Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Radiol. May 28, 2025; 17(5): 106333
Published online May 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i5.106333
Published online May 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i5.106333
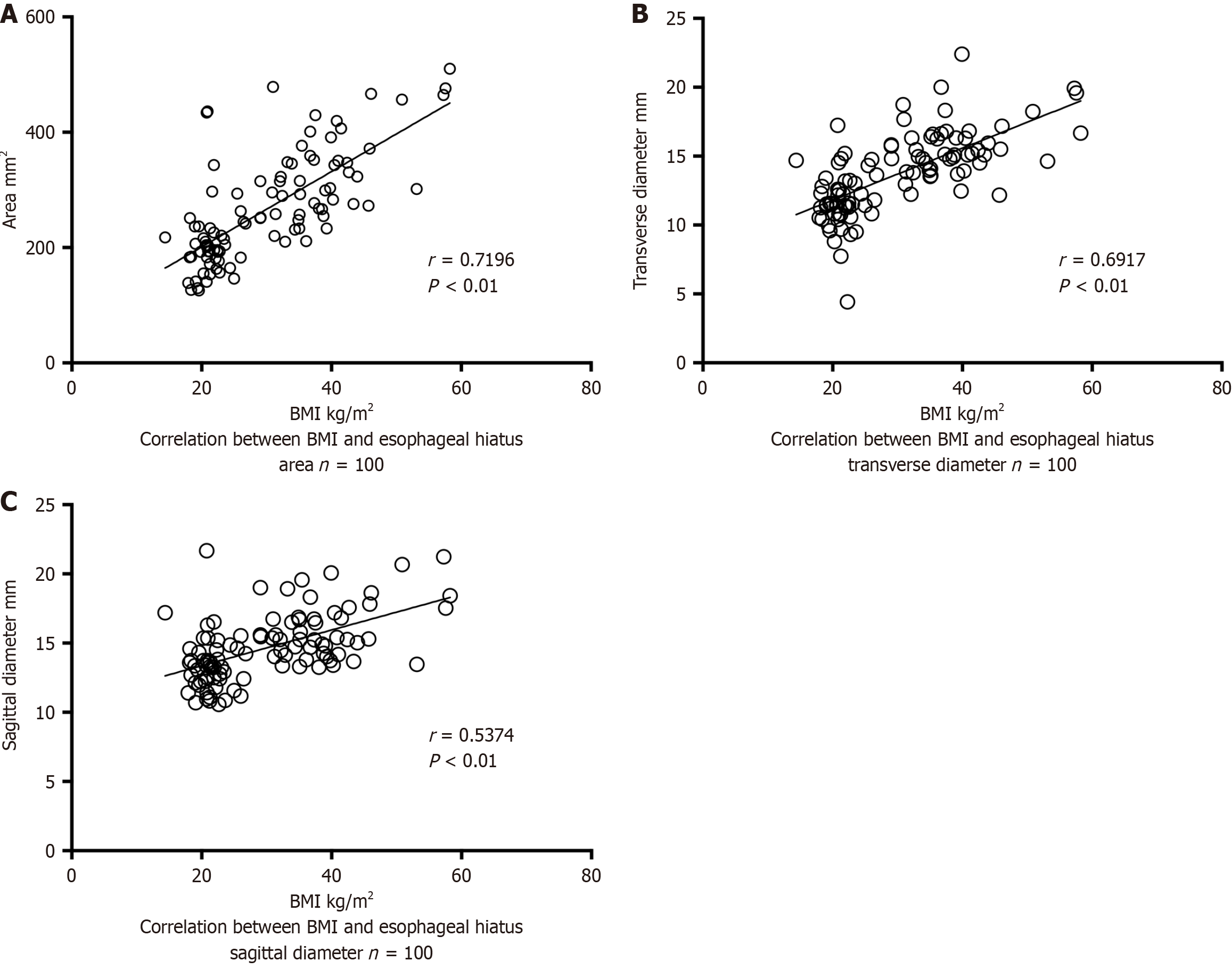
Figure 3 Spearman’s correlation test between body mass index and esophageal hiatus size.
A: Correlation between body mass index (BMI) and esophageal hiatus area with a correlation coefficient of 0.72 (P < 0.01), showing a linear positive correlation of moderate intensity; B: Correlation between BMI and esophageal hiatus transverse diameter with a correlation coefficient of 0.69 (P < 0.01), showing a linear positive correlation of moderate intensity; C: Correlation between BMI and esophageal hiatus sagittal diameter with a correlation coefficient of 0.54 (P < 0.01), showing a linear positive correlation of moderate intensity. BMI: Body mass index.
- Citation: Qi Z, Shi XC, Yan WM, Bai RX. Association of esophageal hiatus size with reflux esophagitis and type I hiatal hernia in patients with obesity. World J Radiol 2025; 17(5): 106333
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v17/i5/106333.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v17.i5.106333