Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Methodol. Dec 20, 2025; 15(4): 105516
Published online Dec 20, 2025. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v15.i4.105516
Published online Dec 20, 2025. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v15.i4.105516
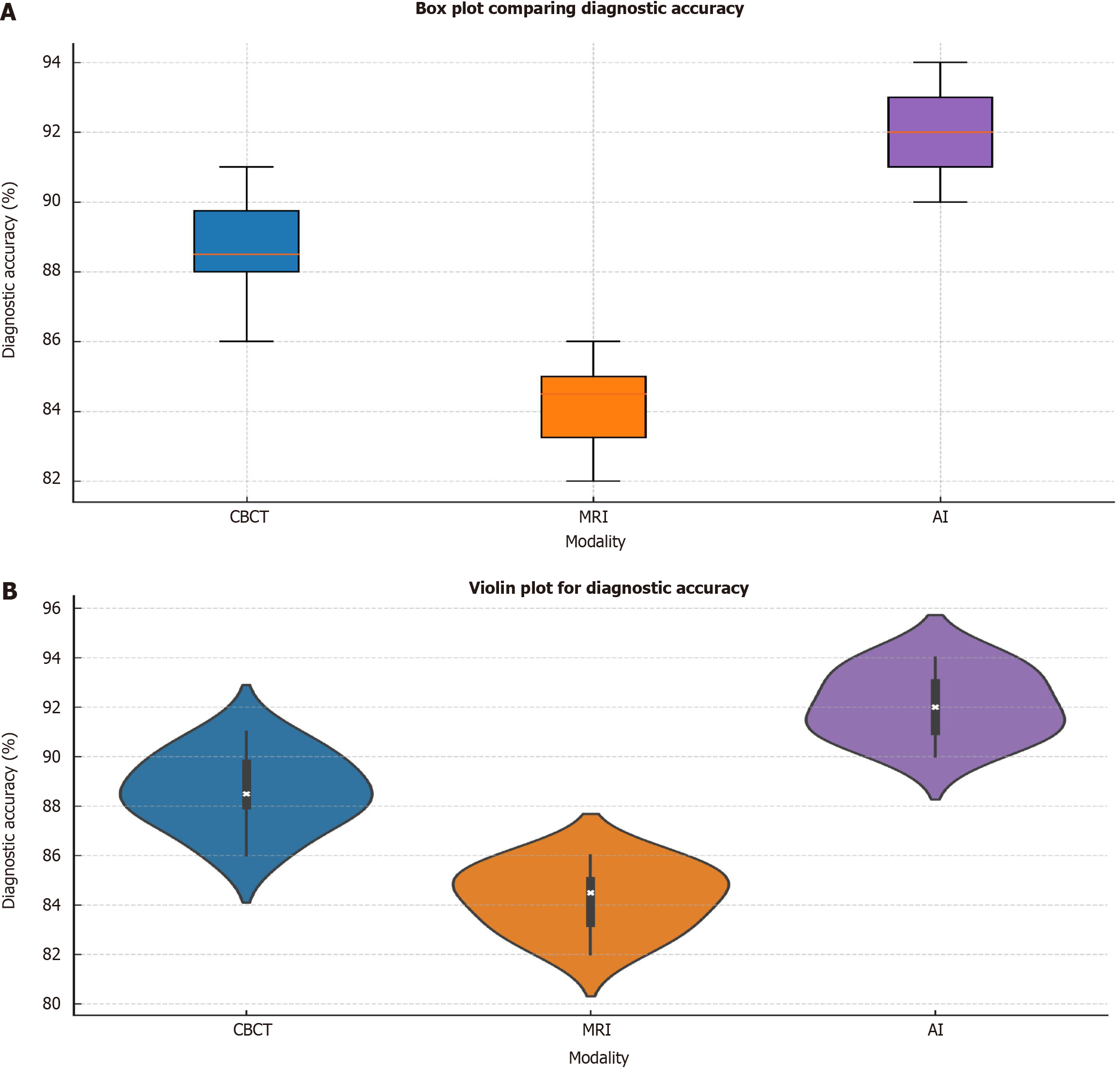
Figure 4 Diagnostic accuracy of cone beam computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and artificial intelligence models.
A: Box plot comparing diagnostic accuracy across cone beam computed tomography (CBCT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and artificial intelligence (AI) modalities. This highlighting the median, interquartile range, and variability for each. AI shows the highest median accuracy, with CBCT and MRI showing lower but similar accuracy levels; B: Violin plot showing the distribution of diagnostic accuracy across CBCT, MRI, and AI modalities. CBCT: Cone beam computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; AI: Artificial intelligence.
- Citation: Das N, Gade KR, Addanki PK. Artificial intelligence for early diagnosis and risk prediction of periodontal-systemic interactions: Clinical utility and future directions. World J Methodol 2025; 15(4): 105516
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v15/i4/105516.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v15.i4.105516