Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Exp Med. Sep 20, 2025; 15(3): 106677
Published online Sep 20, 2025. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v15.i3.106677
Published online Sep 20, 2025. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v15.i3.106677
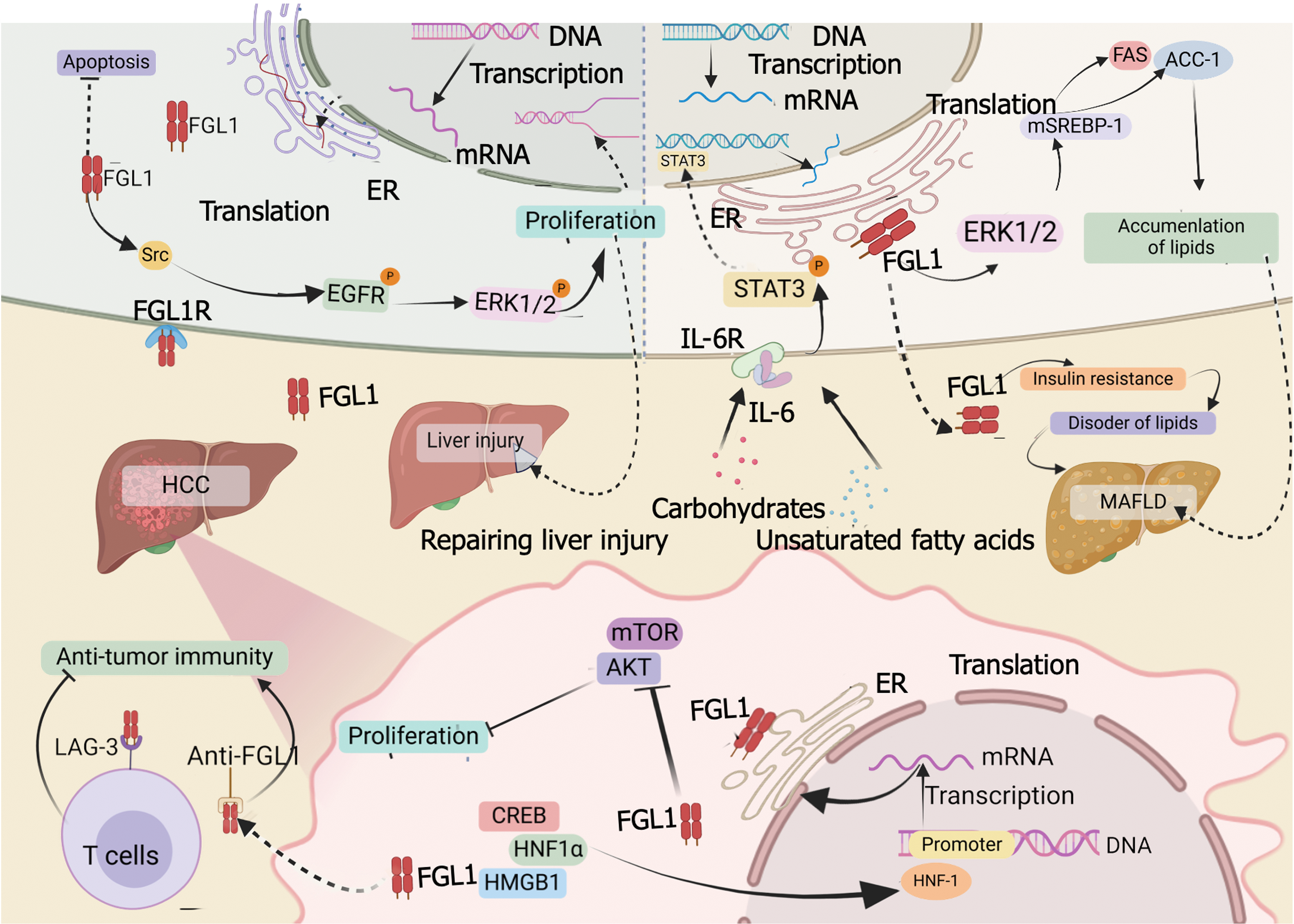
Figure 2 Role of fibrinogen-like protein 1 in liver diseases.
In liver injury, fibrinogen-like protein (FGL) 1 exerts its effects by stimulating the Src family of tyrosine kinases/epidermal growth factor receptor/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 cascade through autocrine signaling, thereby modulating hepatocyte proliferation and apoptotic processes. Under conditions of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease, elevated levels of palmitate and monounsaturated fatty acids upregulate FGL1 expression in hepatocytes via activation of the interleukin-6/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 pathway. This upregulation subsequently triggers lipid deposition and inflammatory responses through mechanisms dependent on extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signaling. In the context of hepatocellular carcinoma, the assembly of the hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 homeobox α/high mobility group box 1 /cyclic adenosine monophosphate-response element binding transcriptional complex boosts FGL1 transcription. Additionally, FGL1 suppresses tumor cell growth by interfering with the cell cycle and inhibiting the protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling axis. Furthermore, FGL1 interacts with lymphocyte activation gene 3 receptors expressed on CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and natural killer cells, leading to the suppression of T cell-mediated antitumor immune responses. FGL: Fibrinogen-like protein; Src: Src family of tyrosine kinases; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FAS: Fatty acid synthase; ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 ; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; LAG: Lymphocyte activation gene; CREB: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein; HNF1α: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 α; HMGB1: High mobility group box 1 protein; IL: Interleukin; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; AKT: Protein kinase B; MAFLD: Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease.
- Citation: Qu RH, Rong Y, Ni WZ, Huang XL, Chen YZ, Li HF. Fibrinogen superfamily proteins: Key regulators in hepatic disorders. World J Exp Med 2025; 15(3): 106677
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v15/i3/106677.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v15.i3.106677