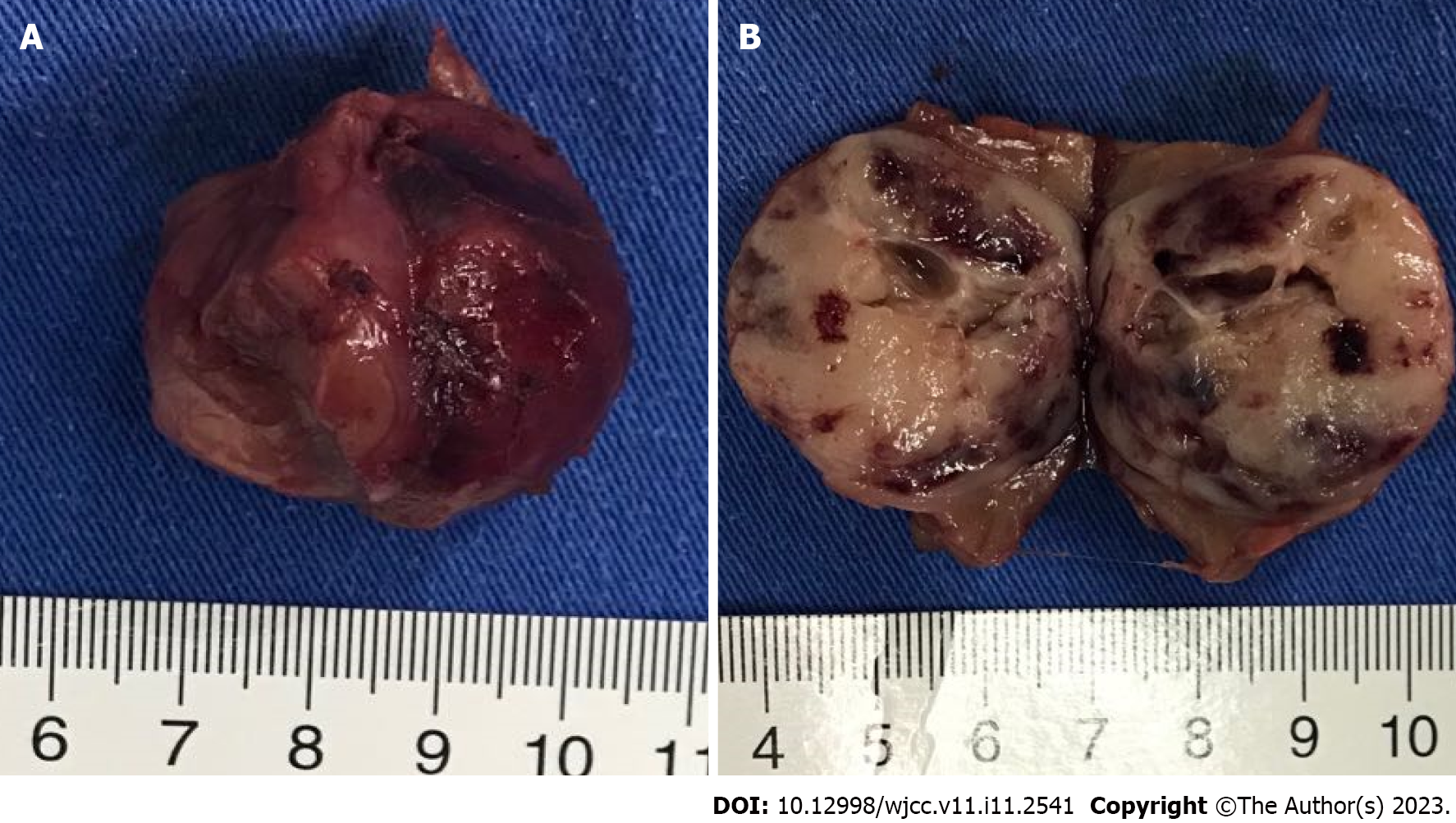
Figure 2 The tumor.
A: General view of the tumor after resection; B: Appearance of the tumor after dissection.
