Copyright
©2013 Baishideng.
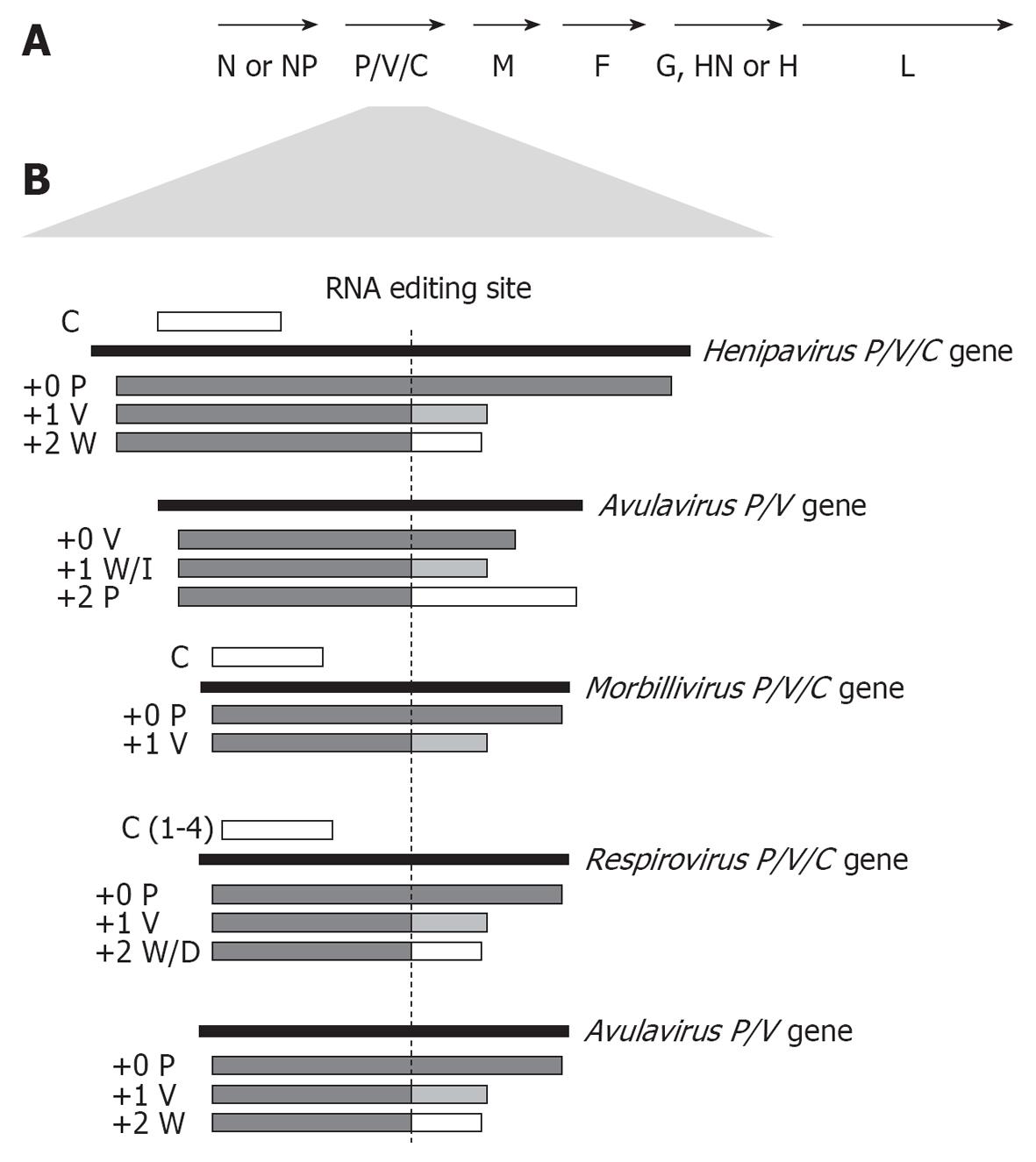
Figure 1 Coding strategies of paramyxovirus P genes.
A: Genome organisation of the Paramyxovirinae subfamily; B: Paramyxoviruses express multiple proteins from the P gene through RNA editing to insert additional non-coded G nucleotides into P gene transcripts at the editing site (indicated), causing a frameshift in the downstream open reading frame (ORF) to generate distinct C-termini. Editing strategies of the 5 best-studied genera are shown, with proteins produced from unedited (+0), or edited (+1 or +2 frameshift) mRNA indicated below the P gene. Several members of the henipavirus, respirovirus and morbillivirus genera, but not the rubulaviruses or avulaviruses, produce one or more C proteins by translation from internal start codon(s) in alternate ORF(s) (indicated as a white bar above the P gene).
- Citation: Audsley MD, Moseley GW. Paramyxovirus evasion of innate immunity: Diverse strategies for common targets. World J Virol 2013; 2(2): 57-70
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v2/i2/57.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v2.i2.57