Copyright
©2013 Baishideng.
World J Otorhinolaryngol. Aug 28, 2013; 3(3): 58-70
Published online Aug 28, 2013. doi: 10.5319/wjo.v3.i3.58
Published online Aug 28, 2013. doi: 10.5319/wjo.v3.i3.58
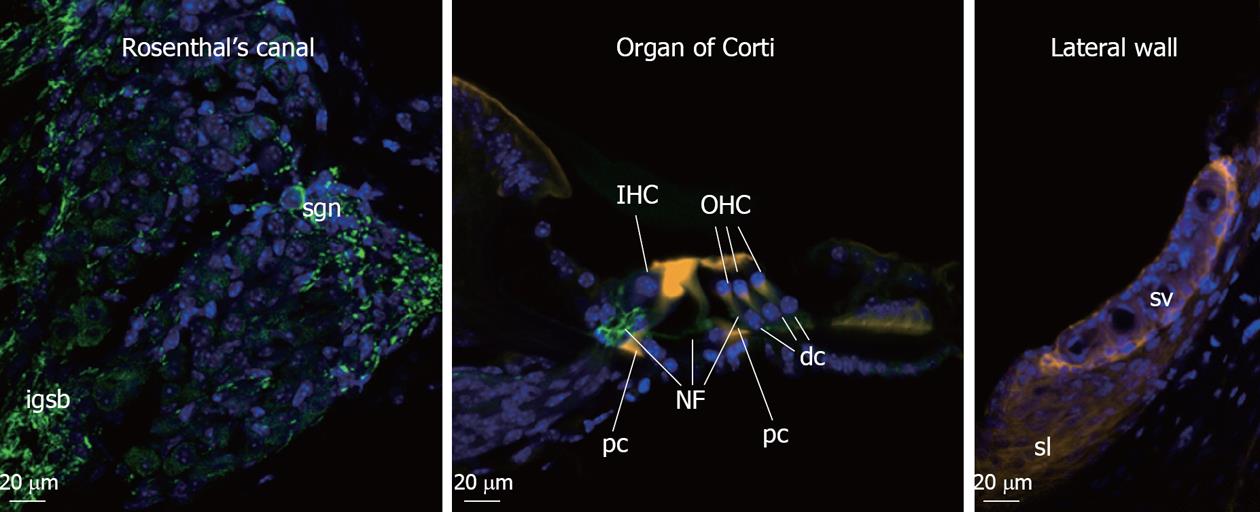
Figure 1 Cochlear cell types susceptible to noise-induced hearing loss.
Fluorescence micrographs of mouse cochlea tissues by confocal scanning microscopy. Transverse cochlear section was immunolabelled to show spiral ganglion neurones and neuritis (with anti-neurofilament-F200 antibody, green), actin filament of the sensory hair cell stereocilia (Phalloidin stain, orange), and cell nuclei (DAPI, blue). In cochlea exposed to noise stress, the integrity of inner and outer hair cell (IHC and OHC) stereocilia is affected, loss of the hair cells and nerve fiber (NF), damage to supporting pillar cells (pc) and Deiters cells (dc), swelling of spiral ganglion neuron (sgn) nerve fiber (intraganglionic spiral bundle, igsb) in the Rosenthal’s canal as well as loss of fibrocytes in lateral wall stria vascularis (sv) and spiral ligament (sl) can be detected.
- Citation: Wong ACY, Froud KE, Hsieh YSY. Noise-induced hearing loss in the 21st century: A research and translational update. World J Otorhinolaryngol 2013; 3(3): 58-70
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6247/full/v3/i3/58.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5319/wjo.v3.i3.58