Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Oncol. Apr 24, 2024; 15(4): 496-522
Published online Apr 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i4.496
Published online Apr 24, 2024. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i4.496
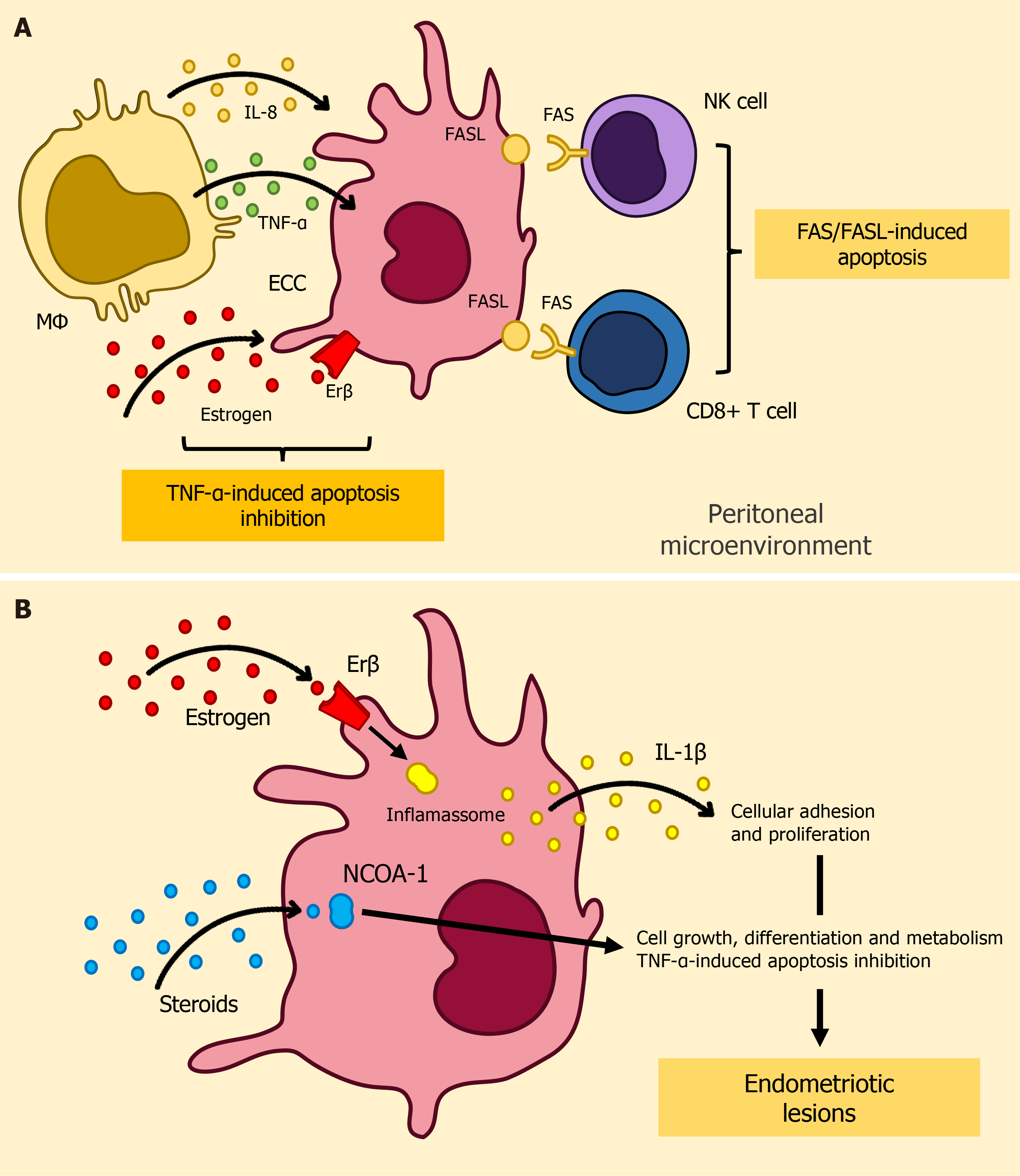
Figure 1 Depiction of immune surveillance evasion mechanisms in endometriosis.
