Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Jun 19, 2025; 15(6): 105751
Published online Jun 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i6.105751
Published online Jun 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i6.105751
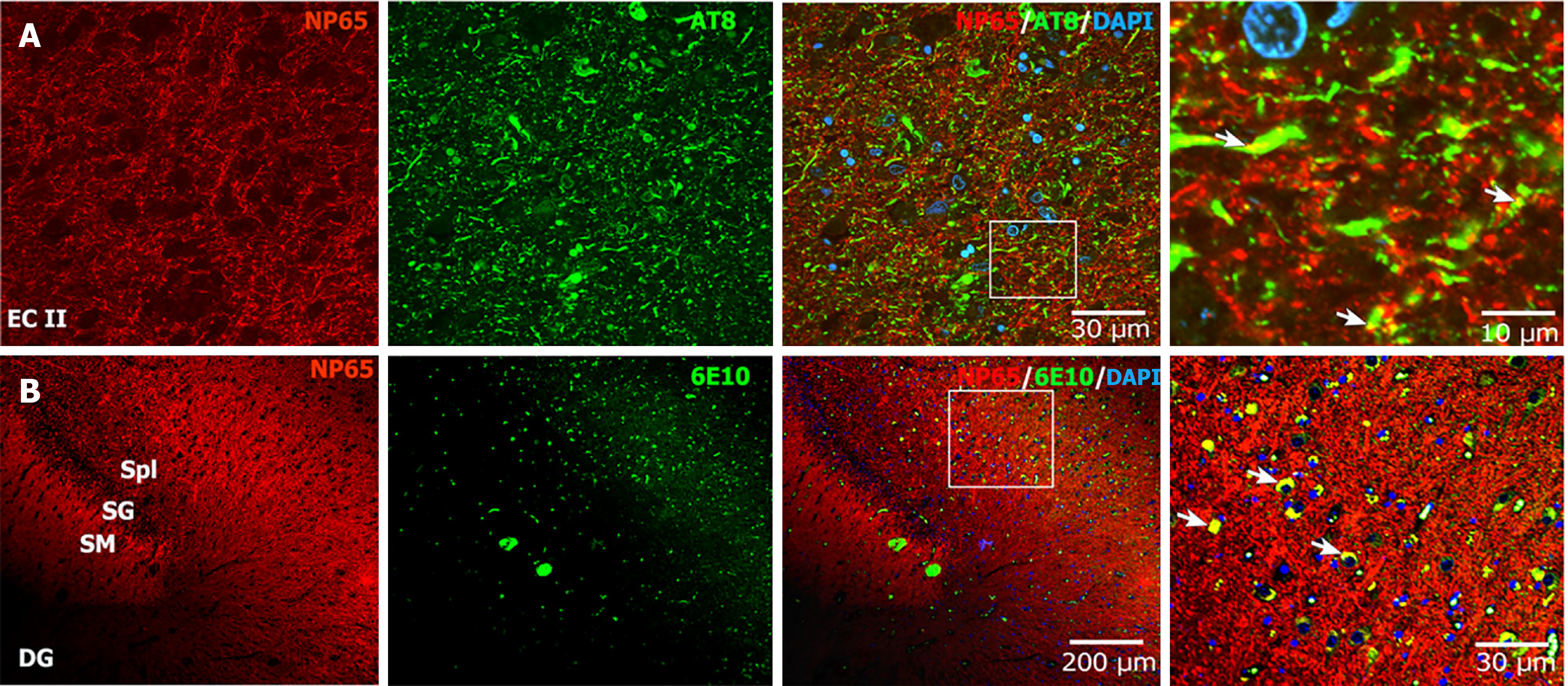
Figure 6 Neuroplastin 65 colocalized with the neurofibrillary tangles and amyloid beta plaques in Alzheimer’s disease brain.
A: The double immunostaining microphotograph of neuroplastin 65 (NP65) with AT-8 (a marker for neurofibrillary tangles) showed that NP65-positive puncta partially colocalized with phosphorylated-microtubule-associated protein tau (yellow, indicated by arrow) in the entorhinal cortex of Alzheimer’s disease brain, scale bar = 30 μm; the left panel shows a higher power view in the rectangle frame, scale bar = 10 μm; B: The double immunostaining microphotograph of NP65 with 6E10 (a marker for amyloid beta) exhibited that NP65-positive puncta partially colocalized with amyloid beta plaques (yellow, indicated by arrow) in the cornu ammonis 3 region of Alzheimer’s disease brain, scale bar = 200 μm; The left panel shows a higher power view in the rectangle frame, scale bar = 30 μm. The nucleus was stained with 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (blue). NP65: Neuroplastin 65; EC: Entorhinal cortex; DG: Dentate gyrus; SM: Stratum moleculare; SG: Stratum granulosum; Spl: Stratum plexiforme; DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
- Citation: Zheng YN, Wang Y, Chen L, Xu LZ, Zhang L, Wang JL, Liu J, Zhang QL, Yuan QL. Increased expression of the neuroplastin 65 protein is involved in neurofibrillary tangles and amyloid beta plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(6): 105751
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i6/105751.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i6.105751