Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. May 6, 2022; 10(13): 4242-4248
Published online May 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i13.4242
Published online May 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i13.4242
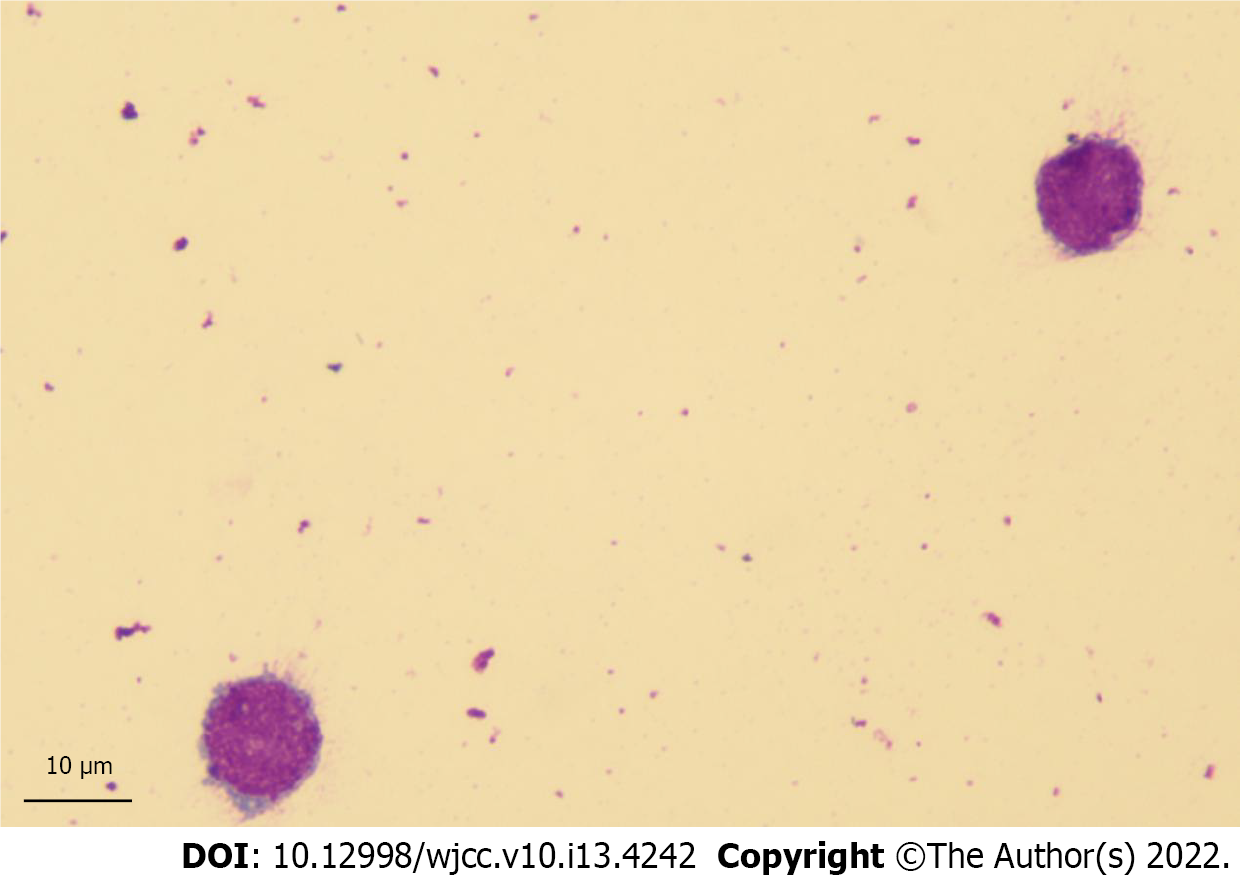
Figure 1 Atypical lymphocytes on cerebrospinal fluid cytology.
Giemsa stain (Magnification: 100 ×).
Figure 2 Flow cytometry detection of blast infiltration of cerebrospinal fluid in the patient.
