Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Oncol. May 24, 2025; 16(5): 105341
Published online May 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i5.105341
Published online May 24, 2025. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i5.105341
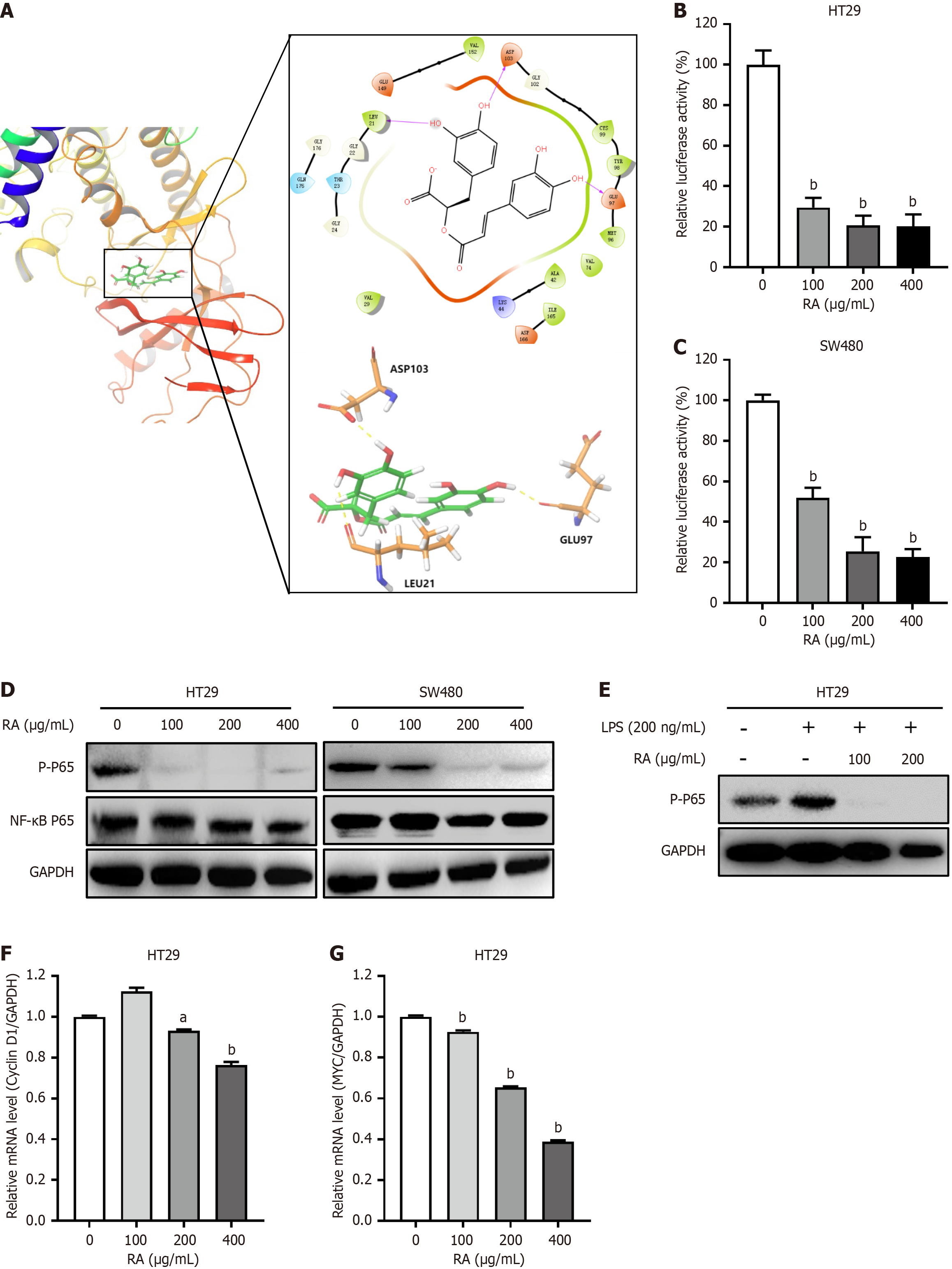
Figure 4 Rosmarinic acid inhibits nuclear factor-kappa B signaling in colorectal cancer cells.
A: Molecular modeling of rosmarinic acid (RA)/inhibitory kappa B kinase beta complex. 3D presentation of the molecular docking complex pose (I), 2D presentation (II), and 3D presentation (III) of the interactions between RA and the key residues of inhibitory kappa B kinase beta; B and C: HT29 (B) and SW480 (C) cells transfected with p-nuclear factor-kappa B-Luc along with Renilla luciferase were incubated with indicated RA overnight, followed by luciferase assay; D: HT29 and SW480 cells were incubated with increasing concentrations of RA for 24 hours, followed by Western blot analysis using antibodies against p-p65 and nuclear factor-kappa B P65. GAPDH was used as a loading control; E: Starved HT29 cells were treated with indicated RA for 12 hours, and then cells were incubated with 200 ng/mL lipopolysaccharide for 30 minutes, followed by Western blot analysis using antibodies against p-p65 and GAPDH; F and G: HT29 cells were incubated with increasing concentrations of RA for 24 hours, followed by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction to evaluate the mRNA levels of cyclin D1 (F) and MYC (G). GAPDH was used as an internal control. n = 3. Data are shown as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.001 vs group ‘0’, bP < 0.0001 vs group ‘0’. RA: Rosmarinic acid; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide.
- Citation: Liu WY, Wang H, Xu X, Wang X, Han KK, You WD, Yang Y, Zhang T. Natural compound rosmarinic acid displays anti-tumor activity in colorectal cancer cells by suppressing nuclear factor-kappa B signaling. World J Clin Oncol 2025; 16(5): 105341
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v16/i5/105341.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v16.i5.105341