Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Orthop. Jul 18, 2025; 16(7): 107087
Published online Jul 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i7.107087
Published online Jul 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i7.107087
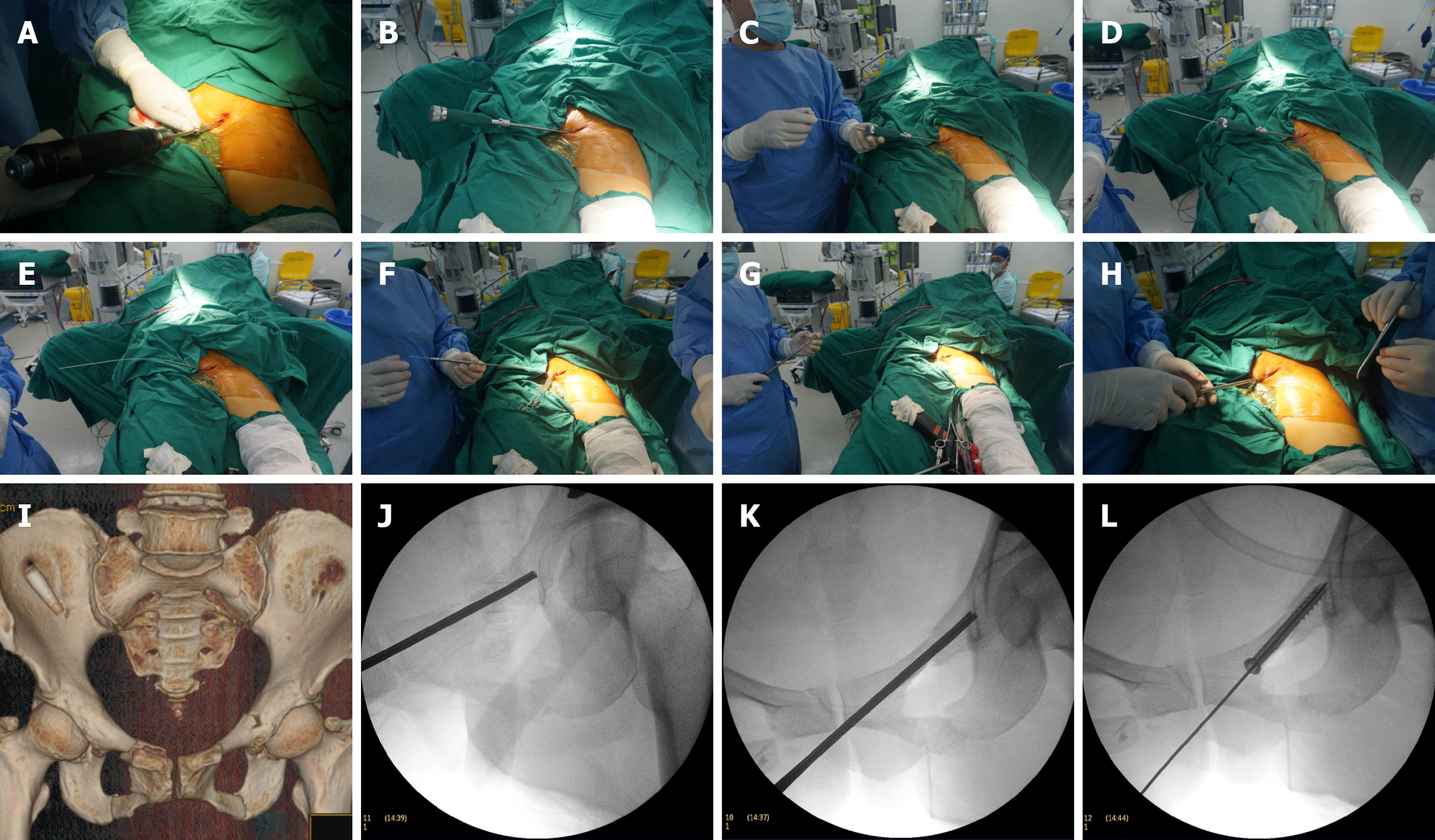
Figure 3 Intraoperative procedure of retrograde hollow screw insertion using the handheld pelvic alignment guide.
A: A 2 cm incision is made over the pubic symphysis, and a 3.5 mm drill bit is used to create an entry hole; B: The handheld pelvic alignment guide probe is inserted into the superior pubic ramus, and fracture reduction is verified under C-arm fluoroscopy; C and D: The inner core and handle are sequentially removed, and a graduated guide wire is inserted through the guide channel; E and F: Screw length is determined based on the probe's markings, and the probe is subsequently removed; G and H: A 6.0 mm hollow screw is inserted along the guide wire to complete the fixation; I: Preoperative 3D computed tomography imaging shows bilateral fractures of the superior and inferior pubic rami; J-L: Intraoperative fluoroscopy demonstrates guide wire positioning, trajectory verification, and screw insertion.
- Citation: Wang Y, Tan ZY, He JM, Shu YX, Pan Z, Zhu DG, Wang J. Novel handheld pelvic alignment guide for hollow screw fixation in osteoporotic pelvic fragility fractures. World J Orthop 2025; 16(7): 107087
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v16/i7/107087.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v16.i7.107087