Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Oncol. May 24, 2025; 16(5): 105341
Published online May 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i5.105341
Published online May 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i5.105341
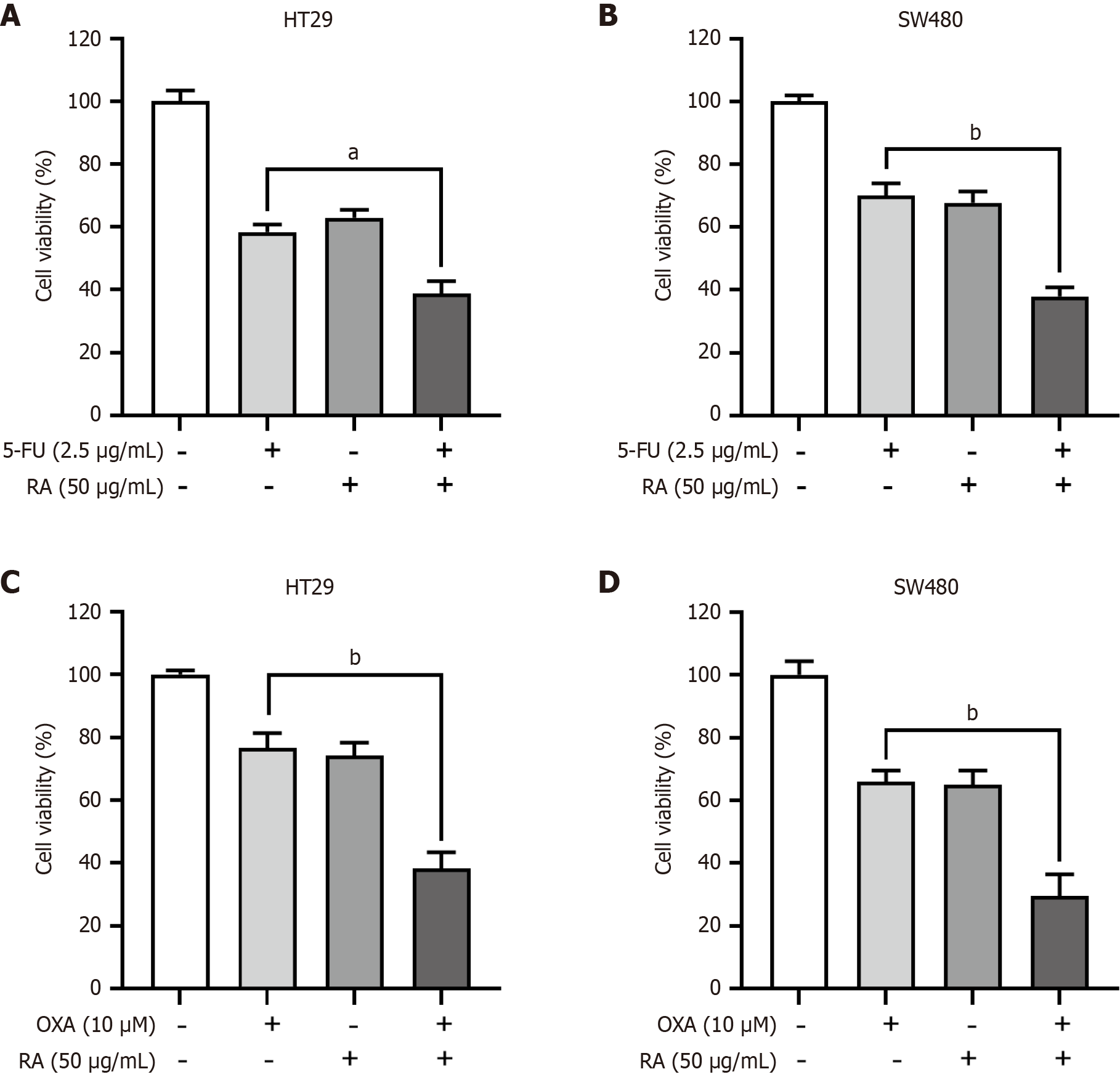
Figure 5 Rosmarinic acid enhances chemotherapeutical effects in colorectal cancer cells.
A and B: HT29 (A) and SW480 (B) cells were incubated with 2.5 μg/mL 5-fluorouracil and/or 50 μg/mL rosmarinic acid for 48 hours, followed by Cell Counting Kit-8 assay; C and D: HT29 (C) and SW480 (D) cells were incubated with 10 μM oxaliplatin and/or 50 μg/mL rosmarinic acid for 48 hours, followed by Cell Counting Kit-8 assay. n = 3. Data are shown as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.001, bP < 0.0001. RA: Rosmarinic acid; OXA: Oxaliplatin. 5-FU: 5-fluorouracil.
- Citation: Liu WY, Wang H, Xu X, Wang X, Han KK, You WD, Yang Y, Zhang T. Natural compound rosmarinic acid displays anti-tumor activity in colorectal cancer cells by suppressing nuclear factor-kappa B signaling. World J Clin Oncol 2025; 16(5): 105341
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v16/i5/105341.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v16.i5.105341