Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Crit Care Med. Sep 9, 2021; 10(5): 260-277
Published online Sep 9, 2021. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v10.i5.260
Published online Sep 9, 2021. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v10.i5.260
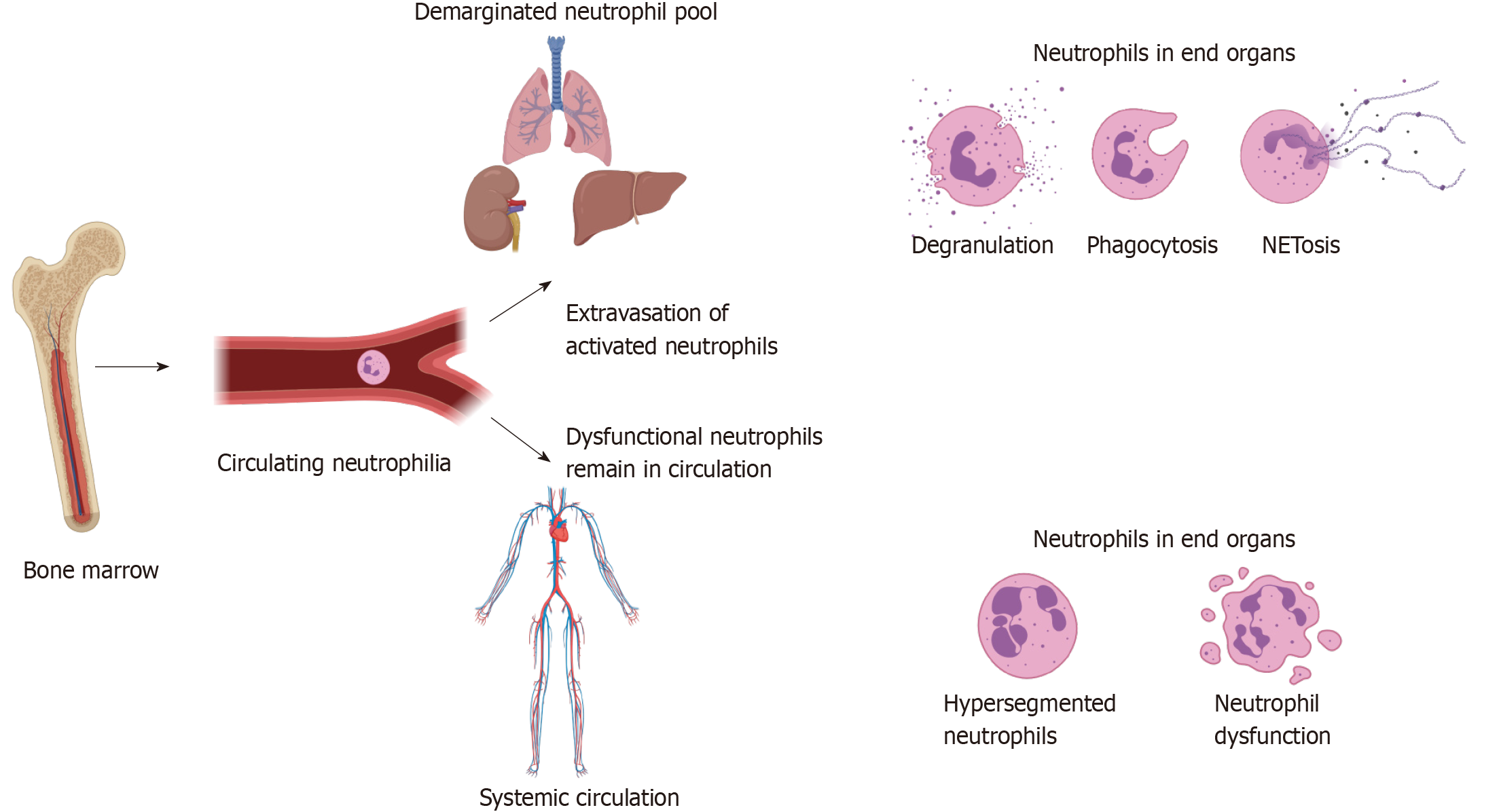
Figure 3 Neutrophil extravasation and resultant immune dysfunction.
Tissue damage caused by injury leads to danger associated molecular pattern, catecholamine and corticosteroid release, which result in neutrophil egress from the bone marrow, as well as increased production through emergency granulopoiesis. This leads to a circulating neutrophilia and altered phenotypes of circulating neutrophils as discussed in text. It is hypothesised that hyperinflammatory cells expressing high levels of adhesion markers transmigrate into the demarginated pool in the lungs, spleen, liver and other end organs, where they may cause further inflammation through NETosis, degranulation and phagocytosis, leading to organ dysfunction. The loss of these highly inflammatory cells from the circulation leads to remaining neutrophils being dysfunctional, predisposing the individual to immune failure and secondary infection. Figure produced using Biorender.
- Citation: Finlay LD, Conway Morris A, Deane AM, Wood AJ. Neutrophil kinetics and function after major trauma: A systematic review. World J Crit Care Med 2021; 10(5): 260-277
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3141/full/v10/i5/260.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5492/wjccm.v10.i5.260