Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Radiol. Oct 28, 2014; 6(10): 779-793
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i10.779
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i10.779
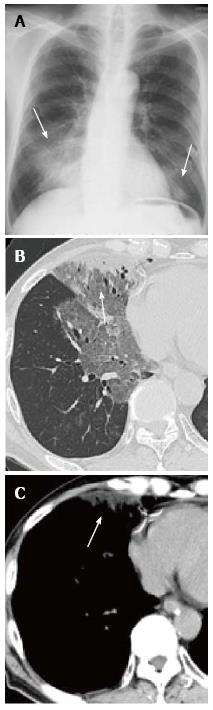
Figure 28 Exogenous lipoid pneumonia in a woman in her 30s: Courtesy of Dr.
Kazuhiro Suzuki, an attending radiologist, at the department of Radiology, Juntendo University School of Medicine. This patient had been taking petrolatum (paraffin) for intractable constipation. The presence of lipid was confirmed by transbronchial lung biopsy. A: Chest radiograph shows bilateral consolidations in the lower lung fields (arrows); B: Thin-section CT demonstrates an area of clearly demarcated ground-glass opacity with a subpleural consolidation (arrow); C: Chest computed tomography (CT) with a mediastinal window setting reveals the subpleural consolidation to be of fat attenuation (arrow, mean CT value -45HU).
- Citation: Nambu A, Ozawa K, Kobayashi N, Tago M. Imaging of community-acquired pneumonia: Roles of imaging examinations, imaging diagnosis of specific pathogens and discrimination from noninfectious diseases. World J Radiol 2014; 6(10): 779-793
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v6/i10/779.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i10.779