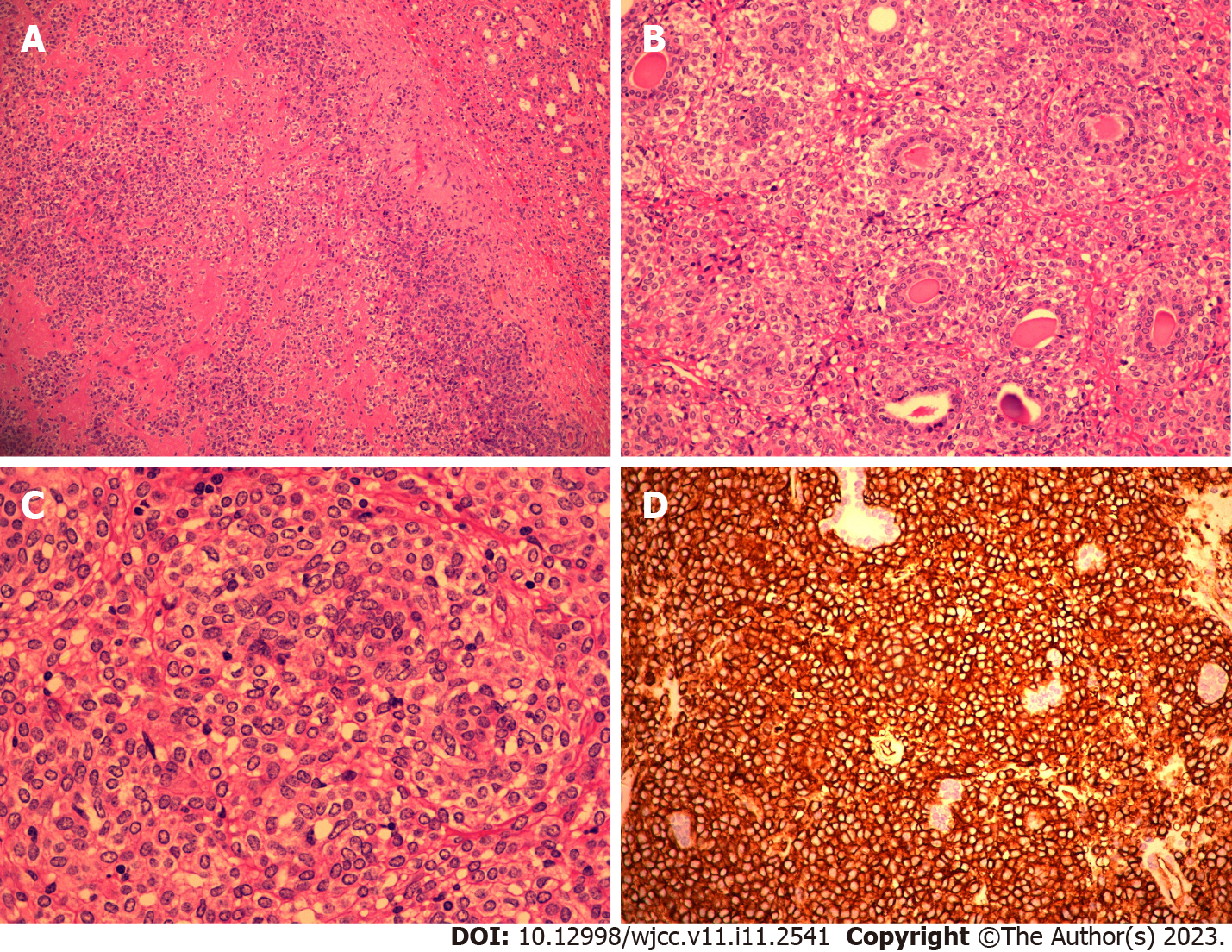
Figure 3 Postoperative pathological and immunohistochemical results confirm juxtaglomerular cell tumor.
A: 10 × magnification of tumor cells; B: 10 × magnification of tumor cells; C: 10 × magnification of tumor cells; D: Immunohistochemical results showing that the tumor cells were positive for CD34 and vimentin, and negative for CD117.
- Citation: Fu X, Deng G, Wang K, Shao C, Xie LP. Pregnancy complicated by juxtaglomerular cell tumor of the kidney: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(11): 2541-2548
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i11/2541.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i11.2541