A: Illustration of FAS/FASL-mediated apoptosis in cytotoxic lymphocytes and TNF-α-induced ectopic endometrial cell apoptosis resistance; B: Key molecular factors contributing to dysregulated apoptosis signaling in endometriosis. CD8+ T cell: Cytotoxic T-cells; ECC: Ectopic Endometrial Cells; Erβ: Estrogen receptor β; FAS (CD95): Cluster of Differentiation 95; FASL: FAS Ligand; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; IL-8: Interleukin-8; MΦ: Macrophage; NCOA-1: Nuclear receptor coactivator 1; NK cell: Natural killer cell; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
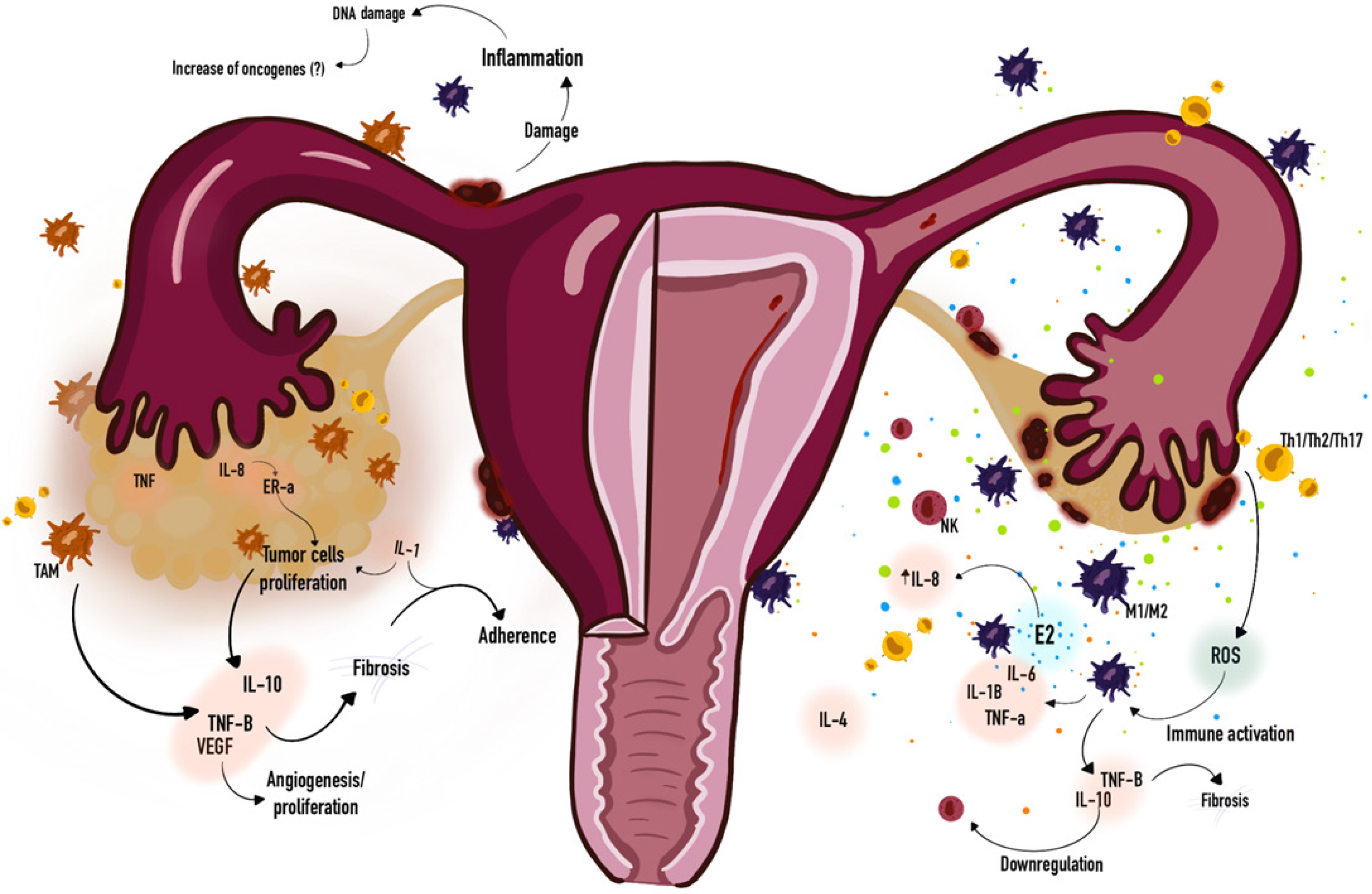
Figure 2 Overview of immune dysregulation similarities between on endometriosis and ovarian cancer.
