Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Immunol. Nov 27, 2014; 4(3): 174-184
Published online Nov 27, 2014. doi: 10.5411/wji.v4.i3.174
Published online Nov 27, 2014. doi: 10.5411/wji.v4.i3.174
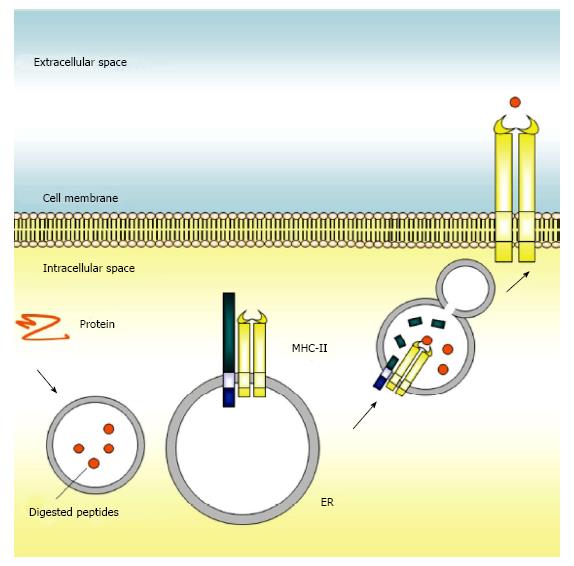
Figure 2 The canonical function of cluster of differentiation 74 in the immune system.
Cluster of differentiation 74 (CD74) is present on endoplasmic reticulum (ER) where it can interact with major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC class II) and contribute to antigen presentation. Once synthesized, CD74 self-assembles as a trimer and serves as a scaffold onto which nascent MHC class II assemble. After trafficking to the late endosome, CD74 is cleaved into a small peptide, CLIP, to block the peptide binding cleft of MHC class II, prevent premature binding of antigenic peptides, and direct the MHC class II complex to the endosomal pathway. The MHC class II molecules with bound antigenic peptides are then exported to the surface of the antigen presenting cell for presentation of foreign peptides to CD4+ T cells.
- Citation: Liu YH, Lin JY. Recent advances of cluster of differentiation 74 in cancer. World J Immunol 2014; 4(3): 174-184
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2219-2824/full/v4/i3/174.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5411/wji.v4.i3.174