Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
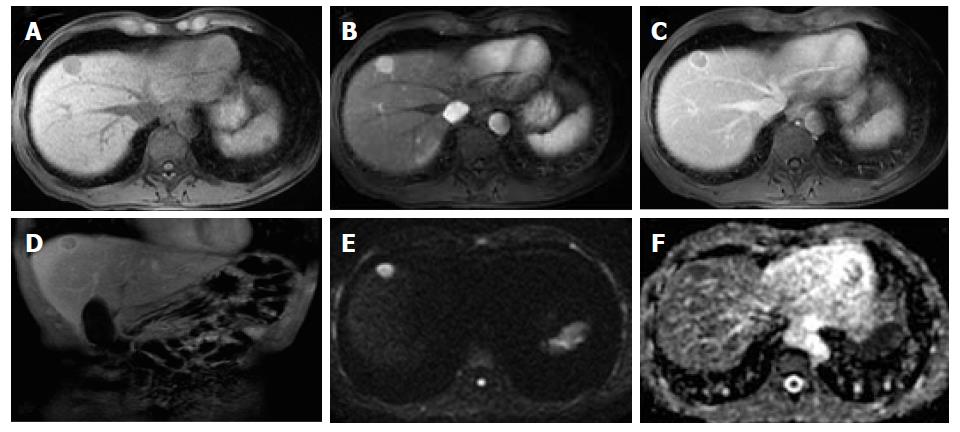
Figure 1 Classical hepatocellular carcinoma, in a patient with hepatitis B infection.
Pre-contrast (A) and post-contrast fat-suppressed 3D-GRE T1-weighted images during the late hepatic arterial (B) and delayed phases (C, D), respectively, diffusion weighted image (DWI) (B = 600); (E) and ADC map (F). A nodular lesion is depicted in the right liver lobe with mildly low T1 signal intensity (arrow, A) that shows hyperenhancement in the late arterial phase (B) and washout and pseudocapsule enhancement in the delayed phases (C, D). Note the bright signal intensity on the B was 600 of the DWI sequence (E) and low signal on the ADC map (F) consistent with restriction to diffusion. These are typical hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) findings in a patient at risk for HCC.
- Citation: Campos-Correia D, Cruz J, Matos AP, Figueiredo F, Ramalho M. Magnetic resonance imaging ancillary features used in Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System: An illustrative review. World J Radiol 2018; 10(2): 9-23
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v10/i2/9.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v10.i2.9