Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Methodol. Dec 20, 2025; 15(4): 105775
Published online Dec 20, 2025. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v15.i4.105775
Published online Dec 20, 2025. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v15.i4.105775
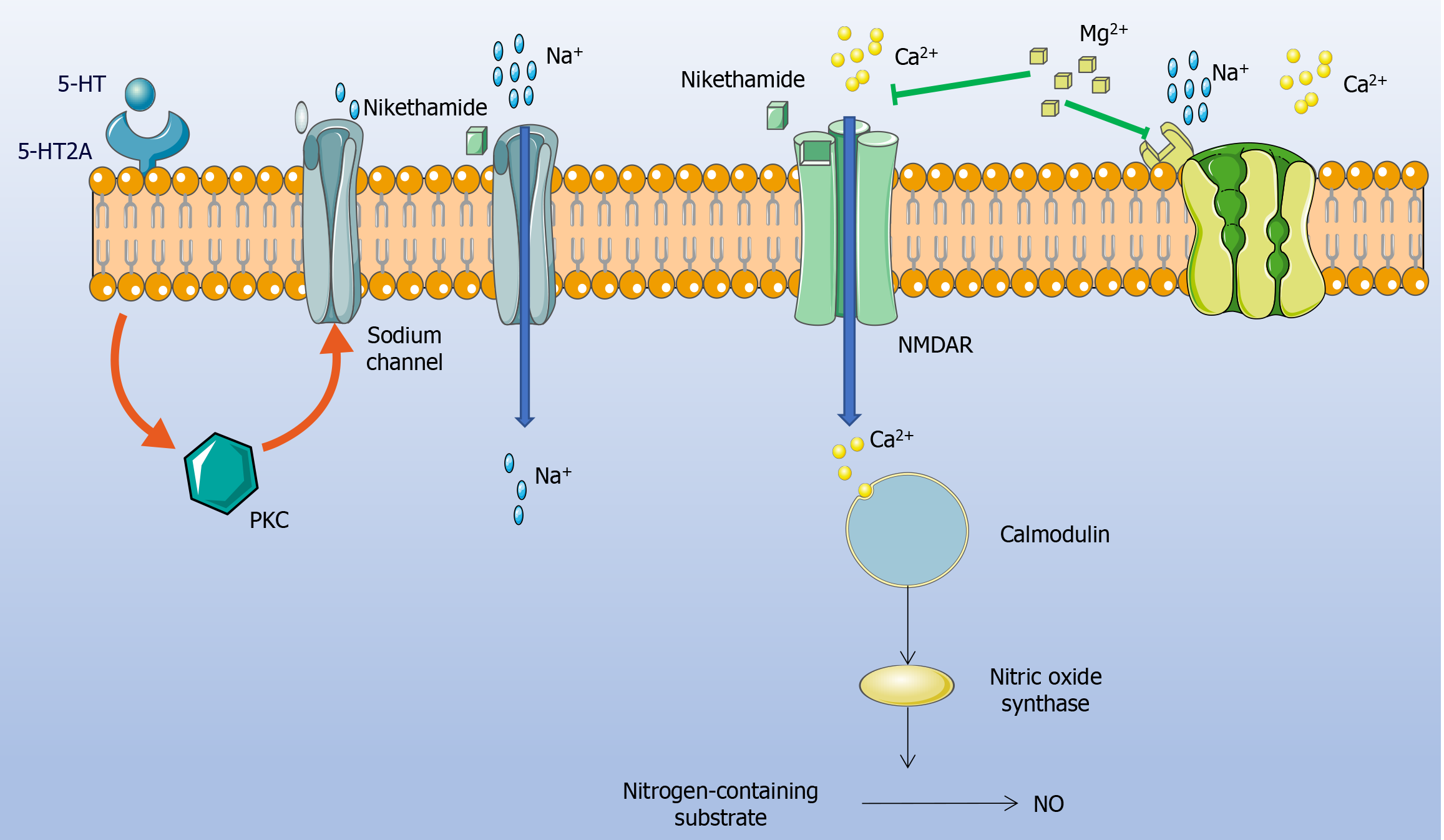
Figure 3 The molecular mechanism of the respiratory rhythm control center in the pre-Bötzinger complex.
The 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is an important neurotransmitter, can activate protein kinase C (PKC) by binding to the 5-HT2A receptor. PKC further regulates the conduction of sodium ions, which is essential for maintaining respiratory rhythm. The activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) leads to the influx of calcium ions (Ca2+) into neurons. Calmodulin is a calcium-binding protein, forms a complex with intracellular Ca2+ and further activates nitric oxide (NO) synthase to generate large amounts of NO. Magnesium ions (Mg2+) is a natural antagonist of NMDARs, can block Ca2+ influx through voltage-gated channels and thus antagonize NMDAR activation. Therefore, Mg2+ can be used as an antagonist to treat seizures caused by glutamate. Ca2+: Calcium ions; Mg2+: Magnesium ions; Na+: Sodium ions; NO: Nitric oxide; PKC: Protein kinase C; 5-HT: 5-hydroxytryptamine.
- Citation: Xu DJ, Zhong Q, Wang GT, Lu X. Preventive and therapeutic effects of magnesium sulfate on nikethamide-induced seizures: Implications for COVID-19 treatment. World J Methodol 2025; 15(4): 105775
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v15/i4/105775.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v15.i4.105775