IL-1: Interleukin-1; IL-1B: Interleukin-1β; IL-4: Interleukin-4; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-8: Interleukin-8; IL-10: Interleukin-10; E2: Prostaglandin E2; ER-a: Estrogen Receptor Alpha; M1/M2: Macrophages; NK: Natural killer cell; TAM: Tumor-associated macrophages; Th1/Th2/Th17: T helper cells; TNF: Tumor Necrosis Factor; TNF-a: Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha; TNF-B: Tumor Necrosis Factor Beta; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
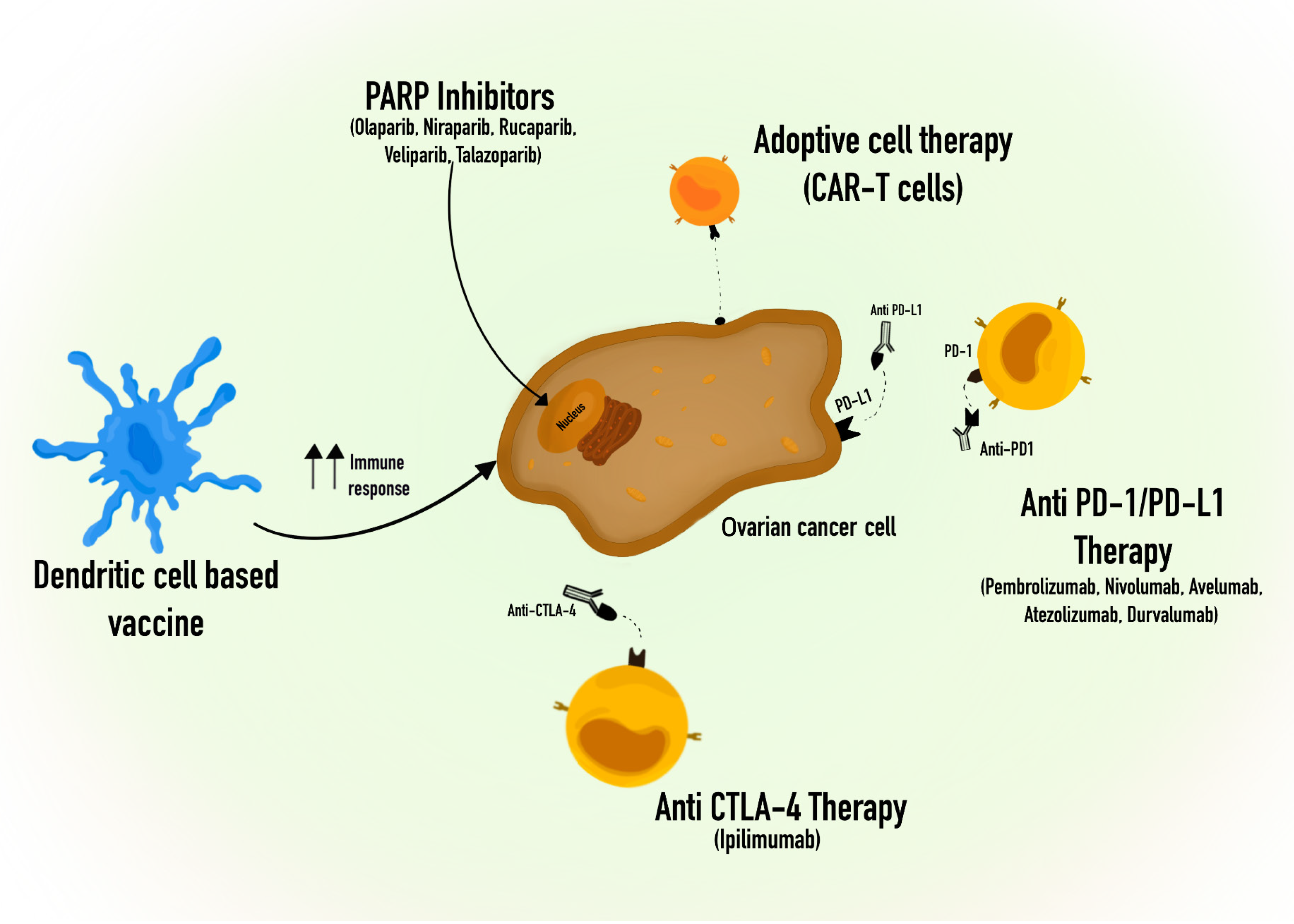
Figure 3 Some of the current immunotherapy approaches of treatment to ovarian cancer.
Anti-CTLA-4: Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Associated Protein 4 Antibody; Anti-PD1: Programmed Cell death Protein 1 Antibody; Anti PD-L1: Programmed Death-ligand 1 Antibody; CAR-T cells: Chimeric Antigen Receptor-T cells; PARP: Poly Adenosine Diphosphate-Ribose Polymerase; PD-1: Programmed Cell death Protein 1; PD-L1: Programmed Death-ligand 1.
