Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
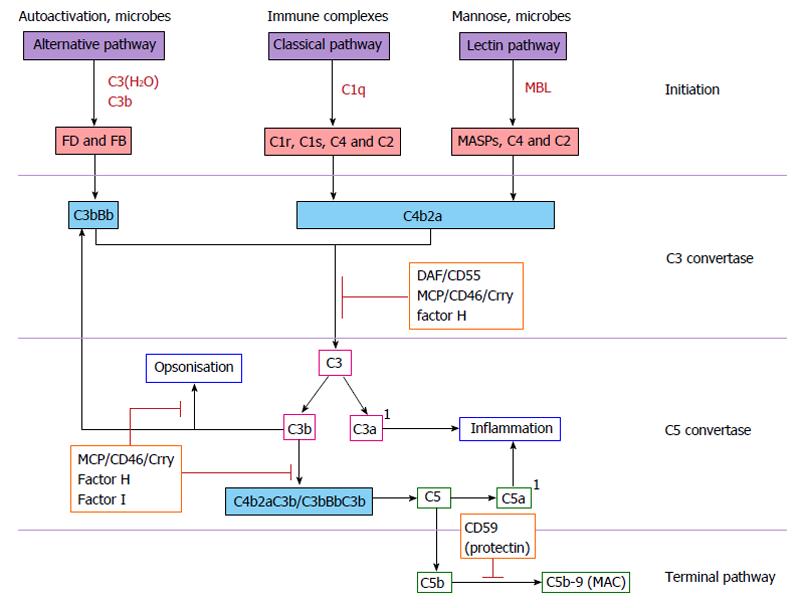
Figure 1 Complement activation pathways.
Complement activation is triggered via activation of either the alternative, classical or lectin pathways, all three of which converge to cleave central component C3. Briefly, activation of the alternative pathway occurs following the spontaneous hydrolysis of C3 to C3(H2O). C3(H2O) binds factor B (FB) to form C3bB which is then cleaved by FD leaving the C3bBb complex. C3bBb is stabilised by properdin to form the alternative pathway C3 convertase. C3 is subsequently cleaved to C3a and C3b to form the C5 convertase C3BbC3b. Activation of the classical complement pathway occurs when immunoglobulin-bound antigens bind to and activate the C1 complex (consisting of C1qr2s2). Activated C1qr2s2 cleaves C4 to C4a and C4b. C4b becomes membrane-bound and binds to pro-enzyme C2, which is then cleaved to C2a and C2b fragments by C1s. C2a remains bound to C4b, forming the classical C3 convertase C4b2a. C3 is cleaved to C3a and C3b to form the C5 convertase C4b2aC3b. The lectin complement pathway is homologous to the classical pathway, with the exception that it is activated by the binding of lectin to microbial cell surface carbohydrates (mannose). Surface-bound lectin activates MBL-associated serine proteases (MASPs), which directly activate C3 and directly cleave C2 and C4. Activation of the terminal complement pathway occurs when the alternative and classical C5 convertases C3bBbC3b or C4b2aC3b cleave C5 in to C5a and C5b. C5b binds to C6 and C7, forming C5b67, which associates with an adjacent membrane. C5b67 then binds to C8 and multiple C9 molecules forming the transmembrane pore C5b-9, also known as the MAC. 1Denotes the anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a. Orange boxes highlight regulatory complement proteins. MBL: Mannose-binding lectin; MAC: Membrane attack complex; DAF: Decay accelerating factor; MCP: Membrane cofactor protein.
- Citation: Fearn A, Sheerin NS. Complement activation in progressive renal disease. World J Nephrol 2015; 4(1): 31-40
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6124/full/v4/i1/31.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v4.i1.31