Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Orthop. May 18, 2025; 16(5): 106377
Published online May 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i5.106377
Published online May 18, 2025. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v16.i5.106377
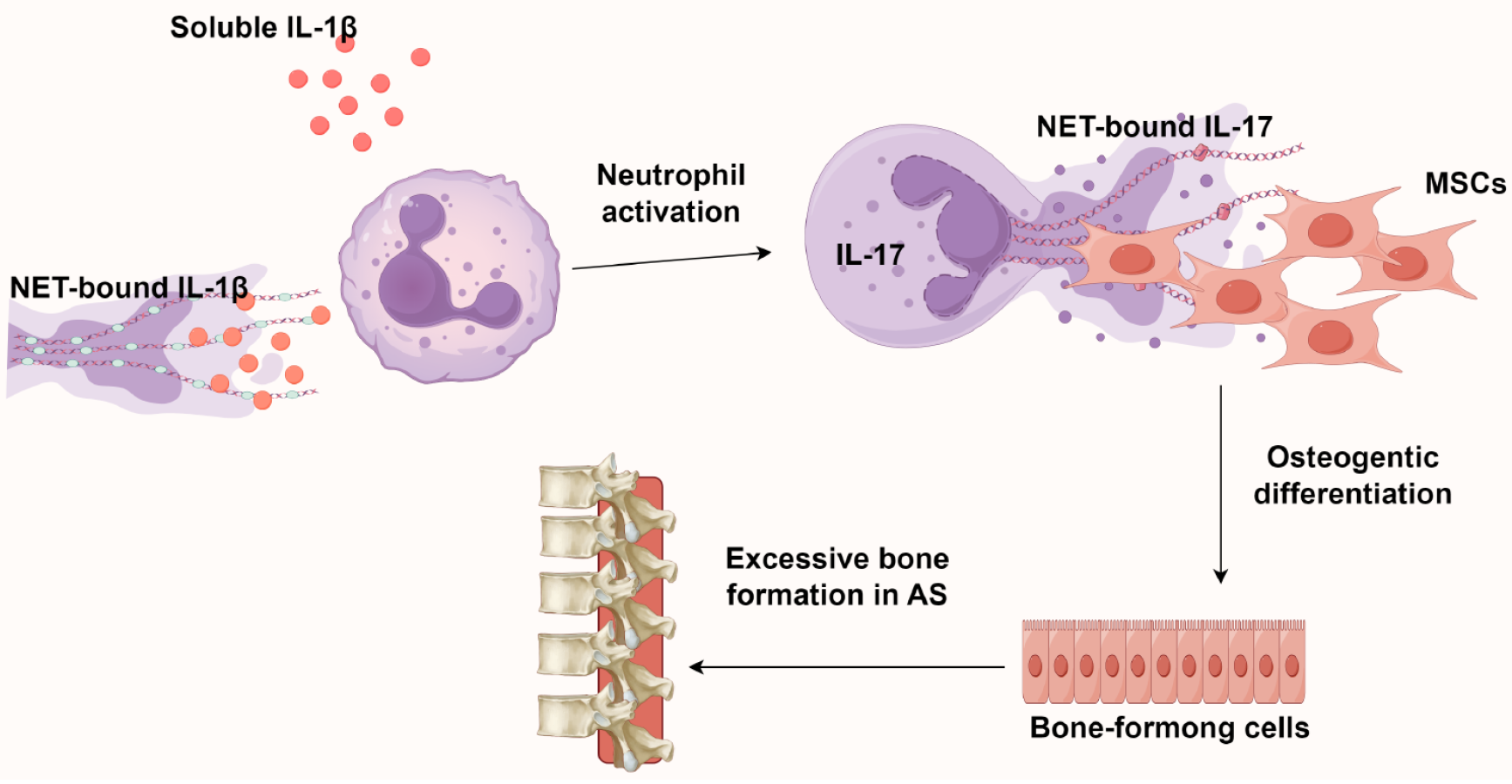
Figure 5 The role of neutrophil extracellular traps in the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis.
The interleukin-17 (IL-17)/neutrophil extracellular traps axis directs mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis, while IL-1β (from both serum and neutrophil extracellular traps) further stimulates neutrophilic IL-17 secretion. This reciprocal interaction establishes a pro-osteogenic inflammatory microenvironment that perpetuates both NETosis and aberrant bone formation. Created by Figdraw, ID: WRRPRa9680. NETs: Neutrophil extracellular traps; IL: Interleukin; MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells; AS: Ankylosing spondylitis.
- Citation: Sun GJ, Xu F, Jiao XY, Yin Y. Advances in research of neutrophil extracellular trap formation in osteoarticular diseases. World J Orthop 2025; 16(5): 106377
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v16/i5/106377.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v16.i5.106377