Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. Nov 28, 2010; 2(11): 440-448
Published online Nov 28, 2010. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v2.i11.440
Published online Nov 28, 2010. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v2.i11.440
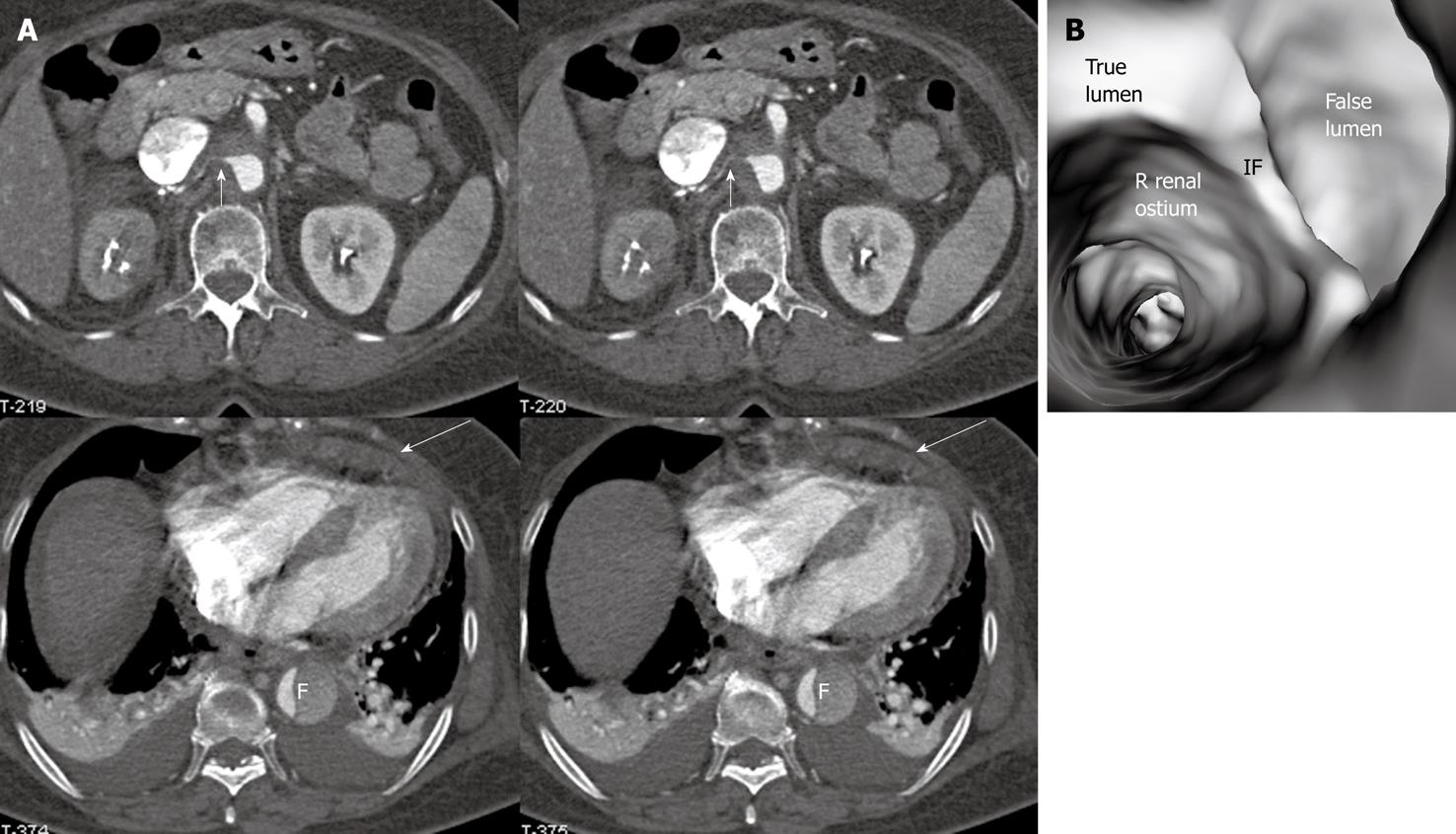
Figure 9 Stanford type B dissection with the true lumen much smaller than the false lumen.
The right renal artery arises from the compressed true lumen resulting in right renal infarction (A). Virtual intravascular endoscopy confirms the origin of the right renal ostium coming from the true lumen which is separated from the false lumen (F) by an intimal flap (IF) (B). Short arrows in A indicate the right renal artery, while long arrows in A refer to pericardial effusion. Pleural effusion is also present at both sides.
- Citation: Sun Z, Cao Y. Multislice CT virtual intravascular endoscopy of aortic dissection: A pictorial essay. World J Radiol 2010; 2(11): 440-448
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v2/i11/440.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v2.i11.440