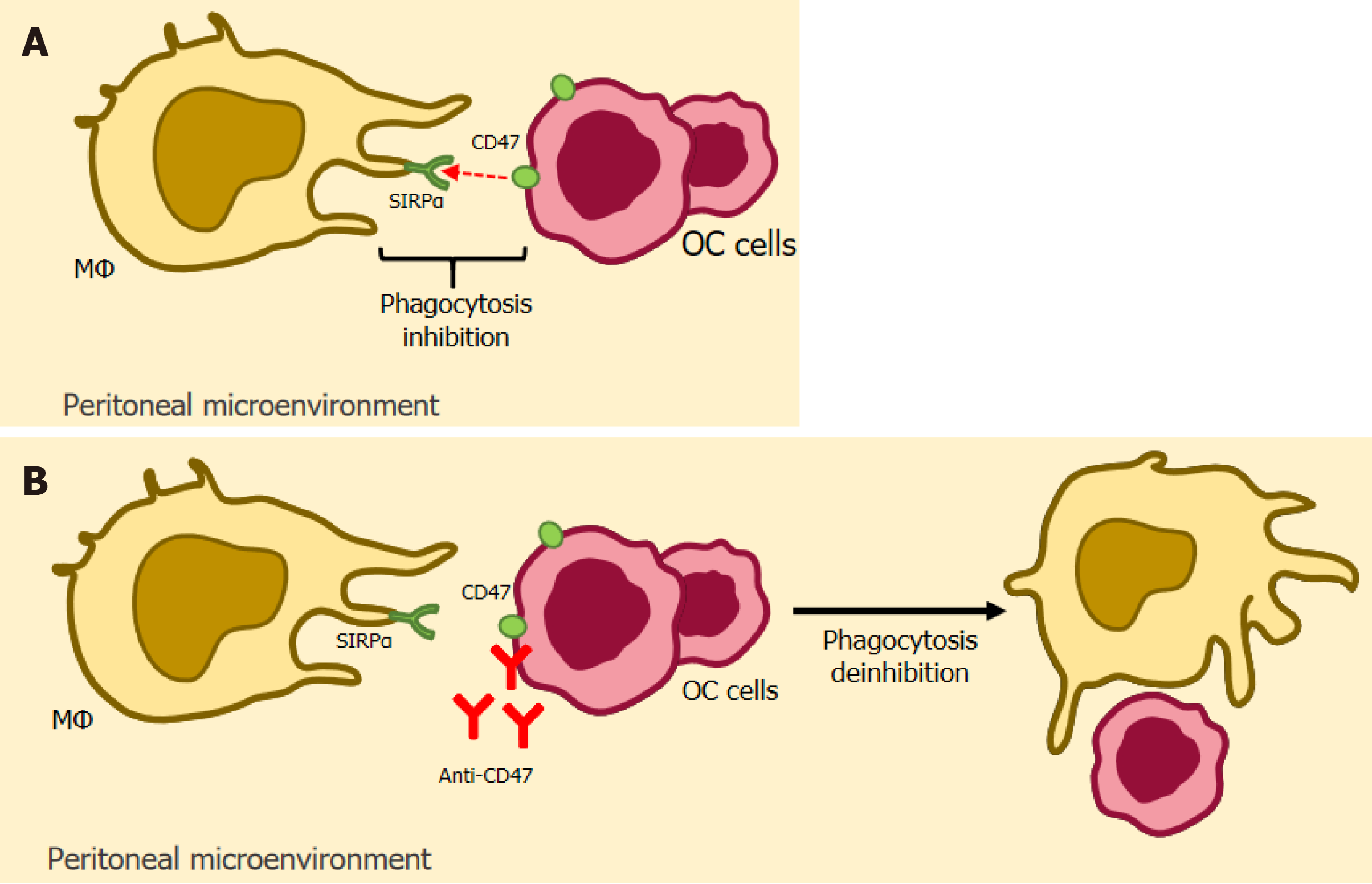
Figure 4 Illustration of anti-CD47-based immunotherapy.
CD47 is a glycoprotein that is very present in the tumor environment and exerts its inhibitory activity by binding to its counter-receptor, the signal regulatory protein-α (SIRPα), expressed in macrophages. It reduces phagocytosis by these, which culminates in the progression of the tumor microenvironment. It is highly expressed patients with endometriosis. A: CD47 binding to SIRPα inhibits phagocytosis; B: Anti-CD47 blocks the binding between CD47 and SIRPα, allowing phagocytosis to occur. Anti-CD47: Integrin-associated protein Antibody; CD47: Integrin-associated protein; MΦ: Macrophage; OC cells: Ovarian Cancer cells; SIRPα: signal regulatory protein alpha.
