Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Aug 19, 2025; 15(8): 105433
Published online Aug 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i8.105433
Published online Aug 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i8.105433
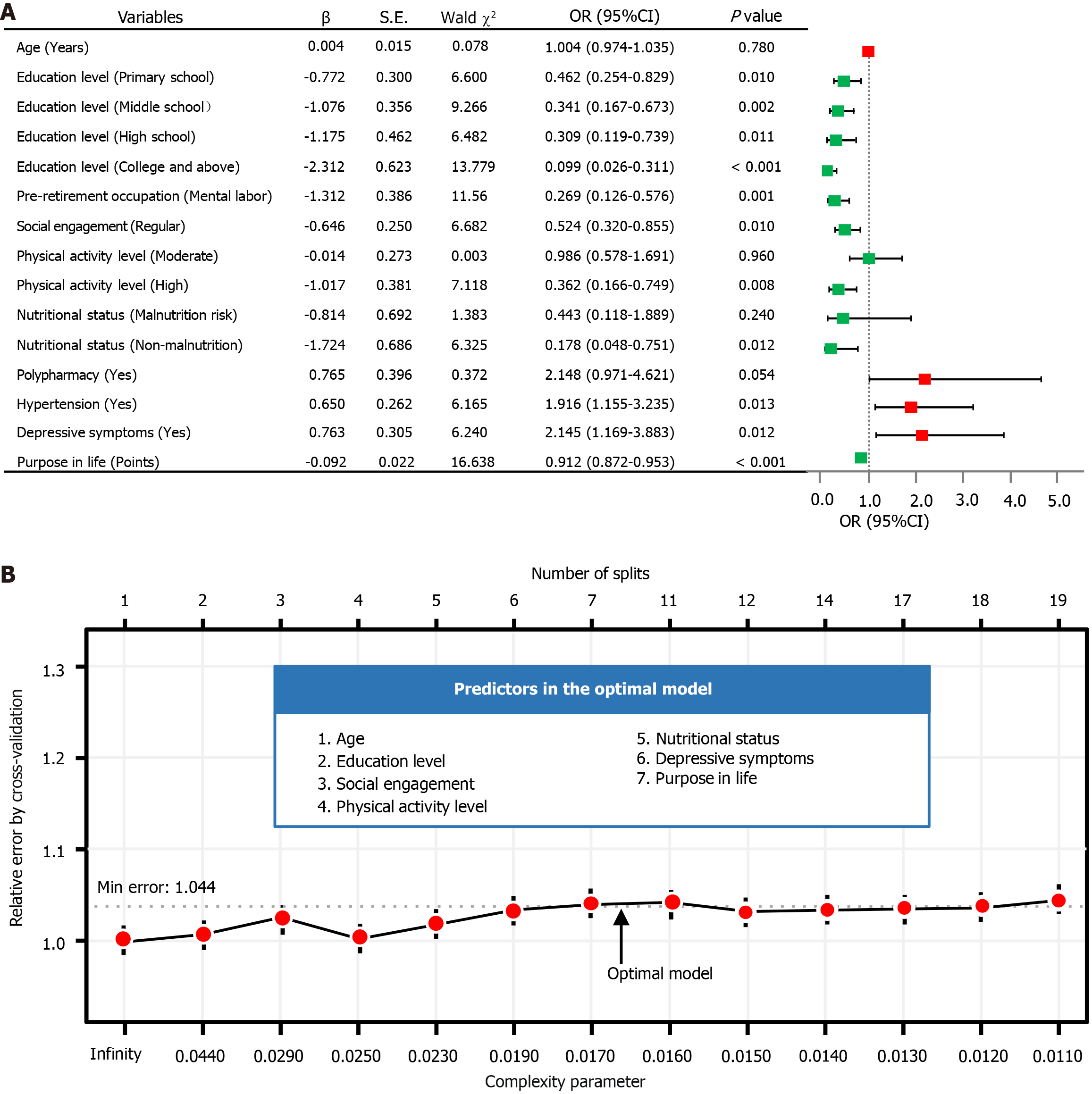
Figure 3 Inference of predictors by two models on training dataset.
A: Multivariable logistic regression (LR) forest plot of motoric cognitive risk; B: Optimization of the decision tree (DT) model using cross-validation. Through the forest plot of LR analysis to construction of the interactive nomogram (odds ratios are tested with Wald χ2 tests with 1 degree of freedom). The figure of DT model displays the dynamic relationship between the relative error (Y-axis), splits number (upper X-axis), and complexity parameter (lower X-axis). OR: Odds ratio; CI: Confidence interval; Min: Minimum.
- Citation: Su LM, Wu B, Chen Z, Wang XY, Shen XH, Wei ZQ, Cheng H, Wang LN. Development and validation of screening tools for motoric cognitive risk syndrome in community settings. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(8): 105433
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i8/105433.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i8.105433