Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Radiol. Sep 28, 2022; 14(9): 329-341
Published online Sep 28, 2022. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v14.i9.329
Published online Sep 28, 2022. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v14.i9.329
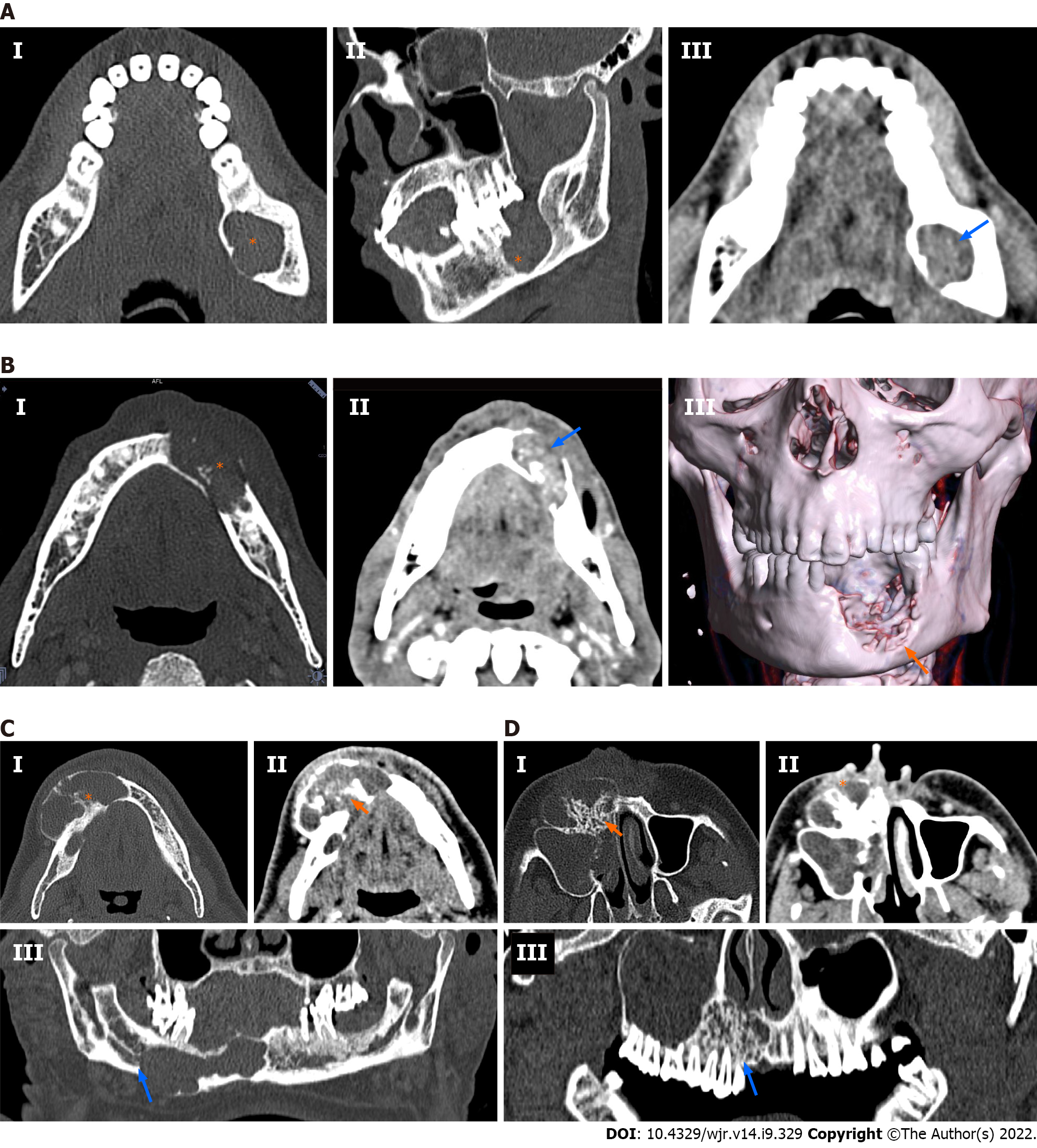
Figure 3 Spectrum of multidetector computed tomography findings in ameloblastoma.
A: A 30-year-old man presented with progressive left lower jaw swelling. Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) showed a unilocular, lytic lesion (asterisk) with no septae involving the left angle of the mandible (Panel I and II: Axial and coronal bone window). The soft tissue component showed enhancement similar (blue arrow) to the surrounding muscles (Panel III: Axial soft tissue window); B: A 52-year-old man with lower mid jaw pain and swelling; contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) showed a sclerotic, lytic multilocular lesion with thin incomplete septae (asterisk) and associated mineralised matrix (Panel I: Axial bone window). There was a significant soft tissue component showing enhancement (blue arrow) similar to the surrounding muscles (Panel II: Axial soft tissue window). Erosion of the buccal cortex was seen in three-dimensional volume-rendered images (Panel III); C: A 53-year-old man with painful progressive lower jaw swelling of 7 mo duration. CECT showed a lytic sclerotic multilocular mandibular mass with multiple thick septae (asterisk), cortical expansion and breach (Panel I: Axial bone window). The solid component present in the tumour showed hypoenhancement (arrow) compared to the surrounding muscles (Panel II: Axial soft tissue window). Hypoenhancing soft tissue was characteristically not seen in central giant cell granulomas, allowing a prospective diagnosis of ameloblastoma. Erosion of the right canal of the inferior alveolar nerve (blue arrow) was clearly seen [Panel III: Curved multiplanar coronal reconstruction (MPR), bone window]; D: A 42-year-old man with upper maxillary swelling and significant malar pain. CECT showed a lytic sclerotic mass with honeycombing (orange arrow) and thick bony septae (Panel I: Axial bone window). There was significant cortical expansion with extension into the right maxillary sinus. The mass was predominantly lytic with minimal solid component (asterisk) seen in the mass, hypoenhancing compared to the surrounding muscles (Panel II: Axial soft tissue window). Erosion of the roots (blue arrow) with honeycomb appearance was visible (Panel III: Curved MPR coronal bone window).
- Citation: Ghosh A, Lakshmanan M, Manchanda S, Bhalla AS, Kumar P, Bhutia O, Mridha AR. Contrast-enhanced multidetector computed tomography features and histogram analysis can differentiate ameloblastomas from central giant cell granulomas . World J Radiol 2022; 14(9): 329-341
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v14/i9/329.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v14.i9.329