Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Radiol. Apr 28, 2023; 15(4): 98-117
Published online Apr 28, 2023. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v15.i4.98
Published online Apr 28, 2023. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v15.i4.98
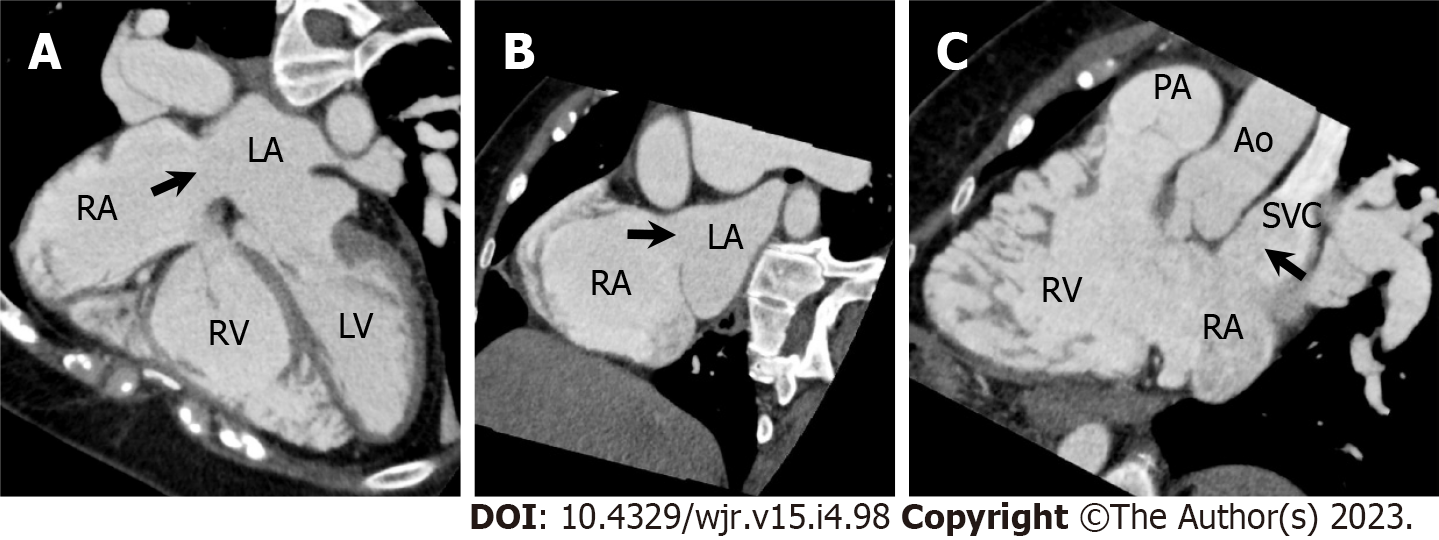
Figure 20 Superior sinus venosus atrial septal defect.
A 57-year-old woman underwent cardiac computed tomography (CCT) to evaluate right ventricular (RV) morphology and function because transthoracic echocardiography revealed gradual RV dilatation over time. She had a previous history of cryptogenic ischemic stroke when she was 3 years old. A–C: Horizontal long axis (A), short axis oblique (B), and RV long axis reformatted CCT images show atrial septal defect (ASD) in superior aspect of interatrial septum at level of entry of superior vena cava (SVC, arrows). Measured size of ASD is 26 mm by 25 mm. Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return is not complicated. Subsequently, she underwent right and left heart catheterization. The Qp/Qs ratio and mean pulmonary artery pressure measured using right heart catheterization were 4.8 and 23 mmHg, respectively. Surgical ASD closure was performed. LA: Left atrium; LV: Left ventricle; RA: Right atrium; PA: Pulmonary artery; Ao: Aorta.
- Citation: Yoshihara S. Evaluation of causal heart diseases in cardioembolic stroke by cardiac computed tomography. World J Radiol 2023; 15(4): 98-117
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v15/i4/98.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v15.i4.98