Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Crit Care Med. Sep 9, 2025; 14(3): 101462
Published online Sep 9, 2025. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v14.i3.101462
Published online Sep 9, 2025. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v14.i3.101462
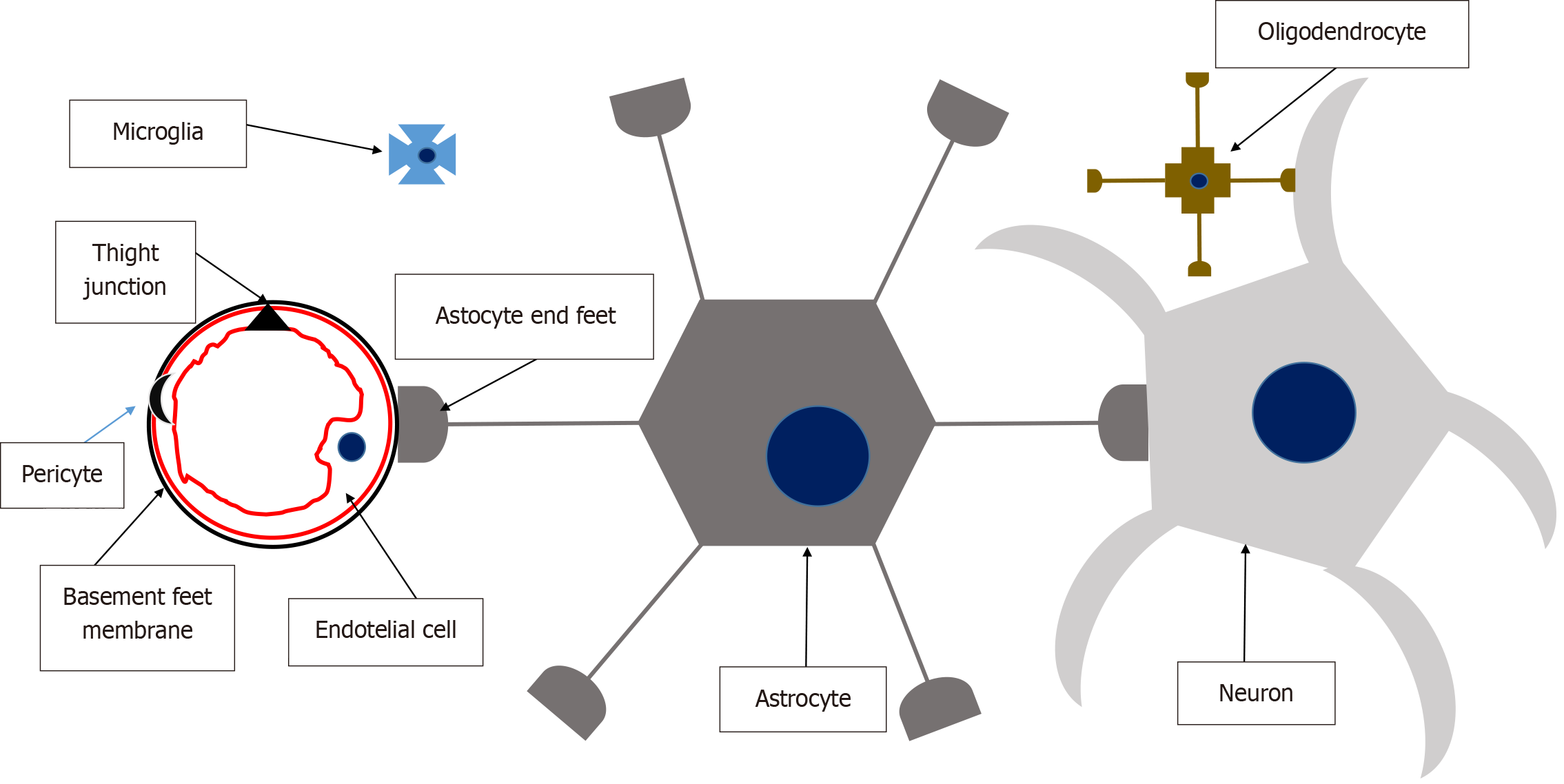
Figure 5 Neurovascular unit.
Cerebral endothelial cells form tight junctions that seal the paracellular aqueous diffusion pathways between cells, maintaining the integrity of the blood-brain barrier. Pericytes are discontinuously distributed along capillaries, positioned between the endothelium and the basement membrane, which forms a specialized extracellular matrix distinct from the astrocytic foot processes that encase it. Astrocytes play a pivotal role as a bridge between neurons and the endothelial complex, facilitating the passage of vasoactive peptides that regulate vascular dilation or constriction. Microglia serve as the immunocompetent cells of the neurovascular unit, providing immune surveillance. Solutes cross the blood-brain barrier through passive diffusion, driven by concentration gradients and lipophilicity, or via facilitated transport mechanisms involving active or passive transport through endothelial cells.
- Citation: Previgliano IJ, Aboumarie HS, Tamagnone FM, Merlo PM, Sosa FA, Feijoo J, Carruega MC. Point of care ultrasound evaluation of cardio-cerebral coupling. World J Crit Care Med 2025; 14(3): 101462
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v14/i3/101462.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v14.i3.101462