Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Nephrol. Jun 25, 2025; 14(2): 103027
Published online Jun 25, 2025. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v14.i2.103027
Published online Jun 25, 2025. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v14.i2.103027
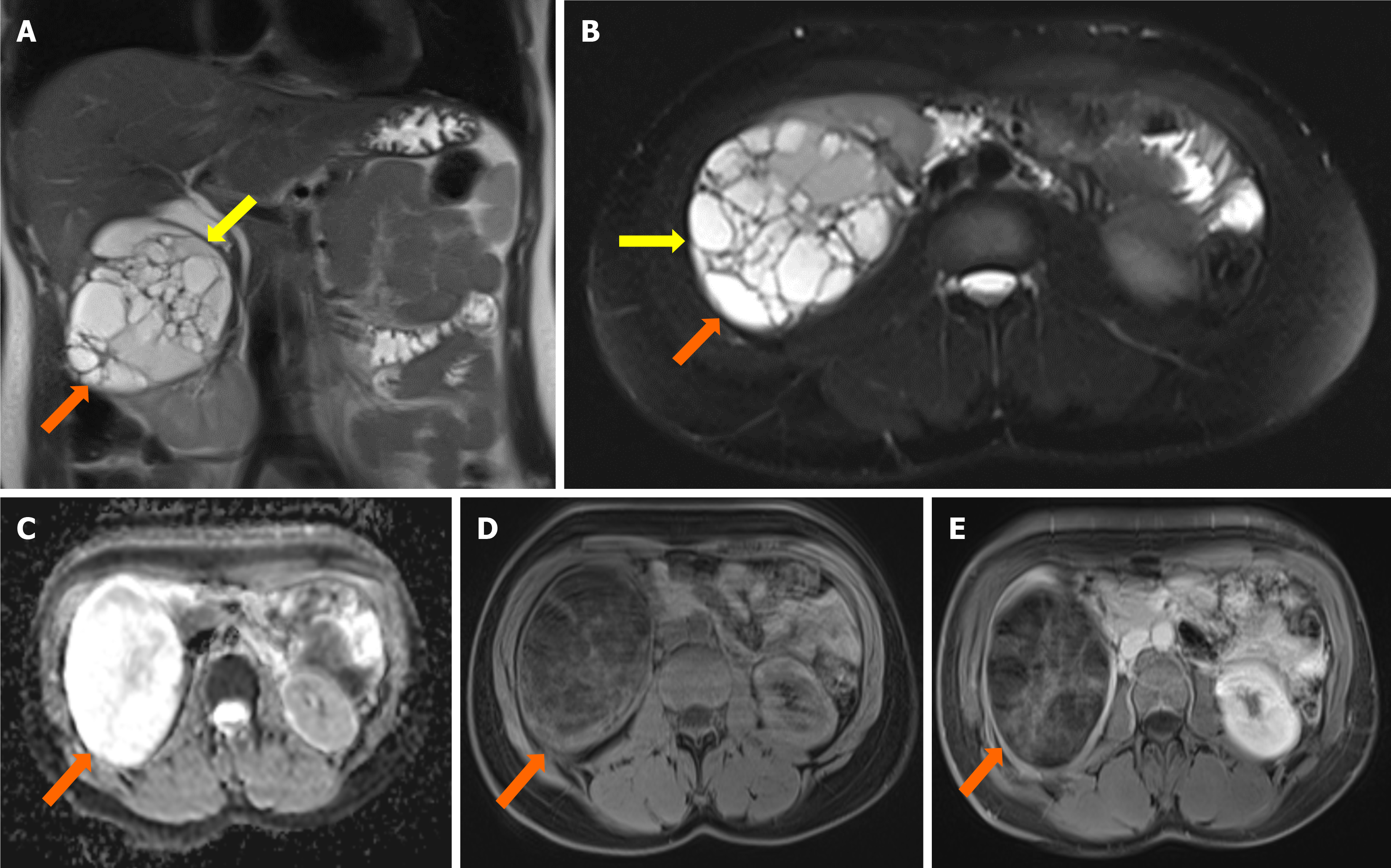
Figure 2 Coronal and axial abdominal magnetic resonance imaging of a multiloculated cystic lesion in the right kidney.
A: Coronal T2-weighted (T2W) image shows a 10 cm-sized multiloculated cystic lesion in the upper part of the right kidney (orange arrows), with a hypointense rim (yellow arrows); B: Axial fat-saturated T2W image highlights the multiloculated cystic lesion (orange arrows) with a hypointense rim (yellow arrows); C: Apparent diffusion coefficient map reveals restricted diffusion within the lesion; D: Axial fat-saturated pre-contrast T1-weighted (T1W) image shows the lesion without significant enhancement; E: Axial fat-saturated post-contrast T1W image demonstrates slight contrast enhancement in the septa of the cystic lesion (orange arrows).
- Citation: Celik AS, Yosunkaya H, Yayilkan Ozyilmaz A, Memis KB, Aydin S. Echinococcus granulosus in atypical localizations: Five case reports. World J Nephrol 2025; 14(2): 103027
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6124/full/v14/i2/103027.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v14.i2.103027