Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Psychiatry. Apr 19, 2024; 14(4): 563-581
Published online Apr 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i4.563
Published online Apr 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i4.563
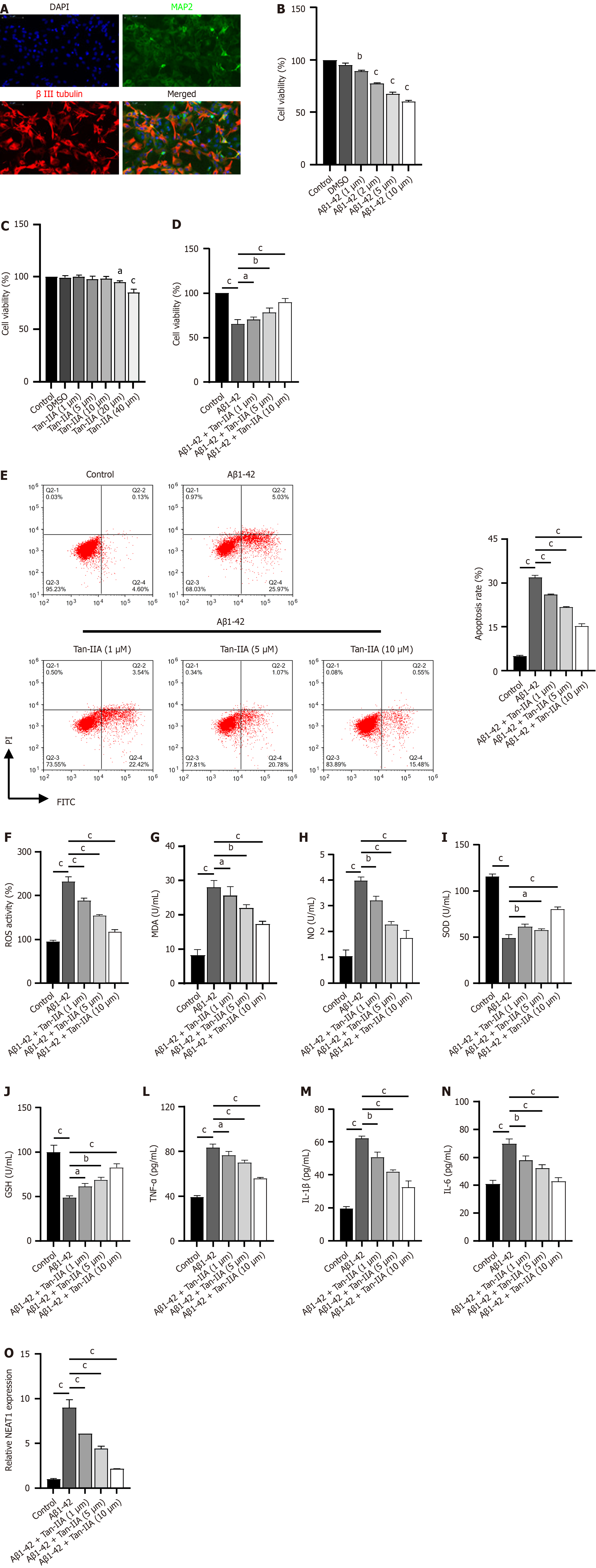
Figure 2 Protective effects of tanshinone IIA in murine neural stem cells induced with amyloid-beta 1-42 peptides.
A: Immunofluorescent identification of neural stem cells (NSCs) for isolation, using DAPI stain (blue), microtubule-associated protein 2 (green), and β III tubulin (red); B-D: 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay of the effect of different amyloid-beta 1-42 (Aβ1-42) and tanshinone IIA (Tan-IIA) doses on NSC viability; E: Flow cytometry results indicating that different Tan-IIA doses improve the effect of Aβ1-42 on the apoptosis of NSCs; F: 2’,7’-dichlorofluorescin diacetate analysis of the reactive oxygen species ratio in NSCs, either with or without prior Tan-IIA treatment; G-N: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay results of different Tan-IIA doses in enhancing the effect of Aβ1-42 in improving levels of oxidative stress factors (malondialdehyde; nitric oxide; superoxide dismutase; glutathione) and neuroinflammation markers (tumor necrosis factor-alpha; interleukin 1β; interleukin 6) in NSCs; O: Reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis of different Tan-IIA doses used to improve the effect of Aβ1-42 on nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1 expression in NSCs. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. MAP2: Microtubule-associated protein 2; DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide; PI: Propidium iodide; FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate; Aβ1-42: Amyloid-beta 1-42; Tan-IIA: Tanshinone IIA; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; MDA: Malondialdehyde; NO: Nitric oxide; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; GSH: Glutathione; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL-1β: Interleukin 1β; IL-6: Interleukin 6; NEAT1: Nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1.
- Citation: Yang LX, Luo M, Li SY. Tanshinone IIA improves Alzheimer’s disease via RNA nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1/microRNA-291a-3p/member RAS oncogene family Rab22a axis. World J Psychiatry 2024; 14(4): 563-581
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v14/i4/563.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v14.i4.563