Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Radiol. Aug 28, 2014; 6(8): 598-606
Published online Aug 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i8.598
Published online Aug 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i8.598
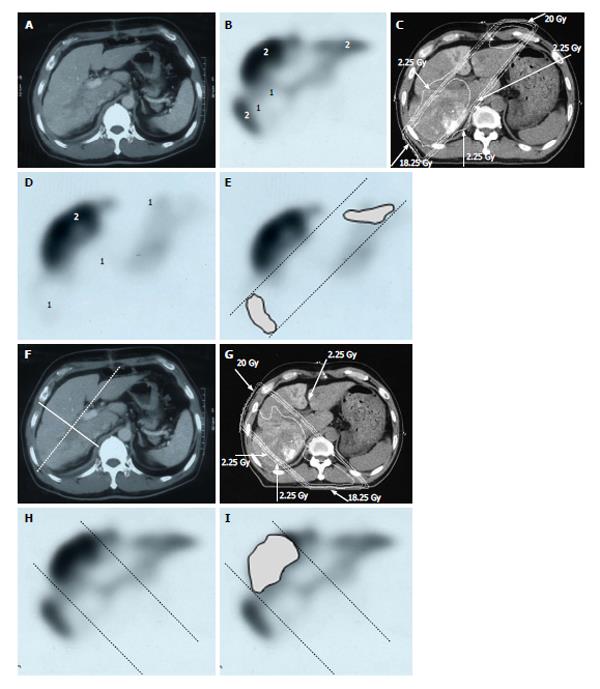
Figure 6 Distribution of functional liver and treatment planning for a 60-year-old male with hepatocellular carcinoma and liver cirrhosis of Child-Pugh grade A.
A: Contrast-enhanced computed tomography shows a PVTT in the right first portal vein originating from the right posterior sub-segment branch of the portal vein; B: GSA-SPECT taken before RT at the same level as A confirms that functional liver (2) is unevenly distributed between the anterior and lateral sides of the right PVTT. 1 = dysfunctional liver; C: The two main radiation beams were angled in the left-anterior to right-posterior direction (20 Gy) and in the right-posterior to left-anterior direction (18.25 Gy beam); D: GSA-SPECT image obtained 2 mo after RT shows functional liver (2) and preservation of the right anterior sub-segment. This image also shows that the extent of dysfunctional liver has increased in the right posterior and left medial sub-segments; E: The extent of radiation-induced dysfunctional liver is shown as the dark gray area; F-I: Hypothetical treatment planning; F: The hypothetical main beams are angled in the right-anterior to left-posterior direction (solid lines), unlike the actual beams (dotted lines); G: The hypothetical radiation beams are angled in the right-anterior to left-posterior direction (20 Gy) and in the left-posterior to right-anterior direction (18.25 Gy). Although the radiation-induced destruction of normal liver can be estimated, it is difficult to predict the extent of radiation-induced destruction of functional liver from CT simulation alone; H: GSA-SPECT image together with the hypothetical main beams; I: The gray area indicates the extent of radiation-induced dysfunctional liver likely to be induced by the hypothetical main beams. The relative difference in the destruction of functional liver between the real and the hypothetical treatment plans can be estimated by comparing E and I. PVTT: Portal vein tumor thrombus; GSA-SPECT: Galactosyl human serum albumin-single photon emission computed tomography with Tc-99m-galactosyl human serum albumin image; RT: Radiotherapy; CT: Computed tomography.
- Citation: Shirai S, Sato M, Noda Y, Kumayama Y, Shimizu N. Incorporating GSA-SPECT into CT-based dose-volume histograms for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma radiotherapy. World J Radiol 2014; 6(8): 598-606
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v6/i8/598.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i8.598