The leukemic population is depicted in red. A: There is a cells of differentiation (CD) 45-dim population of abnormal cells with low-side scatter (painted red); B: These cells are positive for human leukocyte antigen D related (HLA-DR) and CD34; C: These cells are positive for CD34 and negative for CD33; D: These cells are positive for CD19 and CD10. Ssint lin: Side Scatter Lineage; HLA-DR PB: Human leukocyte antigen D related; CD45 NGE: Cluster of differentiation 45 negative; CD45 dim: Cluster of differentiation 45 dim; Mono: Monocyte; Lym: Lymphocyte; CD34 Percp-CY5.5: Cluster of differentiation 34 Peridinin-chlorophyll proteins-Cyanine5.5; CD33 PE: Cluster of differentiation 33 Phycoerytherin; CD19 APC: Cluster of differentiation 19 Allophycocyanin; CD10 PC7: Cluster of differentiation 10 Phycoerytherin-Cyanine 7.
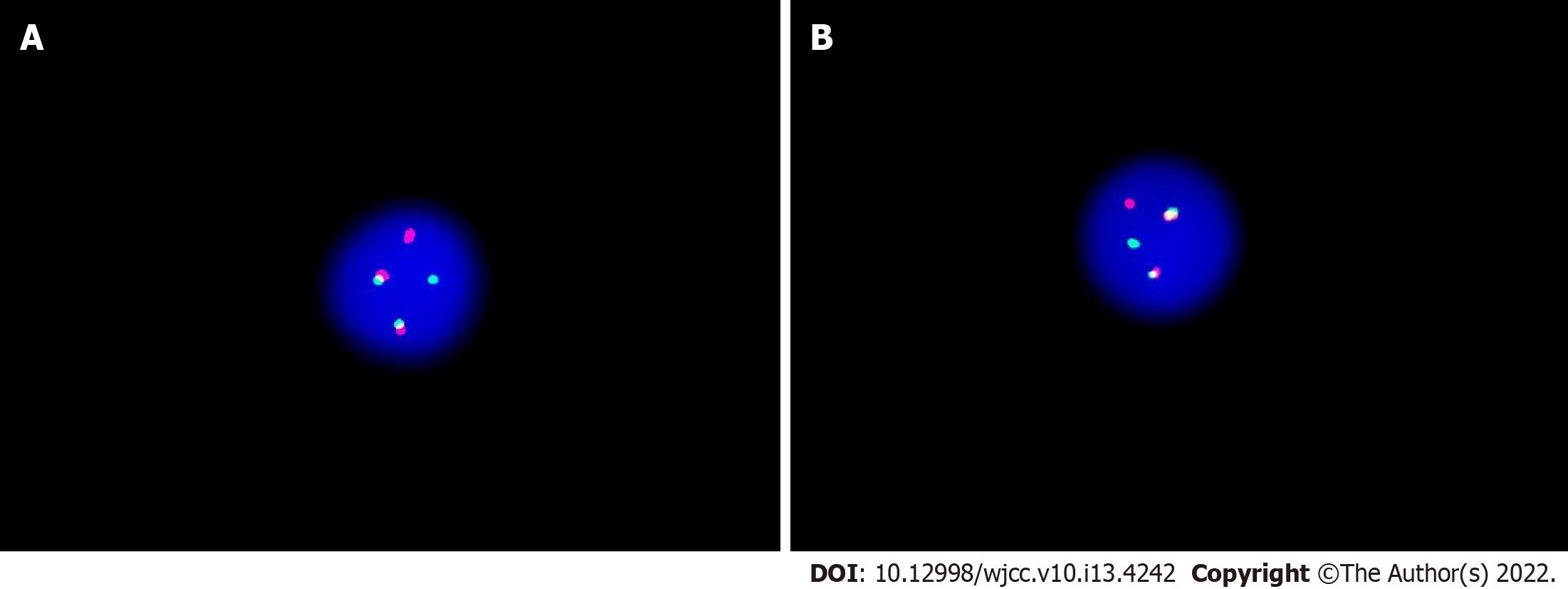
Figure 3 The fusion of BCR-ABL1 loci of cerebrospinal fluid was detected by fluorescence in situ hybridization using the vysis extra signal probeyielding red-green fusion signal.
A: The image shows 1 green, 1 red, and 2 yellow signals a result of fusion of red and green; B: The fusion signal indicates a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22 forming a BCR-ABL fusion gene.
- Citation: Chen Y, Lu QY, Lu JY, Hong XL. Primary isolated central nervous system acute lymphoblastic leukemia with BCR-ABL1 rearrangement: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(13): 4242-4248
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i13/4242.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i13.4242