Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Jun 19, 2025; 15(6): 105751
Published online Jun 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i6.105751
Published online Jun 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i6.105751
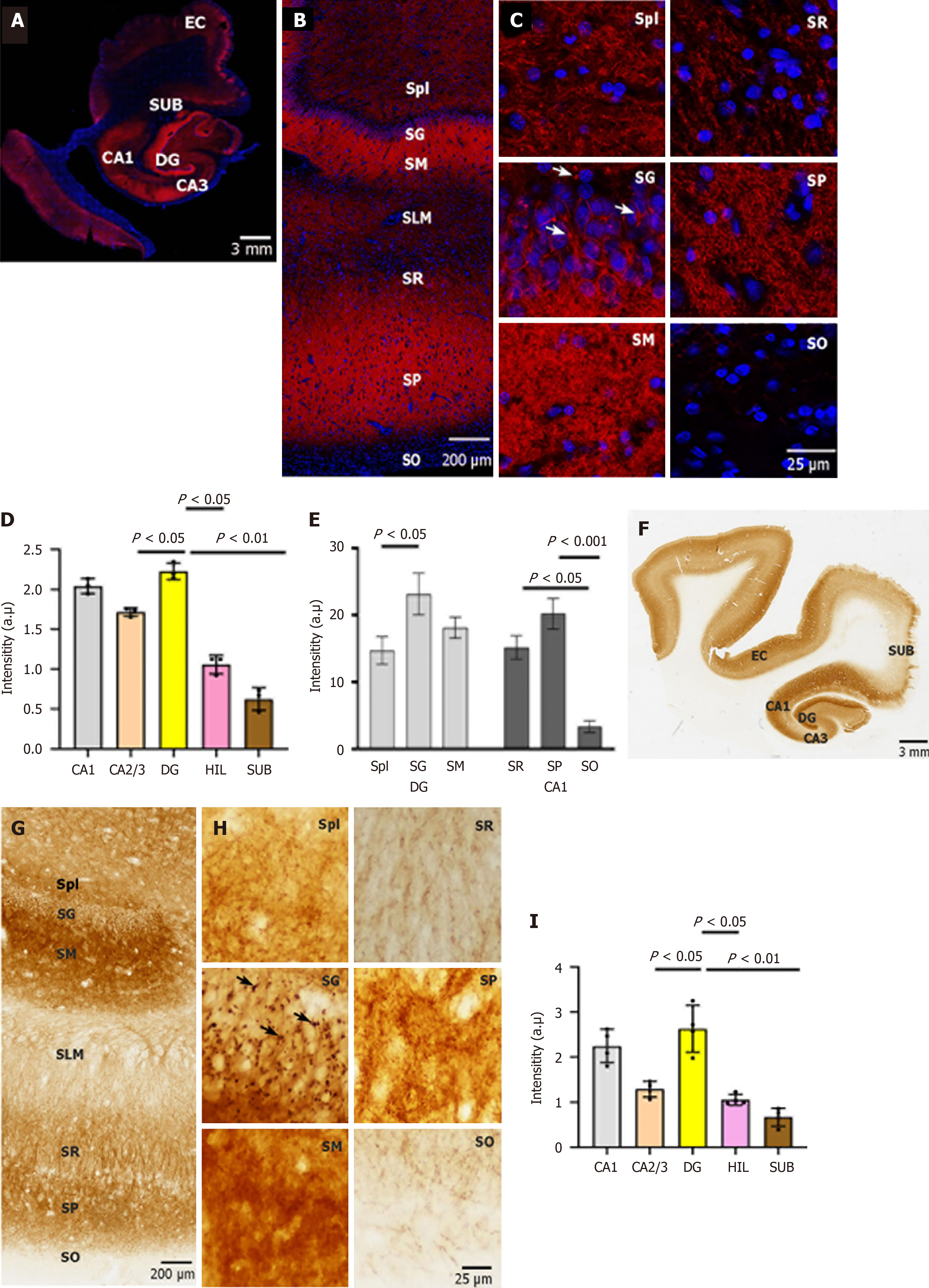
Figure 1 Expression and cellular localization of neuroplastin 65 immunoreactivity in human hippocampal formation.
A: Neuroplastin 65 (NP65) immunofluorescent staining in a coronal section of the human hippocampal formation. A representative view of the human hippocampal formation at a low magnification (scale bars = 3 mm); B and C: NP65 immunofluorescent staining in a coronal section of the human hippocampal formation. Representative micrographs of NP65 immunoreactivity in the cornu ammonis 1 (CA1) region and dentate gyrus at a high magnification view. Note the immunoreactive knots (indicated by an arrow) in the stratum granulosum; D and E: Quantification of NP65 immunofluorescent staining in the sublayers of CA1 and DG and hippocampal areas; F: A representative scan of the human hippocampal formation (scale bars = 3 mm); G and H: Representative micrographs of NP65 immunoreactivity in the CA1 region and dentate gyrus at a high magnification view. Note the immunoreactive knots (indicated by an arrow) in the stratum granulosum; I: Quantification of NP65 immunohistochemical staining in hippocampal areas. DG: Dentate gyrus; CA: Cornu ammonis; HIL: Hilus; SUB: Subiculum; EC: Entorhinal cortex; SG: Stratum granulosum; SM: Stratum moleculare; SPl: Stratum plexiforme; SLM: Stratum lacunosum-molecular; SR: Stratum radiatum; SP: Stratum pyramidale; SO: Stratum oriens.
- Citation: Zheng YN, Wang Y, Chen L, Xu LZ, Zhang L, Wang JL, Liu J, Zhang QL, Yuan QL. Increased expression of the neuroplastin 65 protein is involved in neurofibrillary tangles and amyloid beta plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(6): 105751
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i6/105751.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i6.105751