Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Radiol. Aug 28, 2025; 17(8): 109447
Published online Aug 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i8.109447
Published online Aug 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i8.109447
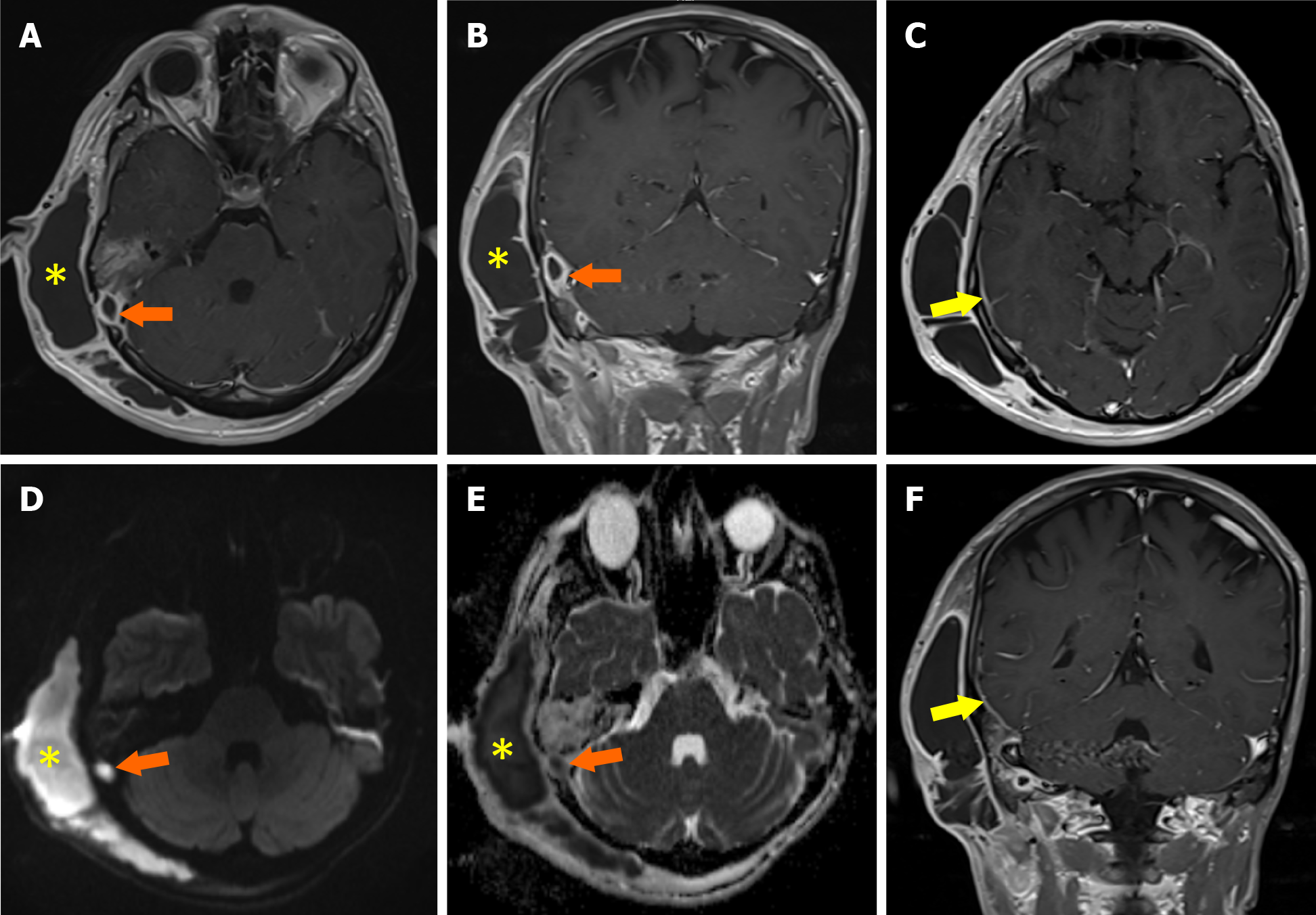
Figure 2 Meningitis with subcutaneous and intracranial abscess.
A: The axial post-contrast T1W; B: Coronal post-contrast T1W; C: Axial post-contrast T1W; D: Axial diffusion-weighted; E: Apparent diffusion coefficient map; F: Coronal post-contrast T1W magnetic resonance images show abscesses in the subcutaneous adipose tissue (yellow asterisks) and intracranial (orange arrows) area with a thick and hyperenhanced wall and centrally restricted diffusion. The axial post-contrast T1W and coronal post-contrast T1W magnetic resonance images show meningeal enhancement compatible with meningitis in the right parietotemporal area (yellow arrows).
- Citation: Memis KB, Aydin S. Role of imaging in chronic otitis media and its complications. World J Radiol 2025; 17(8): 109447
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v17/i8/109447.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v17.i8.109447