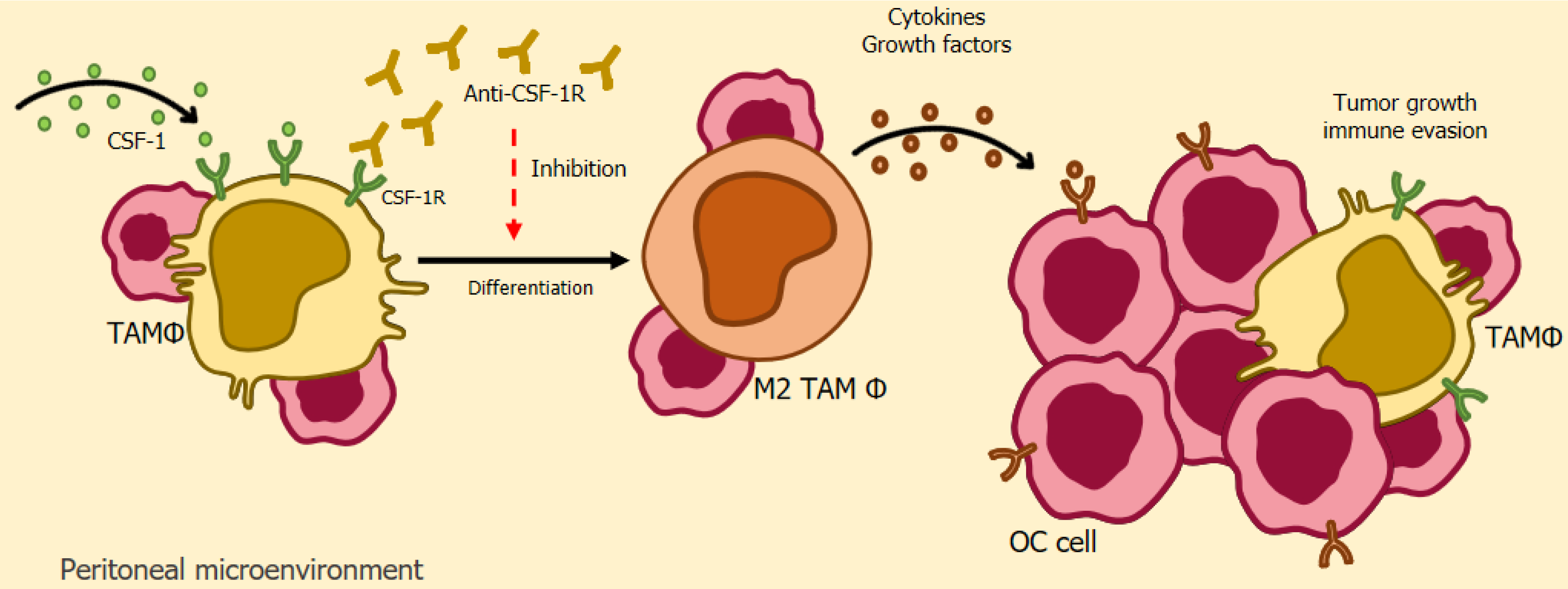
Figure 5 Illustration of anti-CSF-1R-based immunotherapy.
The colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor (CSF-1R) is a receptor that exists in several human cells during homeostasis, but is overexpressed in tumor-associated macrophages in ovarian cancer. The use of a monoclonal antibody directed at blocking CSF-1R in cancer patients, aims to manipulate the activity of TAMs, reducing tumor-associated macrophages in patients, as well as an increase in the levels of TCD8/CD4 cells in animal models. Anti-CSF-1R: Colony-Stimulating Factor 1 receptor Antibody CSF-1: Colony-Stimulating Factor 1; CSF-1R: Colony-Stimulating Factor 1 receptor; M2 TAM Φ: Tumor-associated macrophages M2; OC cell: Ovarian Cancer cells; TAM Φ: Tumor-associated macrophages.
- Citation: Calmon MS, Lemos FFB, Silva Luz M, Rocha Pinheiro SL, de Oliveira Silva LG, Correa Santos GL, Rocha GR, Freire de Melo F. Immune pathway through endometriosis to ovarian cancer. World J Clin Oncol 2024; 15(4): 496-522
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-4333/full/v15/i4/496.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v15.i4.496