Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
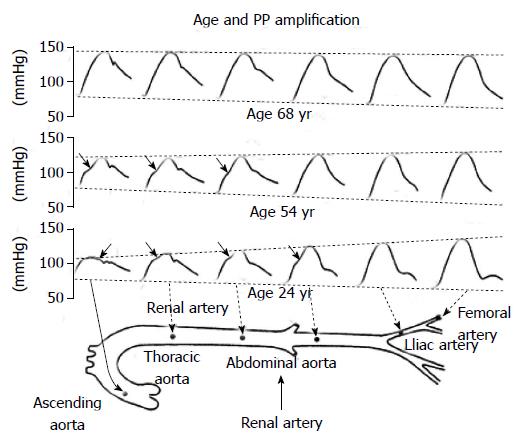
Figure 1 Representative pulse waveforms along the aorta in young, middle-aged and elderly persons.
In younger subjects (age: 24 yr), the rate of propagation is relatively low in arterial vessels, which become progressively narrower and less distensible. Because of the summation of the forward and the backward wave at each point of the arterial tree, peak systolic blood pressure increases markedly from central to peripheral arteries, while end-diastolic blood pressure tends to be reduced and mean arterial pressureremains unchanged. In older subjects (age: 68 yr), because of the more rapid propagation of pressure wave with resulting changes in wave reflections, the amplification of PP disappears, making that central and peripheral BP become identical. At 54 yr of age, the situation is intermediate between younger and older subjects[2].
- Citation: Ohno Y, Kanno Y, Takenaka T. Central blood pressure and chronic kidney disease. World J Nephrol 2016; 5(1): 90-100
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6124/full/v5/i1/90.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v5.i1.90