Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Cardiol. Feb 26, 2016; 8(2): 163-179
Published online Feb 26, 2016. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v8.i2.163
Published online Feb 26, 2016. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v8.i2.163
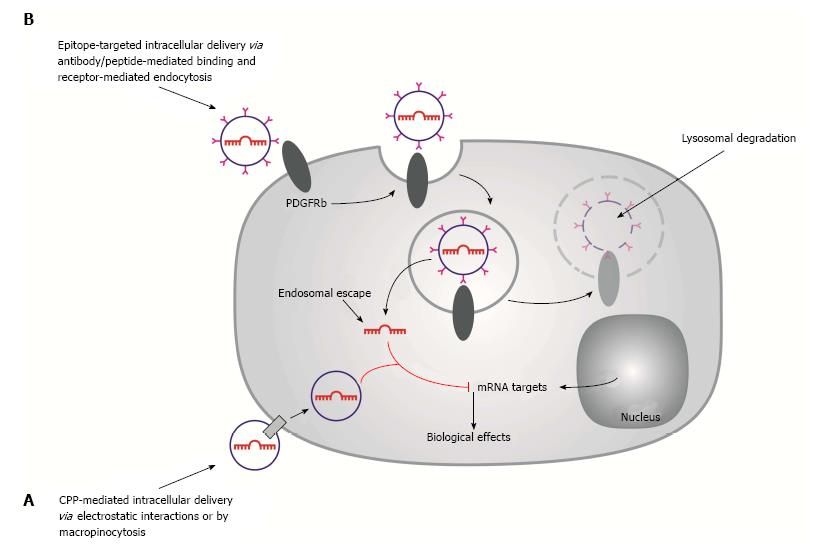
Figure 3 Schematic of passive and active targeted drug delivery systems for microRNA delivery.
A: Passive targeting by cell-penetrating peptide-coated nanoparticles are internalized by receptor-mediated endocytosis; B: Active targeting by PDGFRb-targeted liposomes. Liposomes interact with cell surface receptors (PDGFRb) and internalized via receptor-mediated endocytosis. The endocytotic vesicles fuse to form early endosomes which ultimately become part of the lysosomes, where proteins and nucleic acids are degraded by acid hydrolases. To achieve target gene silencing, microRNAs need to be released from the liposome and escape from the endosomes into the cytoplasm, where the microRNA directs the cleavage of target mRNAs.
- Citation: Kamps JA, Krenning G. Micromanaging cardiac regeneration: Targeted delivery of microRNAs for cardiac repair and regeneration. World J Cardiol 2016; 8(2): 163-179
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v8/i2/163.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v8.i2.163