Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. Nov 28, 2013; 5(11): 386-397
Published online Nov 28, 2013. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v5.i11.386
Published online Nov 28, 2013. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v5.i11.386
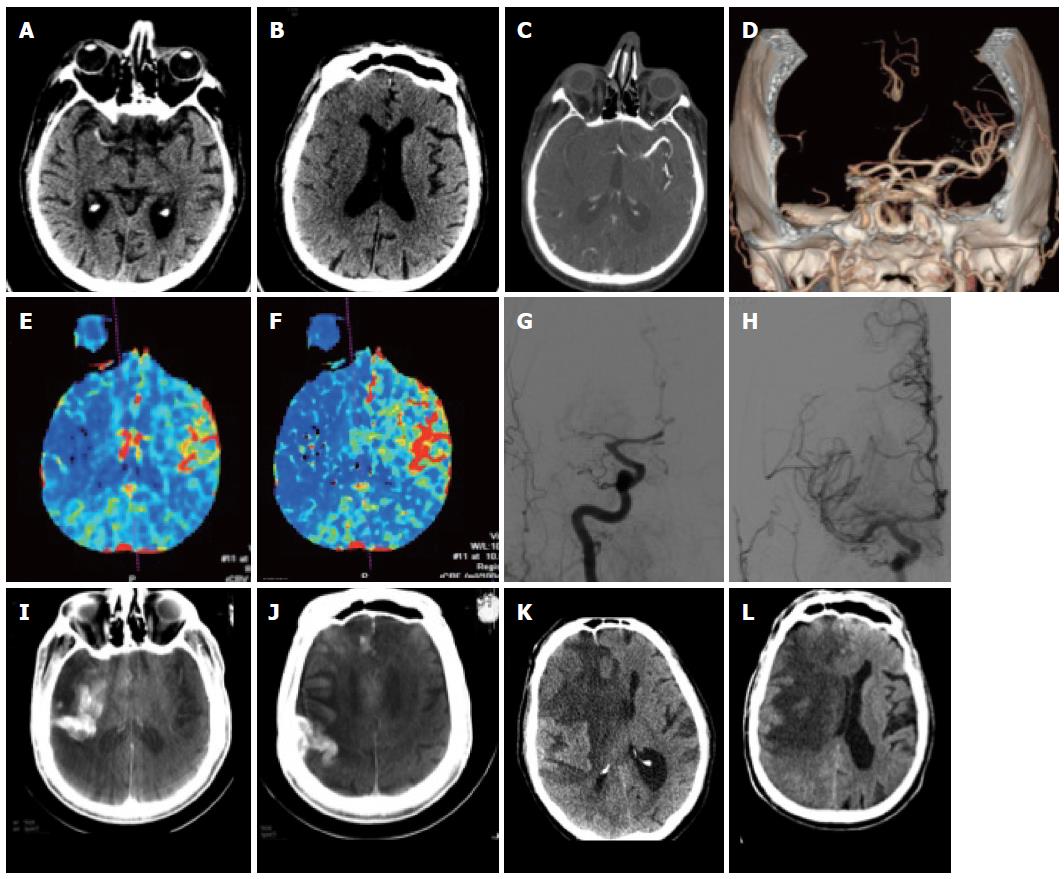
Figure 1 Patient with acute stroke.
A: Unenhanced computed tomography (CT) at 3.5 h after onset shows hyperdense MCA on the right; B, C: There are subtle signs of grey-white dedifferentiation: the insula and the basal ganglia on the right are not distinguishable; the sulci on the right side are also slightly less visible; C-F: CT angiography shows an M1 occlusion on the right (C, D) with hypoperfusion with drops in the rCBV (E) and rCBF (F) maps in the right MCA territory; G, H: This patient underwent DSA that confirmed the right MCA occlusion (G) which was recanalized (H); I, J: On follow-up CT images reconstructed from the expert CT data set acquired with the flat panel angio unit there is initially contrast extravasation; K, L: Further follow-up CT showed marked midline shift due to almost complete right MCA infarction.
- Citation: Pereira VM, Vargas MI, Marcos A, Bijlenga P, Narata AP, Haller S, Lövblad KO. Diagnostic neuroradiology for the interventional neuroradiologist. World J Radiol 2013; 5(11): 386-397
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v5/i11/386.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v5.i11.386